 Researchers cross-inserted a new type of electrode made of fibers inside the light emitting layer unlike existing light emitting devices, through which they could develop a new light-emitting technology using an in-plane electric field generated in parallel to the light-emitting layer.
Researchers cross-inserted a new type of electrode made of fibers inside the light emitting layer unlike existing light emitting devices, through which they could develop a new light-emitting technology using an in-plane electric field generated in parallel to the light-emitting layer.
Tuesday, March 31, 2020
Textile-fiber-embedded multiluminescent device for future wearable devices
 Researchers cross-inserted a new type of electrode made of fibers inside the light emitting layer unlike existing light emitting devices, through which they could develop a new light-emitting technology using an in-plane electric field generated in parallel to the light-emitting layer.
Researchers cross-inserted a new type of electrode made of fibers inside the light emitting layer unlike existing light emitting devices, through which they could develop a new light-emitting technology using an in-plane electric field generated in parallel to the light-emitting layer.
Monday, March 30, 2020
Nanocages trap and separate elusive noble gases
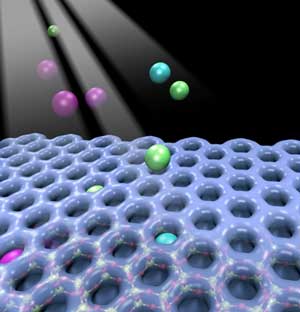 2D nanoscale compound traps noble gases at above-freezing temperatures, a difficult and important industrial challenge.
2D nanoscale compound traps noble gases at above-freezing temperatures, a difficult and important industrial challenge.
Engineers 3D print soft, rubbery brain implants
 Technique may enable speedy, on-demand design of softer, safer neural devices.
Technique may enable speedy, on-demand design of softer, safer neural devices.
Friday, March 27, 2020
Global Graphene Call, business ideas relating to graphene
 A collaboration in Spain is launching the Global Graphene Call designed to develop business ideas linked to graphene.
A collaboration in Spain is launching the Global Graphene Call designed to develop business ideas linked to graphene.
Novel graphene-based filters to make gas purification more effective
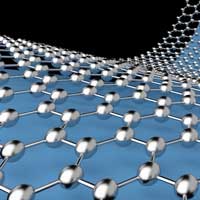 Researchers have shown how a new class of low-cost graphene-based membranes can be selectively tuned to separate different gases from gaseous mixtures.
Researchers have shown how a new class of low-cost graphene-based membranes can be selectively tuned to separate different gases from gaseous mixtures.
3D-printed nanowire sensors could make breath tests for diabetes possible
 Researchers have developed a procedure to produce extremely sensitive and energy-efficient sensors using 3D printing.
Researchers have developed a procedure to produce extremely sensitive and energy-efficient sensors using 3D printing.
Creating safer ceramic coatings with gold and silver nanoparticles
 Scientists report progress toward a new type of glaze that includes gold and silver nanoparticles, which are less toxic and more environmentally friendly than currently used formulations, while still providing vibrant colors.
Scientists report progress toward a new type of glaze that includes gold and silver nanoparticles, which are less toxic and more environmentally friendly than currently used formulations, while still providing vibrant colors.
Double-walled carbon nanotubes have electro-optical advantages
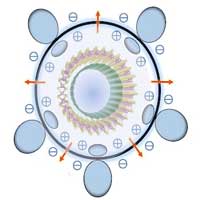 One nanotube could be great for electronics applications, but there's new evidence that two could be tops.
One nanotube could be great for electronics applications, but there's new evidence that two could be tops.
Nanocrystals will help detect methanol and other alcohols
 Researchers developed highly sensitive sensors based on cobalt oxide nanoflakes which are capable of detecting various alcohols in the air. The new sensors can be used for both medical diagnostics and detection of toxic methanol in the air.
Researchers developed highly sensitive sensors based on cobalt oxide nanoflakes which are capable of detecting various alcohols in the air. The new sensors can be used for both medical diagnostics and detection of toxic methanol in the air.
Novel light funnel device could serve as platform for hypersensitive optical detectors
 The light accumulation achieved by the light funnel could be the basis for improving the sensitivity of optical detectors and thus enabling unprecedented optical applications.
The light accumulation achieved by the light funnel could be the basis for improving the sensitivity of optical detectors and thus enabling unprecedented optical applications.
A new battery chemistry promises safer high-voltage lithium-ion batteries
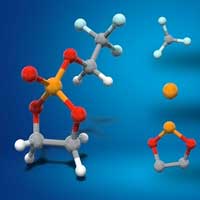 Researchers develop a cyclic phosphate-based battery electrolyte for high voltage and safe operation.
Researchers develop a cyclic phosphate-based battery electrolyte for high voltage and safe operation.
Understanding differences in streptavidin-biotin binding
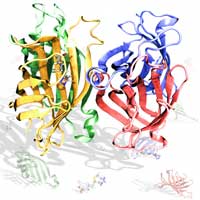 A recent paper uses computational tools to explain the mechanism of how streptavidin and biotin binding is affected by streptavidin's tethering.
A recent paper uses computational tools to explain the mechanism of how streptavidin and biotin binding is affected by streptavidin's tethering.
Thursday, March 26, 2020
Skyrmions seen in a kagome lattice
 Magnetic vortices have been made and seen in a crystal with a special structure.
Magnetic vortices have been made and seen in a crystal with a special structure.
Just add salt to enhance the spatial resolution of single-molecule Raman spectroscopy
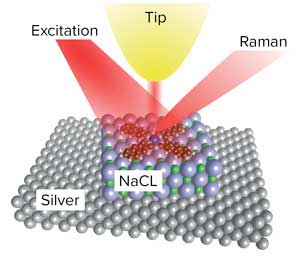 A thin substrate of sodium chloride aids the spectroscopic resolution of single-molecule vibrations.
A thin substrate of sodium chloride aids the spectroscopic resolution of single-molecule vibrations.
Quantum phenomenon governs organic solar cells
 Vibronic coherence contributes to photocurrent generation in organic semiconductor heterojunction diodes.
Vibronic coherence contributes to photocurrent generation in organic semiconductor heterojunction diodes.
Upgrading biomass with selective surface-modified catalysts
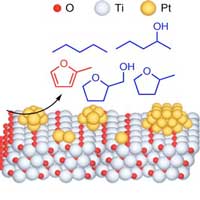 Scientists demonstrated how the conversion of a plant derivative into fuels and other valuable chemicals can be achieved by loading single atoms of platinum onto titanium dioxide.
Scientists demonstrated how the conversion of a plant derivative into fuels and other valuable chemicals can be achieved by loading single atoms of platinum onto titanium dioxide.
Experiments in mice and human cells shed light on best way to deliver nanoparticle therapy for cancer
 Researchers in the cancer nanomedicine community debate whether use nanoparticles can best deliver drug therapy to tumors passively. Now, new research on human and mouse tumors in mice suggests the question is even more complicated.
Researchers in the cancer nanomedicine community debate whether use nanoparticles can best deliver drug therapy to tumors passively. Now, new research on human and mouse tumors in mice suggests the question is even more complicated.
'Native oxide' allows controllable thinning of two-dimensional materials
 An international team of researchers show how to take advantage of the natural interaction of 2D materials with air to reduce their thickness with (sub-)monolayer precision.
An international team of researchers show how to take advantage of the natural interaction of 2D materials with air to reduce their thickness with (sub-)monolayer precision.
As electronics shrink to nanoscale, will they still be good as gold?
 Engineers wonder whether this tried and true precious metal, found in the bowels of most electronic devices, can stand up to the strain of next-generation data processing.
Engineers wonder whether this tried and true precious metal, found in the bowels of most electronic devices, can stand up to the strain of next-generation data processing.
Artificial intelligence identifies optimal material formula
 One algorithm replaces countless time-consuming experiments.
One algorithm replaces countless time-consuming experiments.
Innovative thinner electrolyte can improve functioning of solid oxide fuel cells
 Scientists have synthesized a new thin film that could make energy production more efficient and cleaner.
Scientists have synthesized a new thin film that could make energy production more efficient and cleaner.
Novel hybrid nanocomposite sheds light on therapy of deep-seated orthotopic lung tumors
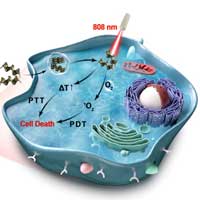 The nanocomposite was developed through the assembly of gold nanobipyramids on black phosphorus nanosheets. This nanocomposite could simultaneously enhance singlet oxygen generation and hyperthermia by localized surface plasmon resonance in cancer therapy.
The nanocomposite was developed through the assembly of gold nanobipyramids on black phosphorus nanosheets. This nanocomposite could simultaneously enhance singlet oxygen generation and hyperthermia by localized surface plasmon resonance in cancer therapy.
Wednesday, March 25, 2020
A new method for the fabrication and characterization of atomic-sized photonic cavities
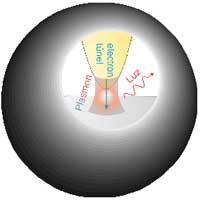 This discovery may be fundamental for the understanding and design of new, nanometric size, opto-electronic devices which will be key for the development of new technologies based on quantum properties, such as sensors or quantum computers.
This discovery may be fundamental for the understanding and design of new, nanometric size, opto-electronic devices which will be key for the development of new technologies based on quantum properties, such as sensors or quantum computers.
3D-Printing complex nanocellulose-based objects
 Researchers have demonstrated 3D printed complex objects with higher cellulose content than that of any other additively manufactured cellulose-?based parts. To achieve this, they used a clever trick.
Researchers have demonstrated 3D printed complex objects with higher cellulose content than that of any other additively manufactured cellulose-?based parts. To achieve this, they used a clever trick.
A nanoscale device to generate high-power Terahertz waves
 Researchers have developed a nanodevice that operates more than 10 times faster than today's fastest transistors.
Researchers have developed a nanodevice that operates more than 10 times faster than today's fastest transistors.
'Whiskey webs' are the new 'coffee ring effect'
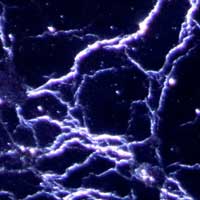 The 'coffee ring effect' has fascinated scientists for decades, but now a team says they have uncovered the mechanism behind an even more striking, web-like pattern that forms when drops of whiskey dry up.
The 'coffee ring effect' has fascinated scientists for decades, but now a team says they have uncovered the mechanism behind an even more striking, web-like pattern that forms when drops of whiskey dry up.
First ultra-low threshold continuous-wave lasing in Germanium-Tin
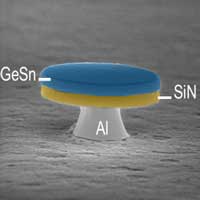 Researchers have implemented a new material engineering method to fabricate a laser microdisk in strained Germanium-Tin (GeSn) alloy. They demonstrate for the first time the laser device with a group IV compound, compatible with Silicon, operating with ultra-low threshold and under continuous wave excitation.
Researchers have implemented a new material engineering method to fabricate a laser microdisk in strained Germanium-Tin (GeSn) alloy. They demonstrate for the first time the laser device with a group IV compound, compatible with Silicon, operating with ultra-low threshold and under continuous wave excitation.
Shifting dimensions: Exciting excitons in phosphorene
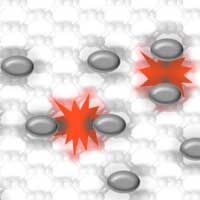 Scientists have shed light on how excitons - an excited state of matter at the core of optoelectronics - move and interact within phosphorene.
Scientists have shed light on how excitons - an excited state of matter at the core of optoelectronics - move and interact within phosphorene.
Tuesday, March 24, 2020
Upconverting nanolasers from subwavelength plasmons
 To design these nanolasers, researchers combined arrays of nanopillars with nanoparticles that can absorb two photons of light and emit them as a single photon with higher energy.
To design these nanolasers, researchers combined arrays of nanopillars with nanoparticles that can absorb two photons of light and emit them as a single photon with higher energy.
A genetic nano-toolkit for the generation of new bacterial magnetic nanoparticles
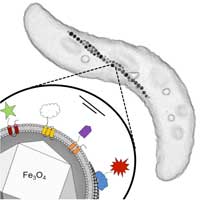 Scientists have developed a modular system for the genetic reprogramming of bacteria, thereby turning the organisms into cell factories for multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles that combine various useful functions and properties. Because of their exceptional magnetic properties and good biocompatibility, these nanoparticles might be a promising new material in the biomedical and biotechnological field.
Scientists have developed a modular system for the genetic reprogramming of bacteria, thereby turning the organisms into cell factories for multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles that combine various useful functions and properties. Because of their exceptional magnetic properties and good biocompatibility, these nanoparticles might be a promising new material in the biomedical and biotechnological field.
Crumpled graphene makes ultra-sensitive cancer DNA detector
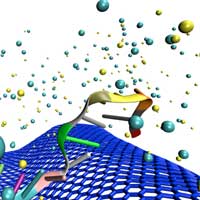 Crumpling graphene makes it more than ten thousand times more sensitive to DNA by creating electrical 'hot spots'.
Crumpling graphene makes it more than ten thousand times more sensitive to DNA by creating electrical 'hot spots'.
Monday, March 23, 2020
Novel metal-organic framework is potential next-gen semiconductor
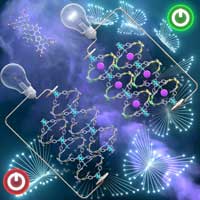 Researchers demonstrated a novel double-helical metal organic framework architecture in a partially oxidized form that conducts electricity, potentially making it a next-generation semiconductor.
Researchers demonstrated a novel double-helical metal organic framework architecture in a partially oxidized form that conducts electricity, potentially making it a next-generation semiconductor.
A key development in the drive for energy-efficient electronics
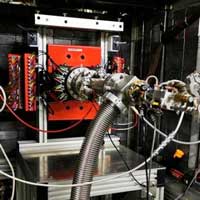 Scientists have made a breakthrough in the development of a new generation of electronics that will require less power and generate less heat. It involves exploiting the complex quantum properties of electrons - in this case, the spin state of electrons.
Scientists have made a breakthrough in the development of a new generation of electronics that will require less power and generate less heat. It involves exploiting the complex quantum properties of electrons - in this case, the spin state of electrons.
Unraveling the optical parameters: New method to optimize plasmon enhanced spectroscopy
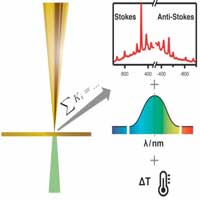 Researchers report the first accessible method to gain unprecedented insights into the plasmonic activity of a single nanoparticle during a typical tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy experiment.
Researchers report the first accessible method to gain unprecedented insights into the plasmonic activity of a single nanoparticle during a typical tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy experiment.
New metasurface helps make the switch to terahertz frequencies
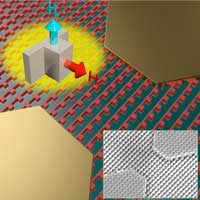 The new highly efficient metasurface switch needs no metal or backing material. This means detectors using the switch would be smaller, thinner, more efficient, and require less power.
The new highly efficient metasurface switch needs no metal or backing material. This means detectors using the switch would be smaller, thinner, more efficient, and require less power.
Engineered nanowrappers carry and release tiny cargo
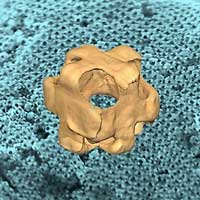 Scientists have discovered a new method for creating hollow metallic nanostructures with regularly spaced and sized pores. The pores are large and regular enough to carry molecule or nanoscale-size particles of drugs and other substances.
Scientists have discovered a new method for creating hollow metallic nanostructures with regularly spaced and sized pores. The pores are large and regular enough to carry molecule or nanoscale-size particles of drugs and other substances.
Wrapped, layered semiconductors catch the light
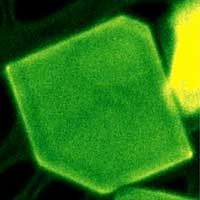 Researchers discovered a new way to integrate semiconductor layers to make heterostructures. They found that layers of different compounds of tin and sulfur spontaneously separated during synthesis. This unique structure translates into excellent light absorption and energy transfer properties.
Researchers discovered a new way to integrate semiconductor layers to make heterostructures. They found that layers of different compounds of tin and sulfur spontaneously separated during synthesis. This unique structure translates into excellent light absorption and energy transfer properties.
Optical control allows physicists to simulate and understand interactions between atoms
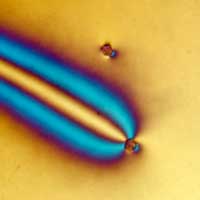 Scientists used silica micro-particles mixed into liquid crystals to investigate how atoms behave and interact. They explored optical control of hexagonal silica micro-particles whose surfaces were altered with dye molecules and dispersed in a liquid crystal.
Scientists used silica micro-particles mixed into liquid crystals to investigate how atoms behave and interact. They explored optical control of hexagonal silica micro-particles whose surfaces were altered with dye molecules and dispersed in a liquid crystal.
Stacked nanodevice quickly detects harmful bacteria in blood
 Engineers have created a tiny device that can rapidly detect harmful bacteria in blood, allowing health care professionals to pinpoint the cause of potentially deadly infections and fight them with drugs.
Engineers have created a tiny device that can rapidly detect harmful bacteria in blood, allowing health care professionals to pinpoint the cause of potentially deadly infections and fight them with drugs.
Graphene flakes on medical devices kill bacteria and prevent infections
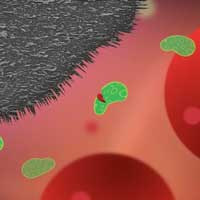 Graphite nanoplatelets integrated into plastic medical surfaces can prevent infections, killing 99.99 per cent of bacteria which try to attach - a cheap and viable potential solution to a problem which affects millions, costs huge amounts of time and money, and accelerates antibiotic resistance.
Graphite nanoplatelets integrated into plastic medical surfaces can prevent infections, killing 99.99 per cent of bacteria which try to attach - a cheap and viable potential solution to a problem which affects millions, costs huge amounts of time and money, and accelerates antibiotic resistance.
Graphene cleans water more effectively
 Graphil is a project that aims to create a market prototype for a new and improved way to purify water, using graphene.
Graphil is a project that aims to create a market prototype for a new and improved way to purify water, using graphene.
How do you power billions of sensors? By converting waste heat into electricity
 Scientists have revealed how the thermoelectric effect, or converting temperature differences into electricity, can be optimally used to power small, flexible devices. Their study has shown why thermoelectric device performance to date has not yet reached its full potential.
Scientists have revealed how the thermoelectric effect, or converting temperature differences into electricity, can be optimally used to power small, flexible devices. Their study has shown why thermoelectric device performance to date has not yet reached its full potential.
Wearable strain sensor based on optical transmittance of a CNT-embedded elastomer
 Rsearchers have developed a novel wearable strain sensor based on the modulation of optical transmittance of a carbon nanotube (CNT)-embedded elastomer. The sensor is capable of sensitive, stable, and continuous measurement of physical signals.
Rsearchers have developed a novel wearable strain sensor based on the modulation of optical transmittance of a carbon nanotube (CNT)-embedded elastomer. The sensor is capable of sensitive, stable, and continuous measurement of physical signals.
Saturday, March 21, 2020
Electric jolt to nanocarbon makes better water purifier
 Scientists have developed a one-step fabrication process that improves the ability of nanocarbons to remove toxic heavy metal ions from water. The findings could aid efforts to improve universal access to clean water.
Scientists have developed a one-step fabrication process that improves the ability of nanocarbons to remove toxic heavy metal ions from water. The findings could aid efforts to improve universal access to clean water.
Friday, March 20, 2020
Putting artificial intelligence to work in the lab
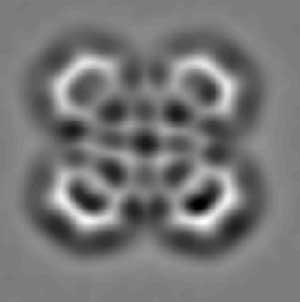 Automated Scanning Probe Microscopy (SPM) controlled by artificial intelligence. First demonstration of fully autonomous, long-term SPM operation.
Automated Scanning Probe Microscopy (SPM) controlled by artificial intelligence. First demonstration of fully autonomous, long-term SPM operation.
Researchers studying biomass enabled nanomaterials for desalination and water purification
 Researchers are working to develop a holistic approach to green technology for water desalination and purification to meet societal demands.
Researchers are working to develop a holistic approach to green technology for water desalination and purification to meet societal demands.
Scientists propose new approach to measuring atoms
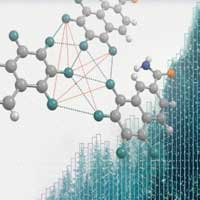 Scientists proposed a new method of statistical analysis of intermolecular interactions and sizes of atoms.
Scientists proposed a new method of statistical analysis of intermolecular interactions and sizes of atoms.
A pigment from ancient Egypt for modern microscopy
 Research team produces new nanosheets for near infrared imaging.
Research team produces new nanosheets for near infrared imaging.
Thursday, March 19, 2020
Stretchable supercapacitors to power tomorrow's wearable devices
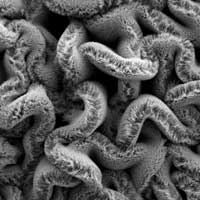 Researchers demonstrate robust supercapacitors that still work when stretched to 8 times their original size.
Researchers demonstrate robust supercapacitors that still work when stretched to 8 times their original size.
Graphene underpins a new platform to selectively ID deadly strains of bacteria
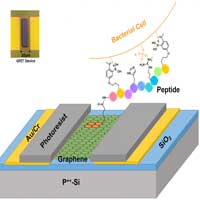 Prototype demonstrates the first selective, electrical detection of two pathogenic bacterial species.
Prototype demonstrates the first selective, electrical detection of two pathogenic bacterial species.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
