Friday, August 31, 2018
2D material cannibalizes itself for atomic building blocks
Watching atoms and electrons at work
Thursday, August 30, 2018
Dual-layer solar cell developed at UCLA sets record for efficiently generating power

Sampling for nanomaterial workplace exposure in the air and on surfaces
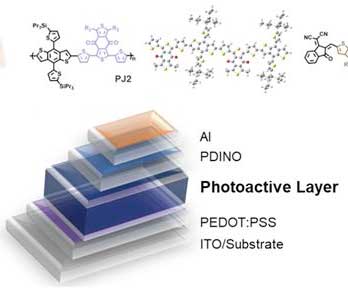
Introducing high-performance non-fullerene organic solar cells
3D-printing colloidal crystals

Wednesday, August 29, 2018
Boron nitride separation process could facilitate higher efficiency solar cells

Charged polymer nanoballs attack tumors directly, without drugs
Tuning into the potential of phosphorene
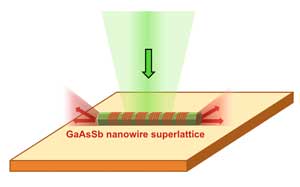
Building miniature lasers using nanowire
International nanotechnology authorities dialogue
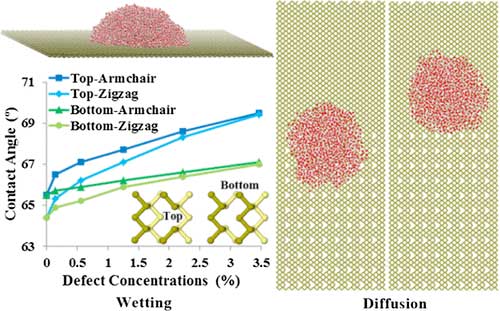
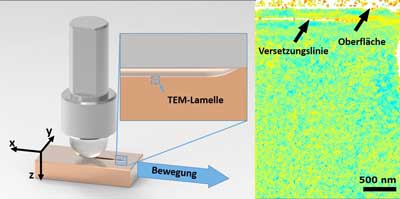
Friction loss at first contact: The material does not forgive
Environmentally friendly photoluminescent nanoparticles for more vivid display colors
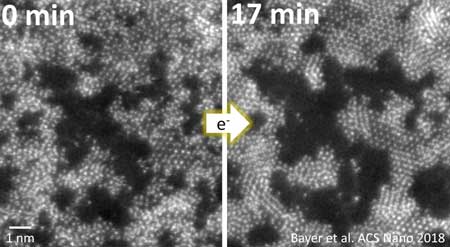
Watching 2D materials grow
Science behind world's lightest graphene watch revealed

Tuesday, August 28, 2018
All that is (nano)gold is not biochemically stable

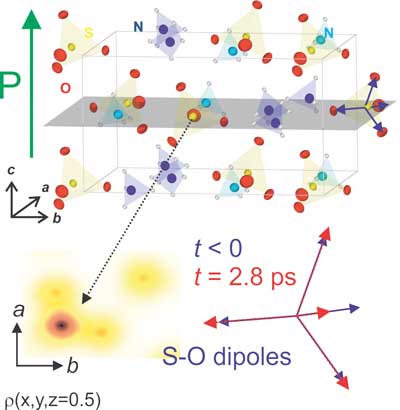
Electric polarization in the macroscopic world and electrons moving at atomic scales
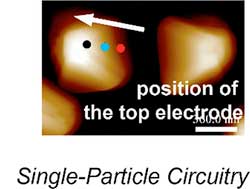
Nanocrystals pave the way for new design of digital devices
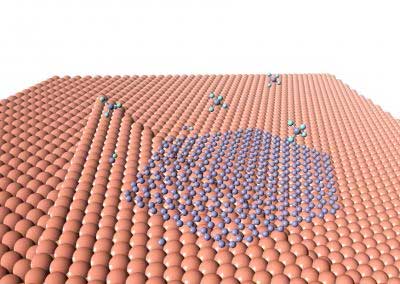
Researchers reveal the growth of graphene near polycrystalline substrate grain boundaries
Researchers develop a method for cloaking nano-sensors for optics and biomedicine
FeCo-selenide -- Next-generation material in energy storage devices?
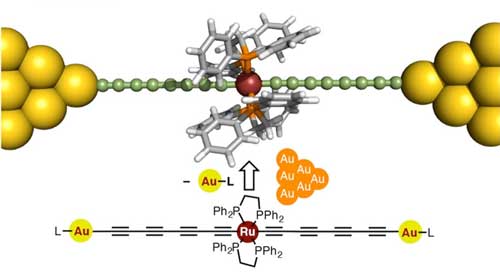
All wired up: New molecular wires for single-molecule electronic devices
A novel DNA-nanoparticle actuator system
Carbon in color: First-ever colored thin films of nanotubes created

Levitating 2D semiconductor for better performance
Monday, August 27, 2018
Reducing friction with an onion-like carbon material

Medical nanorobot enters Guinness World Records

A novel graphene quantum dot structure takes the cake
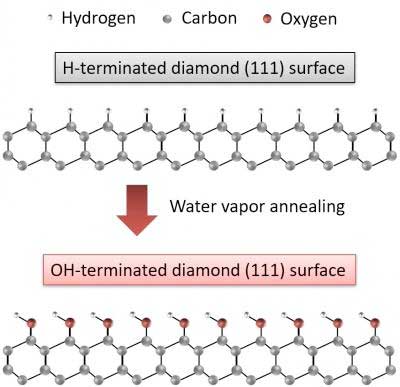
Water vapor annealing technique on diamond surfaces for next-generation power devices
Improved efficiency and stability of quantum dot solar cells using an organic thin film
Friday, August 24, 2018
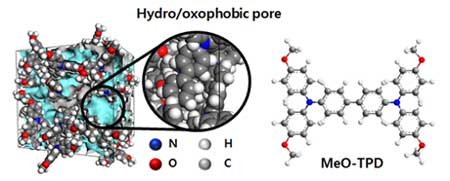
Getting a charge out of MOFs
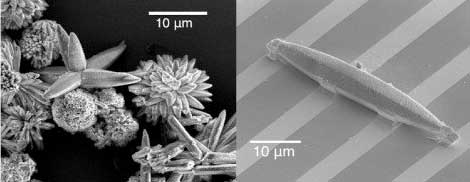
Producing hydrogen from splitting water without splitting hairs

Genetically engineered virus spins gold into beads
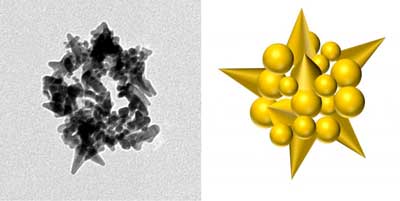
High performance graphene-based catalysts
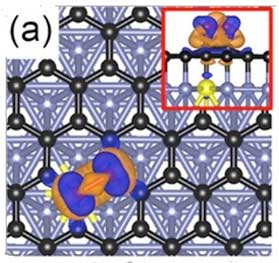
Thursday, August 23, 2018
A human enzyme can biodegrade graphene
Nanotechnology against viruses - flexible nanogels exhibit broad-spectrum antiviral activity
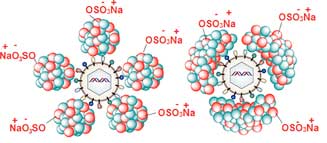
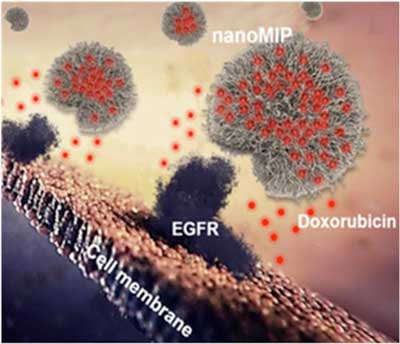
Nanoscale polymer antibodies efficiently target and eliminate cancer cells
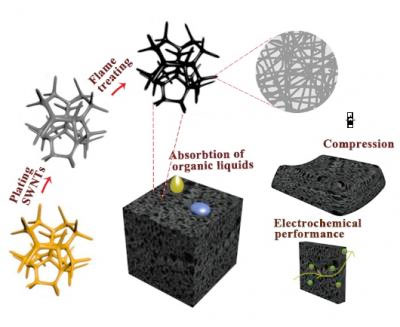
Large scale preparation method of high quality SWNT sponges
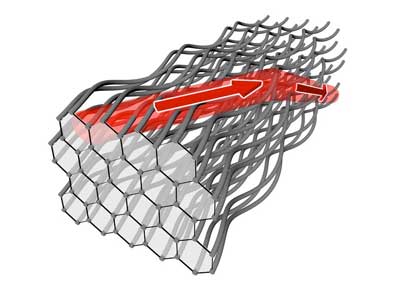
Researchers develop novel process to 3D-print graphene

Added disorder drives transition to photonic topological insulator
Wednesday, August 22, 2018
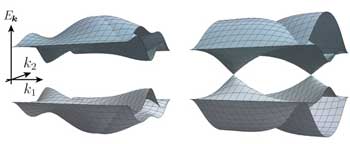
Breaking down band structures
Reimagining MRI contrast: Iron nanoparticles outperform gadolinium
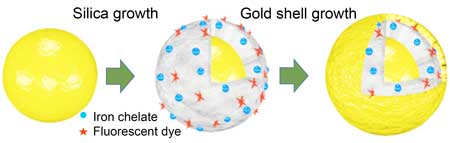
Connecting the (nano) dots: How big-picture thinking can advance nanoparticle manufacturing

New topological insulator could improve efficiency of computer processing and memory
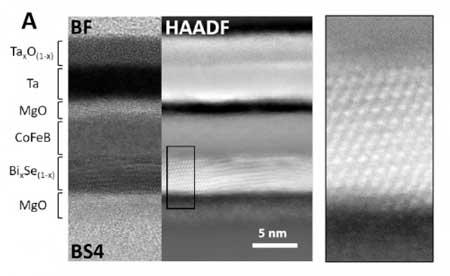
Graphene laminated pipes could reduce corrosion in the oil and gas industry

Tuesday, August 21, 2018
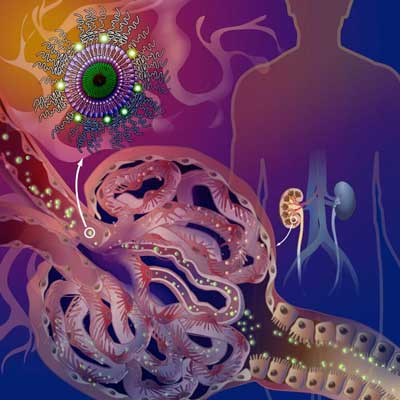
Nanoparticle targets kidney disease for drug delivery
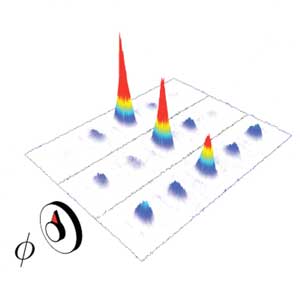
Quantum simulation reveals mobility edge in a low-dimensional disordered landscape
Nanoparticles in the environment can be more hamful than we think

Nanobot pumps destroy nerve agents
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)