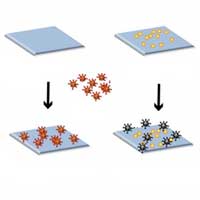
 Scientists are working toward advances that, using nanotechnology, could lead to a hospital bed or doorknob that naturally destroys viruses.
Scientists are working toward advances that, using nanotechnology, could lead to a hospital bed or doorknob that naturally destroys viruses.
Tuesday, February 9, 2021
Biomaterials and nanotechnology could mean better vaccines, virus-fighting surfaces
 Scientists are working toward advances that, using nanotechnology, could lead to a hospital bed or doorknob that naturally destroys viruses.
Scientists are working toward advances that, using nanotechnology, could lead to a hospital bed or doorknob that naturally destroys viruses.
New piezoelectric material remains effective to high temperatures
 Scientists outline the material selection and design of a novel bimorph piezoelectric energy harvester with an extremely high energy harvesting output power density.
Scientists outline the material selection and design of a novel bimorph piezoelectric energy harvester with an extremely high energy harvesting output power density.
Researchers use hot nano-chisel to create artificial bones in a Petri dish
 This work could lead to efficient, detailed artificial bone tissue, opening doors to disease modeling, in vitro cell research on targeted therapies, drug screening and more.
This work could lead to efficient, detailed artificial bone tissue, opening doors to disease modeling, in vitro cell research on targeted therapies, drug screening and more.
Scientists develop a sensitive method to find and trace nanomaterials in blood and tissues
 An international team of researchers developed a sensitive method to find and trace nanomaterials in blood and tissues, and traced nanomaterials across an aquatic food chain, from microorganisms to fish, which is a major source of food in many countries. This method can open new horizons for taking safety actions.
An international team of researchers developed a sensitive method to find and trace nanomaterials in blood and tissues, and traced nanomaterials across an aquatic food chain, from microorganisms to fish, which is a major source of food in many countries. This method can open new horizons for taking safety actions.
New rapid test uses magnetic nanoparticles to detect coronavirus antibodies
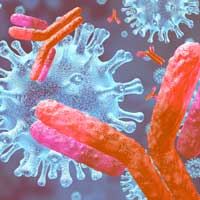 Scientists have developed a rapid test that can reliably identify Covid-19 antibodies in the blood within minutes.
Scientists have developed a rapid test that can reliably identify Covid-19 antibodies in the blood within minutes.
Nanothermometry to improve anticancer strategies
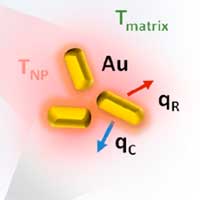 Researchers measure the nanoscale heating of gold-based nanoparticles and find high temperature variations within the nanoscopic volume.
Researchers measure the nanoscale heating of gold-based nanoparticles and find high temperature variations within the nanoscopic volume.
New nanocoating a breakthrough for hydrogen fuel
 Researchers have developed a very effective protection strategy for narrow bandgap semiconductors, stabilizing them during photoreactions.
Researchers have developed a very effective protection strategy for narrow bandgap semiconductors, stabilizing them during photoreactions.
Droplets perform daredevil feats on gel surfaces
 Scientists have succeeded in making droplets flow just as fast on soft surfaces as on hard ones by changing the surface texture.
Scientists have succeeded in making droplets flow just as fast on soft surfaces as on hard ones by changing the surface texture.
Spontaneous organization of supracolloids into three-dimensional structured materials
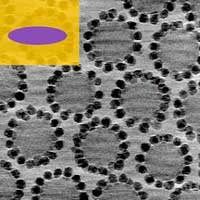 Researchers report a three-dimensional structured material achieved through supracolloids assembly.
Researchers report a three-dimensional structured material achieved through supracolloids assembly.
Two-phase material with surprising properties
 Microstructure and macroscopic electro-mechanical properties are closely coupled in so-called ferroelectric polymers. An explanation for the high temperature dependence of this coupling has now been found.
Microstructure and macroscopic electro-mechanical properties are closely coupled in so-called ferroelectric polymers. An explanation for the high temperature dependence of this coupling has now been found.
From trash to treasure: Silicon waste finds new use in Li-ion batteries
 Researchers fabricate Li-ion battery electrodes with Si swarf/graphite sheet composites, achieving high performance, reduced cost, and environmental friendliness.
Researchers fabricate Li-ion battery electrodes with Si swarf/graphite sheet composites, achieving high performance, reduced cost, and environmental friendliness.
World's first video recording of a space-time crystal
 A team of researchers has succeeded in creating a micrometer-sized space-time crystal consisting of magnons at room temperature. With the help of an ultra-precise X-ray microscope, they were able to capture the recurring periodic magnetization structure in a video.
A team of researchers has succeeded in creating a micrometer-sized space-time crystal consisting of magnons at room temperature. With the help of an ultra-precise X-ray microscope, they were able to capture the recurring periodic magnetization structure in a video.
Radiative cooling and solar heating from one system, no electricity needed
 Study describes passive cooling system that aims to help impoverished communities, reduce cooling and heating costs, lower CO2 emissions.
Study describes passive cooling system that aims to help impoverished communities, reduce cooling and heating costs, lower CO2 emissions.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
