 By combining purpose-built materials and neural networks, researchers have shown that sound can be used in high-resolution imagery.
By combining purpose-built materials and neural networks, researchers have shown that sound can be used in high-resolution imagery.
Monday, August 10, 2020
Deep learning and metamaterials make the invisible visible
 By combining purpose-built materials and neural networks, researchers have shown that sound can be used in high-resolution imagery.
By combining purpose-built materials and neural networks, researchers have shown that sound can be used in high-resolution imagery.
Some of the fastest light pulses ever take on solid materials
 Scientists use attosecond laser pulses to probe the shortest-lived processes in nature in solid materials instead of gases.
Scientists use attosecond laser pulses to probe the shortest-lived processes in nature in solid materials instead of gases.
How to greatly increase the delivery of cancer-fighting nanoparticles into a tumour
 Researchers have discovered a dose threshold that provides a potentially universal method for gauging nanoparticle dosage and could help advance a new generation of cancer therapy, imaging and diagnostics.
Researchers have discovered a dose threshold that provides a potentially universal method for gauging nanoparticle dosage and could help advance a new generation of cancer therapy, imaging and diagnostics.
Using a metal-organic framework to desalinate water with sunlight
 Researchers have been able to transform brackish water and seawater into safe, clean drinking water in less than 30 minutes using metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) and sunlight. They were able to generate 139.5L of clean water per kilogram of MOF per day.
Researchers have been able to transform brackish water and seawater into safe, clean drinking water in less than 30 minutes using metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) and sunlight. They were able to generate 139.5L of clean water per kilogram of MOF per day.
Breaking molecular traffic jams with finned nanoporous materials
 New porous catalyst with ultra-small fins facilitates molecular transport.
New porous catalyst with ultra-small fins facilitates molecular transport.
Double layer of 2D materials unlocks crucial properties
 By layering different two-dimensional materials, physicists have created a novel structure with the ability to absorb almost all light of a selected wavelength.
By layering different two-dimensional materials, physicists have created a novel structure with the ability to absorb almost all light of a selected wavelength.
Nanocatalysts remotely control chemical reactions inside living cells
 Researchers developed a remote magnetic-sensitive artificial catalyst, which shows high catalytic efficiency within living cells.
Researchers developed a remote magnetic-sensitive artificial catalyst, which shows high catalytic efficiency within living cells.
Discovery of 'massless' electrons in phase-change materials provides next step for future electronics
 Researchers have found electrons that behave as if they have no mass, called Dirac electrons, in a compound used in rewritable discs, such as CDs and DVDs. The discovery of 'massless' electrons in this phase-change material could lead to faster electronic devices.
Researchers have found electrons that behave as if they have no mass, called Dirac electrons, in a compound used in rewritable discs, such as CDs and DVDs. The discovery of 'massless' electrons in this phase-change material could lead to faster electronic devices.
Ultraflat graphene with greatly enhanced mechanical properties
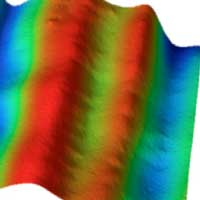 Researchers investigate the effect of original surface topography of Cu(111) substrate on surface roughening after graphene growth.
Researchers investigate the effect of original surface topography of Cu(111) substrate on surface roughening after graphene growth.
From nanocellulose to gold
 When nanocellulose is combined with various types of metal nanoparticles, materials are formed with many new and exciting properties. They may be antibacterial, change colour under pressure, or convert light to heat.
When nanocellulose is combined with various types of metal nanoparticles, materials are formed with many new and exciting properties. They may be antibacterial, change colour under pressure, or convert light to heat.
Scientists develop biomimetic nanoprobes to image brain tumors
 Biomimetic nanoprobes are prepared by composing ferric oxide and fluorescent dye, and coating the surface of nanoprobes by bioorthogonally labeled brain tumor cell membrane for crossing the BBB and targeting brain tumor cells.
Biomimetic nanoprobes are prepared by composing ferric oxide and fluorescent dye, and coating the surface of nanoprobes by bioorthogonally labeled brain tumor cell membrane for crossing the BBB and targeting brain tumor cells.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
