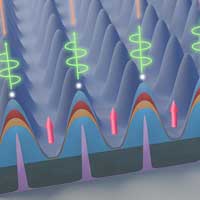
 Researchers have taken an important step toward developing a communications network that exchanges information across long distances by using photons, mass-less measures of light that are key elements of quantum computing and quantum communications systems.
Researchers have taken an important step toward developing a communications network that exchanges information across long distances by using photons, mass-less measures of light that are key elements of quantum computing and quantum communications systems.
Wednesday, November 4, 2020
Building a quantum network one node at a time
 Researchers have taken an important step toward developing a communications network that exchanges information across long distances by using photons, mass-less measures of light that are key elements of quantum computing and quantum communications systems.
Researchers have taken an important step toward developing a communications network that exchanges information across long distances by using photons, mass-less measures of light that are key elements of quantum computing and quantum communications systems.
Laser-powered nanomotors chart their own course (w/video)
 Researchers have developed a system of gold nanorods that acts like a tiny light-driven motor, with its direction of motion is determined by the orientation of the motors. This work may lead to smaller and more precise nanomachines.
Researchers have developed a system of gold nanorods that acts like a tiny light-driven motor, with its direction of motion is determined by the orientation of the motors. This work may lead to smaller and more precise nanomachines.
Scientists grow carbon nanotube forest much longer than any other (w/video)
 Novel technique yields a carbon nanotube forest of record length, potentially revolutionizing the future of many industries.
Novel technique yields a carbon nanotube forest of record length, potentially revolutionizing the future of many industries.
Luminescent wood could light up homes of the future
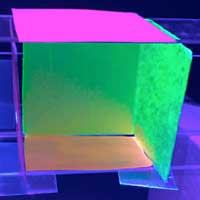 Researchers have developed a bio-based, luminescent, water-resistant wood film that could someday be used as cover panels for lamps, displays and laser devices.
Researchers have developed a bio-based, luminescent, water-resistant wood film that could someday be used as cover panels for lamps, displays and laser devices.
Shaping the future of biomedical applications
 Bio-compatible electrostrictive materials will play a leading role in the future generation of medical micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMS).
Bio-compatible electrostrictive materials will play a leading role in the future generation of medical micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMS).
Scientists develop method to detect charge traps in organic semiconductors
 The findings of this new research may change views about what limits the performance of organic solar cells, photodetectors and OLEDs.
The findings of this new research may change views about what limits the performance of organic solar cells, photodetectors and OLEDs.
Liquid biopsy made more sensitive using 'loosely stacked' detection layers
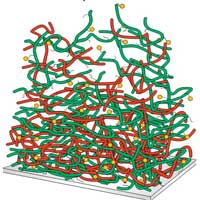 Researchers use electrically charged polymers to detect biomarkers in body fluids. Not just one layer of this, but dozens. In this way they manage reaching a 25 times higher sensitivity.
Researchers use electrically charged polymers to detect biomarkers in body fluids. Not just one layer of this, but dozens. In this way they manage reaching a 25 times higher sensitivity.
Researchers develop a high-power, portable terahertz laser
 The instrument could bring powerful sensing and imaging capabilities out of the lab and into hospitals, airports, or other settings.
The instrument could bring powerful sensing and imaging capabilities out of the lab and into hospitals, airports, or other settings.
Material found in meteorites portends new possibilities for spintronic computing
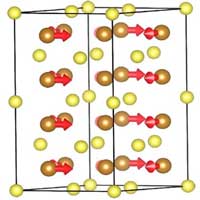 This discovery provides a new route to design materials with tunable electrical and magnetic behaviors for potential applications in information storage and spintronics computing.
This discovery provides a new route to design materials with tunable electrical and magnetic behaviors for potential applications in information storage and spintronics computing.
100,000-fold enhancement in the nonlinearity of silicon
 Researchers develop silicon nanoresonators that can control the scattering of light when excited by another laser. This research may lead to faster and completely optical computer switches and circuits.
Researchers develop silicon nanoresonators that can control the scattering of light when excited by another laser. This research may lead to faster and completely optical computer switches and circuits.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
