Tuesday, July 31, 2018
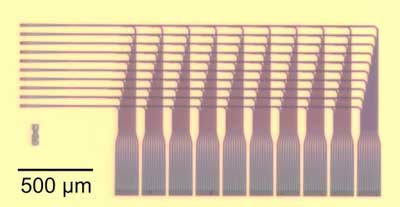
Chip lights up optical neural network demo
The quest for longer-lasting solar cells

Dental plaque is no match for catalytic nanoparticles

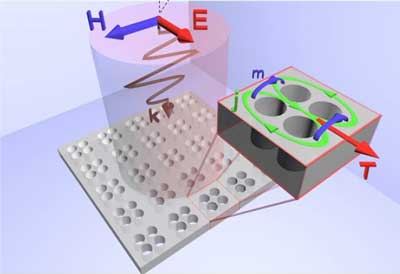
A colossal breakthrough for topological spintronics
Titanium dioxide as a nanoscale sensor of mechanical stress
Better way found to determine the integrity of metals

Monday, July 30, 2018
Supercomputing the 'how' of chemical reactions
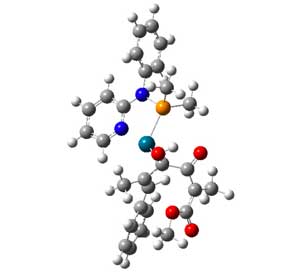
Magnetic nanoparticles deliver chemotherapy to difficult-to-reach spinal tumors
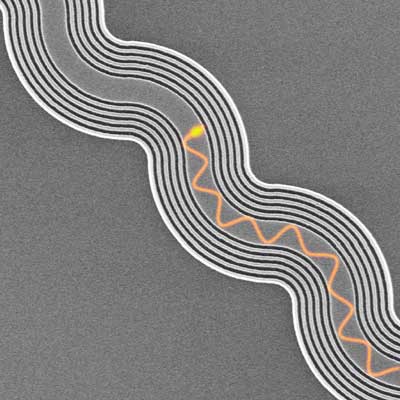
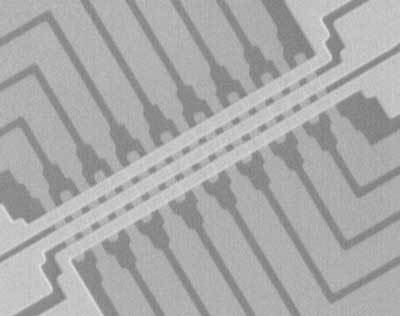
Trapping light that doesn't bounce off track for faster electronics

Nano-sized traps show promise in diagnosing pathogenic bacterial infections

Memory-processing unit could bring memristors to the masses
Extreme conditions in semiconductors

Great Pyramid of Giza inspires nanoparticle design

Looking inside the lithium battery's black box
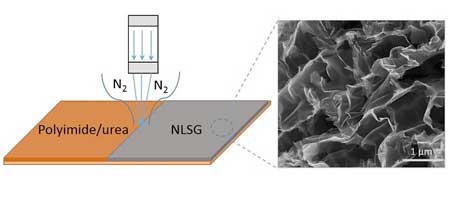
Lasers write better graphene anodes
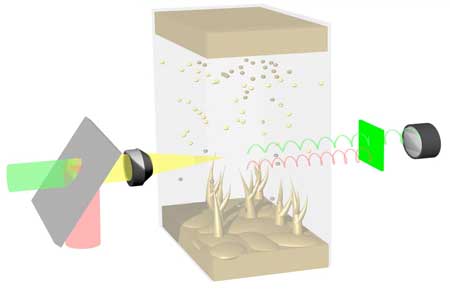
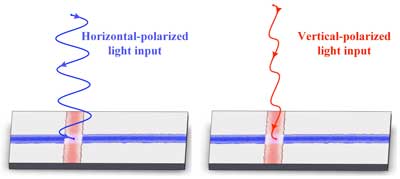
Researchers construct all-optical nanowire pocket calculator
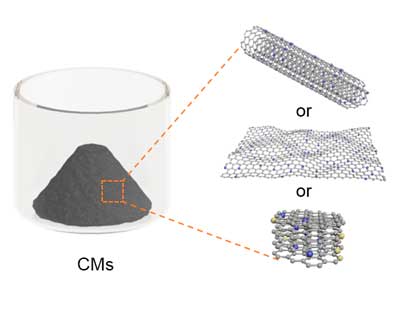
Researchers propose a facile, general, and effective strategy to prepare carbon nanomaterials
Individual silver nanoparticles observed in real time

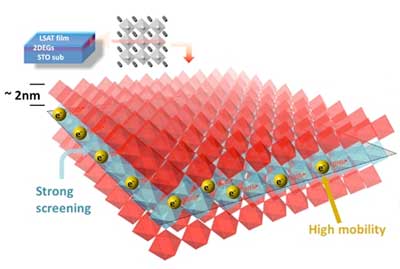
An expressway for electrons in oxide heterostructures
Friday, July 27, 2018
Tin type
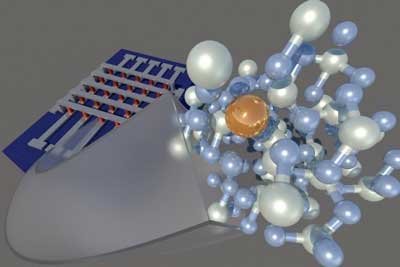
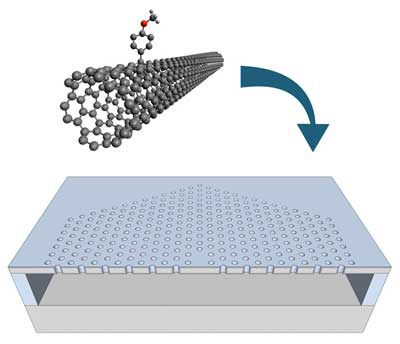
Carbon nanotubes on holey silicon make bright source of single photons
Thursday, July 26, 2018
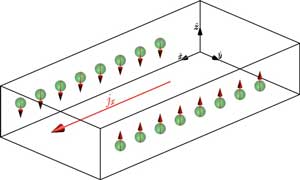
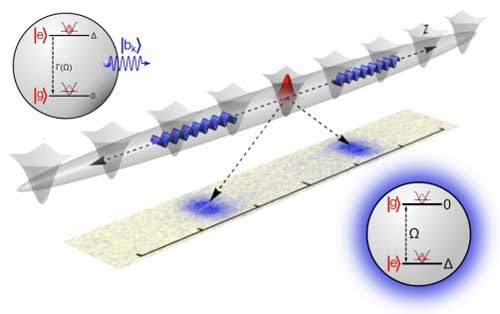
Scientists develop novel approach to spontaneous emission using atomic matter waves
New optics: Nano-hedgehogs of light
New two-dimensional material could revolutionize solar fuel generation
Technique to easily fabricate ceramic films used as OPV inter-layers developed
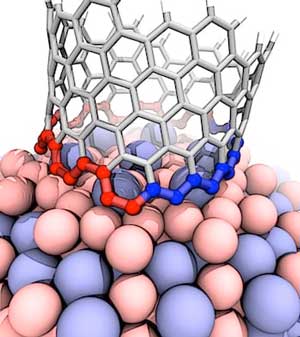
Two-faced edge makes nanotubes obey
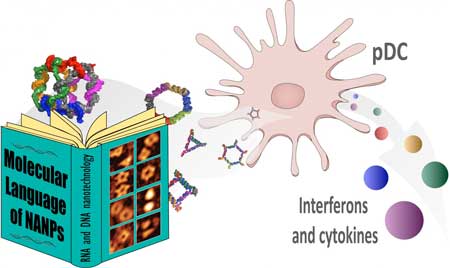
Researchers report unraveling the immune recognition of nucleic acid nanoparticles
Researchers design a nano-carrier to release drugs into damaged cells
Wednesday, July 25, 2018
Scientists use excitons to take electronics into the future
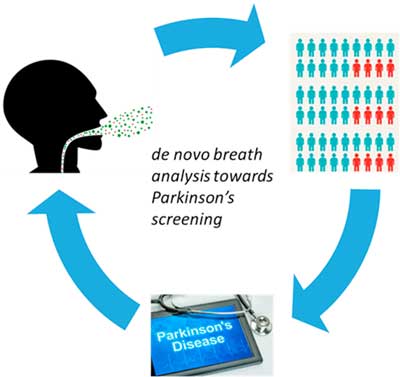
A nanotechnology breath test for early-stage Parkinson's
DOE grant to study single nanoparticles and their ability to act as electrocatalysts

What happens in a solar cell when the lights go out?
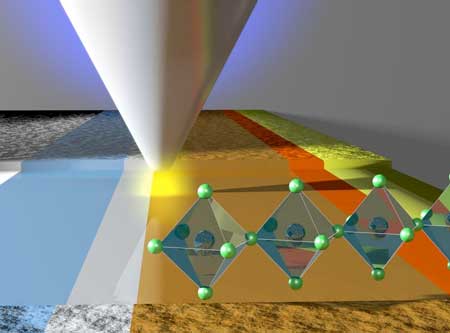
Vibrations at an exceptional point

Scientists unlock the properties of new 2D material
Tuesday, July 24, 2018
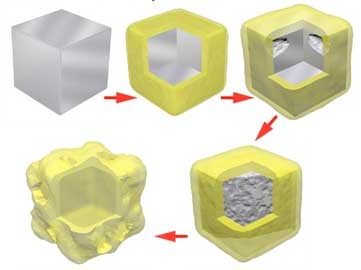
Researchers use nanotechnology to improve the accuracy of measuring devices
Made-to-measure silicon building blocks
Improving nanotube biosensors for implantable sensing

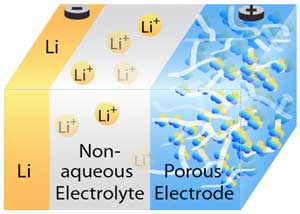
Liquid microscopy technique reveals new problem with lithium-oxygen batteries
Generation of random numbers by measuring phase fluctuations from a laser diode with a silicon-on-in

Monday, July 23, 2018
Real-time imaging of chemical processes
Scientists develop new materials that move in response to light

Researchers charge quest to end 'voltage fade'
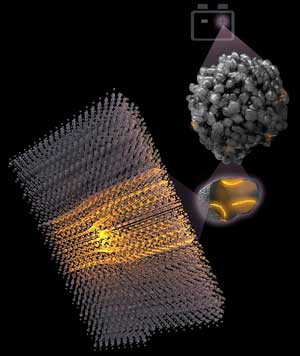
Scientists introduce new way to mimic 'machine of machines' (w/video)

Engineers model agraphene-based artificial synapse after the human brain
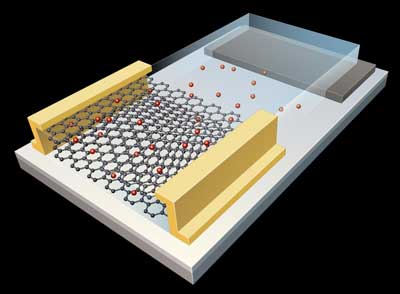
Cell-sized robots can sense their environment
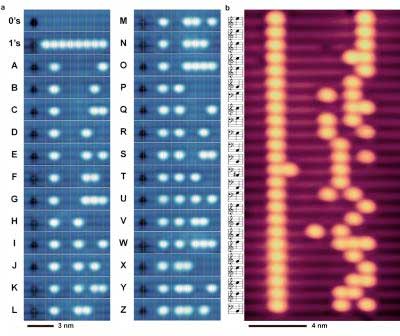
Writing the future of rewritable memory
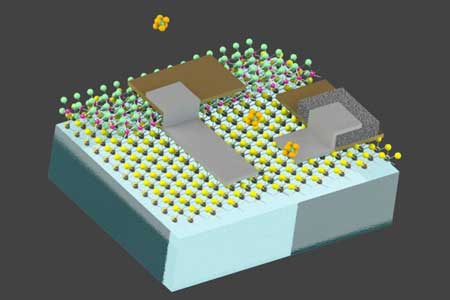
A new metamaterial for solar cells and nanooptics
Nanocrystals emit light by efficiently 'tunneling' electrons

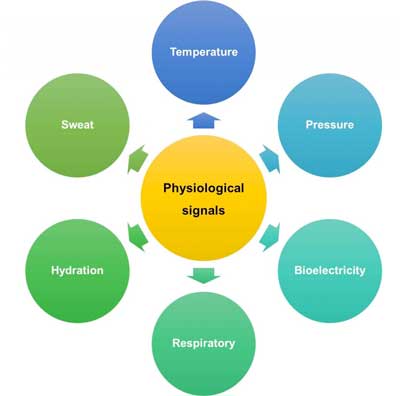
An overview of healthcare monitoring by flexible electronics
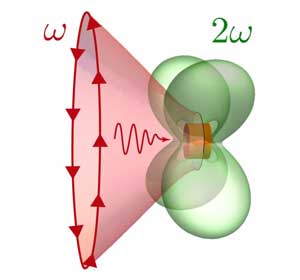
Physicists design a nano-resonator with strong nonlinear response
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
