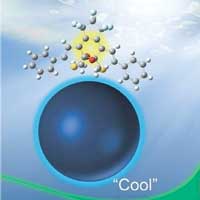
 Researchers have found a drastically amplified ring-opening reaction yield in aqueous nanoparticle colloids of a photochromic diarylethene when induced by an intense nanosecond laser pulse, and clarified its amplification mechanism.
Researchers have found a drastically amplified ring-opening reaction yield in aqueous nanoparticle colloids of a photochromic diarylethene when induced by an intense nanosecond laser pulse, and clarified its amplification mechanism.
Thursday, September 24, 2020
Nanosecond laser-induced amplification of a photochromic reaction in a diarylethene nanoparticle
 Researchers have found a drastically amplified ring-opening reaction yield in aqueous nanoparticle colloids of a photochromic diarylethene when induced by an intense nanosecond laser pulse, and clarified its amplification mechanism.
Researchers have found a drastically amplified ring-opening reaction yield in aqueous nanoparticle colloids of a photochromic diarylethene when induced by an intense nanosecond laser pulse, and clarified its amplification mechanism.
High-performance single-atom catalysts for high-temperature fuel cells
 Individual platinum atoms participate in catalytic reaction to faciitate the electrode process by up to 10 times. Single-atom platinum catalysts are stable at 700 degrees Celsius and expected to stimulate the commercialization of next-gen reversible fuel cells.
Individual platinum atoms participate in catalytic reaction to faciitate the electrode process by up to 10 times. Single-atom platinum catalysts are stable at 700 degrees Celsius and expected to stimulate the commercialization of next-gen reversible fuel cells.
Metal wires of carbon complete toolbox for carbon-based computers
 Metallic carbon circuit element enables work on faster, efficient carbon-based transistors.
Metallic carbon circuit element enables work on faster, efficient carbon-based transistors.
Bridging the gap between the magnetic and electronic properties of topological insulators
 Scientists shed light on the relationship between the magnetic properties of topological insulators and their electronic band structure. Their experimental results shed new insights into recent debates regarding the evolution of the band structure with temperature in these materials, which exhibit unusual quantum phenomena and are envisioned to be crucial in next-generation electronics, spintronics, and quantum computers.
Scientists shed light on the relationship between the magnetic properties of topological insulators and their electronic band structure. Their experimental results shed new insights into recent debates regarding the evolution of the band structure with temperature in these materials, which exhibit unusual quantum phenomena and are envisioned to be crucial in next-generation electronics, spintronics, and quantum computers.
Dynamic tattoos promise to warn wearers of health threats
 You can't walk into a doctor's office and get a dynamic tattoo yet, but they are on the way. Early proof-of-concept studies provide convincing evidence that tattoos can be engineered, not only to change color, but to sense and convey biomedical information, including the onset of cancer.
You can't walk into a doctor's office and get a dynamic tattoo yet, but they are on the way. Early proof-of-concept studies provide convincing evidence that tattoos can be engineered, not only to change color, but to sense and convey biomedical information, including the onset of cancer.
The groove of the self-organized active nematic ribbon
 Researchers report the creation of a 3D active nematic. The material passes through several spatial patterns, from collapsing into a ribbon to wrinkling in 3D.
Researchers report the creation of a 3D active nematic. The material passes through several spatial patterns, from collapsing into a ribbon to wrinkling in 3D.
Scientists take a 'spin' onto magnetoresistive RAM
 Magnetoresistive random access memory (MRAM) is the forerunning candidate for the next generation digital technology. However, manipulating MRAM efficiently and effectively has been challenging. A revolutionary breakthrough generates spin current to switch the pinned magnetic moments at will.
Magnetoresistive random access memory (MRAM) is the forerunning candidate for the next generation digital technology. However, manipulating MRAM efficiently and effectively has been challenging. A revolutionary breakthrough generates spin current to switch the pinned magnetic moments at will.
'Stretching rack' for cells
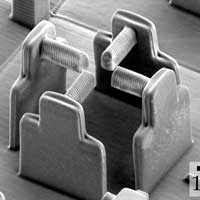 An ingenious device, only a few micrometers in size, enables to study the reaction of individual biological cells to mechanical stress.
An ingenious device, only a few micrometers in size, enables to study the reaction of individual biological cells to mechanical stress.
The return of the spin echo
 Multiple echoes as a result of a strong link between spins and microwave photons - this effect presents exciting, new opportunities for working with quantum information.
Multiple echoes as a result of a strong link between spins and microwave photons - this effect presents exciting, new opportunities for working with quantum information.
White graphene: high defect tolerance and elasticity unveiled by nanomechanics experts
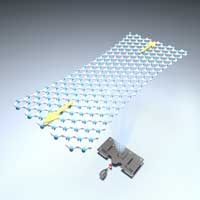 After revealing the realistic strength and stretchability of graphene, researchers have carried forward the success by unveiling the high defect tolerance and elasticity of hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN), another 2D material known as 'white graphene'. This follow-up study will promote future development and applications of strain engineering, piezoelectronics and flexible electronics.
After revealing the realistic strength and stretchability of graphene, researchers have carried forward the success by unveiling the high defect tolerance and elasticity of hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN), another 2D material known as 'white graphene'. This follow-up study will promote future development and applications of strain engineering, piezoelectronics and flexible electronics.
Researchers develop smallest particle sensor in the world
 With this innovation, smartphones, smart watches or fitness wristbands can for the first time measure the quality of the ambient air in real time and sound the alarm in the event of increased fine dust values.
With this innovation, smartphones, smart watches or fitness wristbands can for the first time measure the quality of the ambient air in real time and sound the alarm in the event of increased fine dust values.
New brain cell-like nanodevices work together to identify mutations in viruses
 These systems could potentially overcome computational hurdles faced by current digital technologies.
These systems could potentially overcome computational hurdles faced by current digital technologies.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
