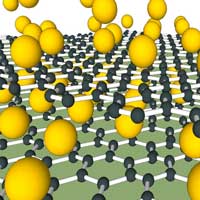
 Adding calcium to graphene creates an extremely promising superconductor, but where does the calcium go? In a new study, researchers have for the first time confirmed what actually happens to those calcium atoms.
Adding calcium to graphene creates an extremely promising superconductor, but where does the calcium go? In a new study, researchers have for the first time confirmed what actually happens to those calcium atoms.
Wednesday, September 16, 2020
What happens between the sheets (of graphene)?
 Adding calcium to graphene creates an extremely promising superconductor, but where does the calcium go? In a new study, researchers have for the first time confirmed what actually happens to those calcium atoms.
Adding calcium to graphene creates an extremely promising superconductor, but where does the calcium go? In a new study, researchers have for the first time confirmed what actually happens to those calcium atoms.
Anti-reflective nanocoating inspired by fly eyes
 Researchers have artificially reproduced a nanoscale coating on different types of surfaces that usually covers the eyes of fruit flies, and which provides anti-reflective, anti-adhesive properties.
Researchers have artificially reproduced a nanoscale coating on different types of surfaces that usually covers the eyes of fruit flies, and which provides anti-reflective, anti-adhesive properties.
Researchers discover new way of controlling conductivity of materials at the nanoscale
 Researchers have found a completely new method to check the electronic properties of oxide materials. This opens the door to even tinier components and perhaps more sustainable electronics.
Researchers have found a completely new method to check the electronic properties of oxide materials. This opens the door to even tinier components and perhaps more sustainable electronics.
Physicists make electrical nanolasers even smaller
 Researchers have cleared the obstacle that had prevented the creation of electrically driven nanolasers for integrated circuits. The approach enables coherent light source design on the scale not only hundreds of times smaller than the thickness of a human hair but even smaller than the wavelength of light emitted by the laser.
Researchers have cleared the obstacle that had prevented the creation of electrically driven nanolasers for integrated circuits. The approach enables coherent light source design on the scale not only hundreds of times smaller than the thickness of a human hair but even smaller than the wavelength of light emitted by the laser.
Molecular 'dances' determine how liquids take up heat
 Scientists have uncovered a link between the microscopic movements of particles in a liquid and its ability to absorb heat.
Scientists have uncovered a link between the microscopic movements of particles in a liquid and its ability to absorb heat.
Analysing molecular structures in more detail
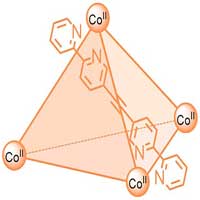 Research team develops new NMR methods for investigating paramagnetic complexes and supramolecular cages.
Research team develops new NMR methods for investigating paramagnetic complexes and supramolecular cages.
Novel photoresist enables 3D-printing of smallest porous structures
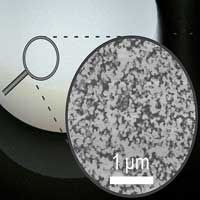 Researchers have developed a photoresist for two-photon microprinting. It has now been used for the first time to produce three-dimensional polymer microstructures with cavities in the nano range.
Researchers have developed a photoresist for two-photon microprinting. It has now been used for the first time to produce three-dimensional polymer microstructures with cavities in the nano range.
Why do hospital germs bind more strongly to certain surfaces than to others?
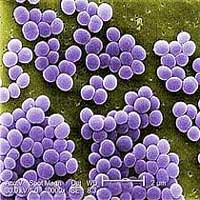 A team of physicists has shown why hospital germs adhere strongly to surfaces from which water simply rolls off, but bind so poorly to surfaces that are easily wetted by water. These results from studies in both experimental and theoretical physics may help to improve antibacterial surfaces.
A team of physicists has shown why hospital germs adhere strongly to surfaces from which water simply rolls off, but bind so poorly to surfaces that are easily wetted by water. These results from studies in both experimental and theoretical physics may help to improve antibacterial surfaces.
Single photons from a silicon chip
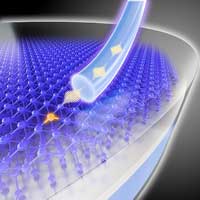 Physicists designed a silicon-based light source to generate single photons that propagate well in glass fibers.
Physicists designed a silicon-based light source to generate single photons that propagate well in glass fibers.
Machine-learning helps sort out massive MOF materials' databases
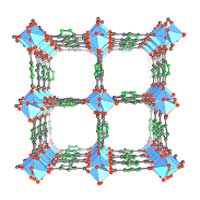 Scientists have used machine-learning to organize the chemical diversity found in the ever-growing databases for the popular metal-organic framework materials.
Scientists have used machine-learning to organize the chemical diversity found in the ever-growing databases for the popular metal-organic framework materials.
Mapping the center of atoms
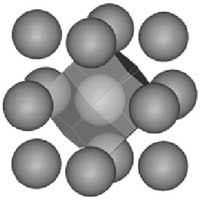 Titanium isotopes reveal unexpected stability of trapped neutrons inside nuclei
Titanium isotopes reveal unexpected stability of trapped neutrons inside nuclei
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
