Wednesday, May 2, 2018
A new approach to study properties of nanodroplets
Researchers have found new methods to measure the internal pressure and surface tension of nano-sized drops of liquid like those involved in cloud formation and airborne pollutants to study how they behave in different environments.
Innovative nanotransistor for easy measurement of electrolyte concentration in blood
Scientists developed a new method that will make it easier to measure the concentration of different electrolytes in the body using a nanotransistor.
It all comes down to roughness
Researchers have explained how the surface characteristics of microspheres affect rapid increases in the viscosity of suspensions, thus laying the groundwork for applications such as smoothly flowing cement.
Novel reaction could spark alternate approach to ammonia production
Researchers used nanoscale spikes of carbon to catalyze a reaction that generates ammonia from nitrogen and water, aided by lithium salt and the application of an electric field. The study reveals a type of catalyst that has been theoretically suggested but never demonstrated.
New insight into why most nanoparticles don?t make it through biological barriers
The biological barriers our bodies have developed evolve to keep us safe from infection and parasites. But they also filter out many of the nanoparticle drugs that hold such promise for treatment. Working out why is central to the development of next-generation drugs.
A new point-of-need nanodiagnostic for better healthcare
The Nano4 project takes fast, reliable and low-cost molecular point of care (POC) diagnostic tools down to the nano-scale, offering better healthcare outcomes for patients.

Nanodiamond turns into controllable light source
Researchers have developed a controlled light source based on nanodiamond. Experiments have shown that diamond shell doubles the emission speed light sources and helps to control them without any additional nano- and microstructures.
Organic printing nanoinks may restore sight to blind people
Fabricated using cheap and widely-available organic pigments used in printing inks and cosmetics, a simple retinal prosthesis consists of tiny pixels like a digital camera sensor on a nanometric scale. Researchers hope that it can restore sight to blind people.
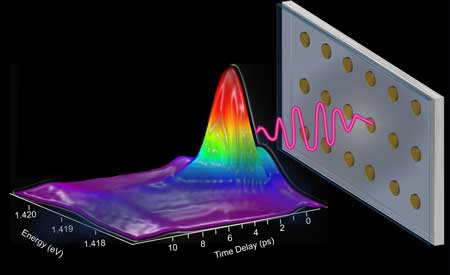
Ultrafast laser pulse created by golden nanoparticles
The creation of a fast, tunable and stable nanoparticle-array laser is a stepping stone to affordable and efficient sensing and switching.
New class of single atoms catalysts for carbon nanotubes exhibit outstanding electrochemical reduction of CO2 to CO
Experiments using X-rays have helped characterise a new class of single atom catalysts supported on carbon nanotubes that exhibit outstanding electrochemical reduction of CO2 to CO.

Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
