 Over the course of their journey from the open fields to the produce displays at grocery stores, fresh vegetables and fruits can sometimes become contaminated by microorganisms. These items can then spoil other produce, spreading the contamination further and increasing the number of food items that can cause illnesses. A new nanoparticle coating prevents that.
Over the course of their journey from the open fields to the produce displays at grocery stores, fresh vegetables and fruits can sometimes become contaminated by microorganisms. These items can then spoil other produce, spreading the contamination further and increasing the number of food items that can cause illnesses. A new nanoparticle coating prevents that.
Wednesday, April 22, 2020
New dual-action coating keeps bacteria from cross-contaminating fresh produce
 Over the course of their journey from the open fields to the produce displays at grocery stores, fresh vegetables and fruits can sometimes become contaminated by microorganisms. These items can then spoil other produce, spreading the contamination further and increasing the number of food items that can cause illnesses. A new nanoparticle coating prevents that.
Over the course of their journey from the open fields to the produce displays at grocery stores, fresh vegetables and fruits can sometimes become contaminated by microorganisms. These items can then spoil other produce, spreading the contamination further and increasing the number of food items that can cause illnesses. A new nanoparticle coating prevents that.
Electronic skin fully powered by sweat can monitor health
 Electronic skin monitors body's vitals signs while being powered by sweat.
Electronic skin monitors body's vitals signs while being powered by sweat.
A novel method to precisely deliver therapeutics inside the body
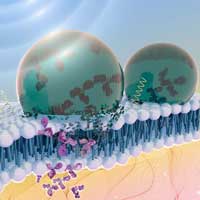 A new way to deliver therapeutic proteins inside the body uses an acoustically sensitive carrier to encapsulate the proteins and ultrasound to image and guide the package to the exact location required. Ultrasound then breaks the capsule, allowing the protein to enter the cell.
A new way to deliver therapeutic proteins inside the body uses an acoustically sensitive carrier to encapsulate the proteins and ultrasound to image and guide the package to the exact location required. Ultrasound then breaks the capsule, allowing the protein to enter the cell.
Novel method for gentle laser processing of perovskites at the nanoscale
 Scientists have developed a method for precise, fast and high-quality laser processing of halide perovskites, promising light-emitting materials for solar energy, optical electronics, and metamaterials.
Scientists have developed a method for precise, fast and high-quality laser processing of halide perovskites, promising light-emitting materials for solar energy, optical electronics, and metamaterials.
Spider combs tame unruly nanofibers
 Researchers have patterned an antiadhesive nanostructure inspired by the comb on spiders'legs onto a foil surface, creating a handy tool to control sticky lab-made nanomaterials for medical, smart textile and other applications.
Researchers have patterned an antiadhesive nanostructure inspired by the comb on spiders'legs onto a foil surface, creating a handy tool to control sticky lab-made nanomaterials for medical, smart textile and other applications.
Windows will soon generate electricity, following solar cell breakthrough
 Two square metres of solar window will do the same job as a standard rooftop solar panel.
Two square metres of solar window will do the same job as a standard rooftop solar panel.
The future of semiconductors is clear
 A clear semiconductor based on tin could improve solar power generation.
A clear semiconductor based on tin could improve solar power generation.
Scientists uncover major cause of resistance in solid electrolytes
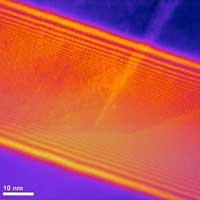 The study involved two powerful techniques - electron holography and atom probe tomography - that allowed scientists to observe the boundaries at an unprecedentedly small scale. The resulting insights provide new avenues for tuning chemical properties in the material to improve performance.
The study involved two powerful techniques - electron holography and atom probe tomography - that allowed scientists to observe the boundaries at an unprecedentedly small scale. The resulting insights provide new avenues for tuning chemical properties in the material to improve performance.
A hydrogel to cool down electronic devices, recover waste heat
 Researchers have developed a hydrogel that can both cool down electronics, such as cell phone batteries, and convert their waste heat into electricity.
Researchers have developed a hydrogel that can both cool down electronics, such as cell phone batteries, and convert their waste heat into electricity.
'Nanocardboard' flyers could serve as martian atmospheric probes
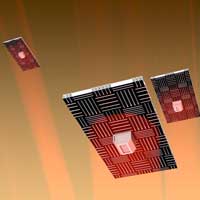 Engineers are suggesting a new way to explore the sky: tiny aircraft that weigh about as much as a fruit fly and have no moving parts. These flyers are plates of 'nanocardboard,' which levitate when bright light is shone on them. As one side heats up, the temperature differential gets air circulating through its hollow structure and shooting out of the corrugated channels that give it its name, thrusting it off the ground.
Engineers are suggesting a new way to explore the sky: tiny aircraft that weigh about as much as a fruit fly and have no moving parts. These flyers are plates of 'nanocardboard,' which levitate when bright light is shone on them. As one side heats up, the temperature differential gets air circulating through its hollow structure and shooting out of the corrugated channels that give it its name, thrusting it off the ground.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
