Thursday, May 24, 2018
Rare element to provide better material for high-speed electronics
Researchers have discovered a new two-dimensional material, derived from the rare element tellurium, to make transistors that carry a current better throughout a computer chip.
Battling brain cancer with nanotechnology
Nanoparticles carrying two drugs can cross the blood-brain barrier and shrink glioblastoma tumors.

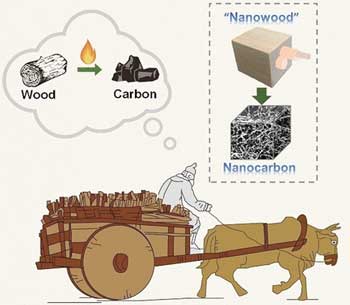
Wood to supercapacitors
Sustainable highly conductive electrode materials from ultrathin carbon nanofiber aerogels derived from nanofibrillated cellulose.
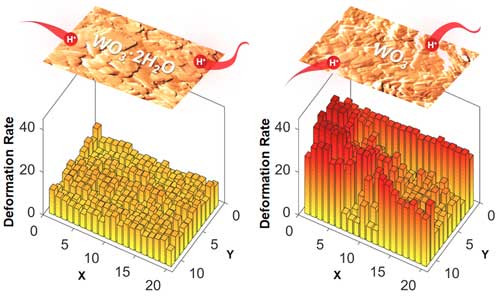
Microscopy advance reveals unexpected role for water in energy storage material
A material with atomically thin layers of water holds promise for energy storage technologies, and researchers have now discovered that the water is performing a different role than anyone anticipated.
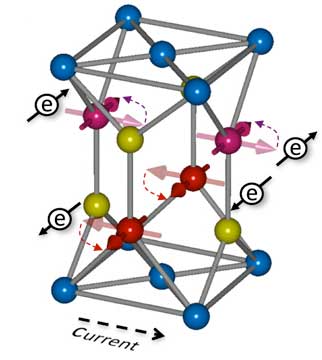
Antiferromagnetic materials allow for processing at terahertz speeds
Increased data volume and writing speed in a new antiferromagnetic-based memory.
A thermal diode based on nanoscale thermal radiation
Researchers explore rectification in the near-field, where heat fluxes are much larger than those in the far-field and can exceed the blackbody limit of far-field thermal radiation, and demonstrate that rectification coefficients between VO2 and doped Si can exceed 50% in the near-field for moderate temperature differences.

Could a particle accelerator using laser-driven implosion become a reality?
Scientists have discovered a novel particle acceleration mechanism called 'Micro-bubble implosion,' in which super-high energy hydrogen ions (relativistic protons) are emitted at the moment when bubbles shrink to atomic size through the irradiation of hydrides with micron-sized spherical bubbles by ultraintense laser pulses.
Recombinant E. coli as a biofactory for the biosynthesis of diverse nanomaterials
A metabolic research group has developed a recombinant E. coli strain that biosynthesizes 60 different nanomaterials covering 35 elements on the periodic table.

Electron tomography technique leads to 3-D reconstructions at the nanoscale
A new transmission electron microscopy technique determines three-dimensional position of individual atoms.
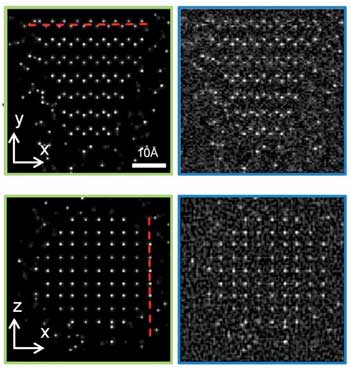
Silicon breakthrough could make key microwave technology much cheaper and better
Researchers using powerful supercomputers have found a way to generate microwaves with inexpensive silicon, a breakthrough that could dramatically cut costs and improve devices such as sensors in self-driving vehicles.
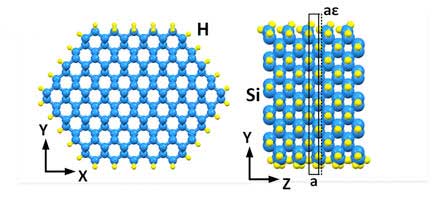
Switching with molecules
Molecular switch will facilitate the development of pioneering electro-optical devices.
Scientists crack code to cheap, small carbon nanotubes
Imagine a box you plug into the wall that cleans your toxic air and pays you cash. That's essentially what researchers produced after discovering the blueprint for turning the carbon dioxide into carbon nanotubes with small diameters.

Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
