 Researchers have demonstrated a way to disguise which transistor is which by building them out of a sheet-like material called black phosphorus. This built-in security measure would prevent hackers from getting enough information about the circuit to reverse engineer it.
Researchers have demonstrated a way to disguise which transistor is which by building them out of a sheet-like material called black phosphorus. This built-in security measure would prevent hackers from getting enough information about the circuit to reverse engineer it.
Monday, December 7, 2020
New transistor design disguises key computer chip hardware from hackers
 Researchers have demonstrated a way to disguise which transistor is which by building them out of a sheet-like material called black phosphorus. This built-in security measure would prevent hackers from getting enough information about the circuit to reverse engineer it.
Researchers have demonstrated a way to disguise which transistor is which by building them out of a sheet-like material called black phosphorus. This built-in security measure would prevent hackers from getting enough information about the circuit to reverse engineer it.
Paper-based graphene biosensor can detect COVID-19 in less than five minutes
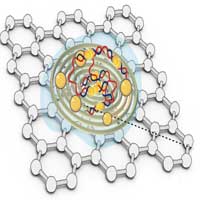 There are two components to this biosensor: a graphene platform to measure an electrical read-out and probes to detect the presence of viral RNA.
There are two components to this biosensor: a graphene platform to measure an electrical read-out and probes to detect the presence of viral RNA.
Defects slow the electron's dance
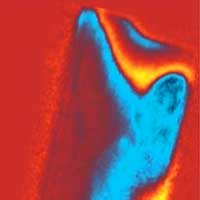 Researchers used two advanced microscopy techniques to learn how crystal defects in a type of solar power cell affect their performance. The study involved crystalline solar cells called lead halide perovskite cells.
Researchers used two advanced microscopy techniques to learn how crystal defects in a type of solar power cell affect their performance. The study involved crystalline solar cells called lead halide perovskite cells.
Scientists produce a quantum state that is part light and part matter
 Discovery provides insight for developing next generation optoelectronic and infrared devices.
Discovery provides insight for developing next generation optoelectronic and infrared devices.
Split wave component for neuromorphic computers
 Researchers demonstrate targeted magnetic waves that are generated and divided in micrometer-sized wafers.
Researchers demonstrate targeted magnetic waves that are generated and divided in micrometer-sized wafers.
Harnessing quantum properties to create single-molecule devices
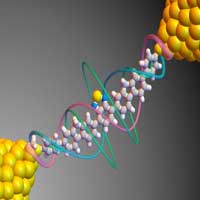 Researchers discover 6-nanometer-long single-molecule circuit with enormous on/off ratio due to quantum interference; finding could enable faster, smaller, and more energy-efficient devices.
Researchers discover 6-nanometer-long single-molecule circuit with enormous on/off ratio due to quantum interference; finding could enable faster, smaller, and more energy-efficient devices.
The world's first DNA 'tricorder' in your pocket
 By pairing an iPhone with a handheld DNA sequencer, users can create a mobile genetics laboratory, reminiscent of the tricorder featured in Star Trek.
By pairing an iPhone with a handheld DNA sequencer, users can create a mobile genetics laboratory, reminiscent of the tricorder featured in Star Trek.
Scientists model photoluminescence kinetics in semiconductor nanoplatelets for better optoelectronic performance
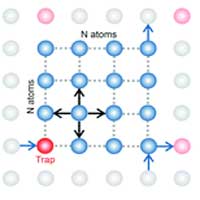 Researchers have built two models that accurately explain the light-emitting behavior of semiconductor nanoplatelets, minuscule structures that can become the building blocks for optoelectronics of the future.
Researchers have built two models that accurately explain the light-emitting behavior of semiconductor nanoplatelets, minuscule structures that can become the building blocks for optoelectronics of the future.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
