Wednesday, September 12, 2018
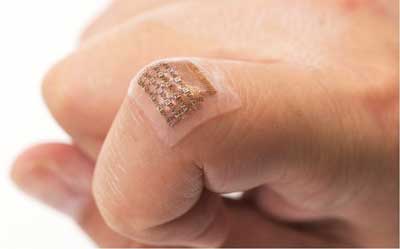
Wearable ultrasound patch monitors blood pressure deep inside body
Enabling 'internet of photonic things' with miniature sensors
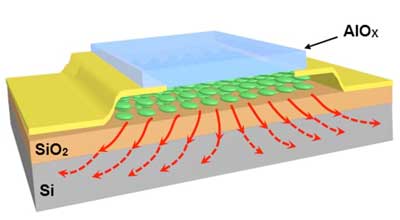
Nano-sandwiching improves heat transfer, prevents overheating in nanoelectronics
Scaling up single-crystal graphene to over a foot long
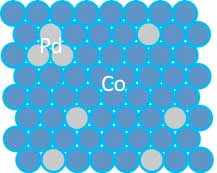
Detecting hydrogen using the extraordinary hall effect in cobalt-palladium thin films
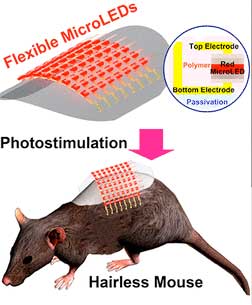
A wearable device for regrowing hair
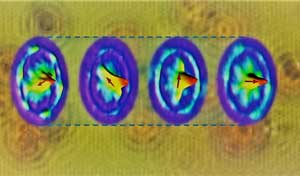
Scientists discover a 'tuneable' novel quantum state of matter
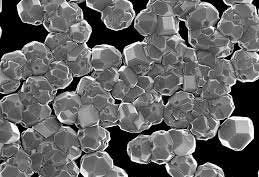
Researchers speed up 3D-printing with nanodiamonds
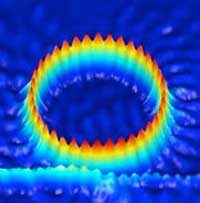
Probing individual edge states with unprecedented precision

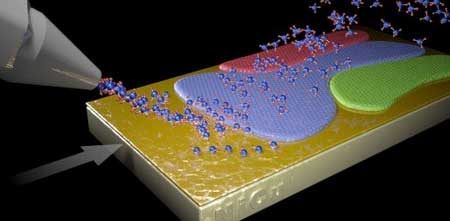
How medicine literally gets under your skin with nanocontainers
Bismuth shows novel conducting properties

Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
