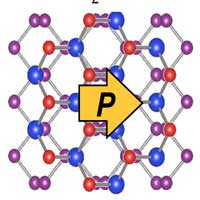
 For the first time, researchers have discovered a way to obtain polarity and photovoltaic behavior from certain nonphotovoltaic, atomically flat (2D) materials. The key lies in the special way in which the materials are arranged.
For the first time, researchers have discovered a way to obtain polarity and photovoltaic behavior from certain nonphotovoltaic, atomically flat (2D) materials. The key lies in the special way in which the materials are arranged.
Thursday, April 1, 2021
2D materials combine, becoming polarized and giving rise to photovoltaic effect
 For the first time, researchers have discovered a way to obtain polarity and photovoltaic behavior from certain nonphotovoltaic, atomically flat (2D) materials. The key lies in the special way in which the materials are arranged.
For the first time, researchers have discovered a way to obtain polarity and photovoltaic behavior from certain nonphotovoltaic, atomically flat (2D) materials. The key lies in the special way in which the materials are arranged.
Hot nanoparticles produce giant and explosive bubbles
When gold nano particles in water are illuminated by a laser, they get very hot: well above the boiling point of water. The formation of vapour bubbles caused by this, is well-known. New experiments, however, using a very high speed camera, now show that before this, a bubble is formed that is much larger and, subsequently, explodes violently.
Properties of graphene change in humid conditions
Graphene exhibits very different properties in humid conditions, according to researchers.
To observe photoswitches, stick on a platinum atom
Adding a platinum atom to a kind of photoswitch makes them easier to observe, report researchers.
Nanoparticles may promote cancer metastasis
Findings caution against possible side effects of cancer nanomedicines and other common nanoparticles but paves the way for safer design and better treatment strategies.
A ground-breaking chemical protocol: on-surface synthesis of acene polymers
A new chemical protocol introduces the on-surface design of anthracene-based polymers with a small electronic bandgap, interesting for organic optoelectronics.
Research paves the way for next generation of optical tweezers
A team of researchers has created a new method of moving microscopic objects around using micro-robotics.
Breakthrough in air purification with a catalyst that works at room temperature
Turning ammonia into harmless substances using gold nanoparticles on a metal oxide framework.
Magnetic nanoparticles can 'burn' cancer cells
Magnetic hyperthermia is still a highly experimental cancer treatment, but new research shows that the therapy is tunable.
Highly fire retardant coating developed from nanocellulose
A spray- or brush-applied fire retardant coating made from nanocellulose is well suited for improving the fire properties of wood-based materials. It reduces the access of oxygen to the surface, thus significantly inhibiting combustion.
Tiny optical elements could one day replace traditional refractive lenses
A research team has developed tiny optical elements from metal nanoparticles and a polymer that one day could replace traditional refractive lenses to realize portable imaging systems and optoelectronic devices.
Octopus-inspired skin-adhesive sensors
Researchers demonstrate a facile, low-cost, scalable fabricating method for water-resistant and skin-adhesive wearable graphene-coated fabric sensors.
Researchers study super-repellent nanosurfaces for safer fruits, vegetables
The National Institute of Food and Agriculture in the U.S. awarded a grant to study and develop super-repellent and anti-fouling surfaces for foods.
Bionic underwater nanogenerator takes cues from electric eels
Researchers have developed a bionic stretchable nanogenerator that takes inspiration from electric eels.
Scientists observe the role of cavitation in glass fracturing
 Cavitation has been widely assumed to be the underlying mechanism governing the fracture of metallic glasses, as well as other glassy systems. Up until now, however, scientists have been unable to directly observe the cavitation behavior of fractures, despite their intensive efforts.
Cavitation has been widely assumed to be the underlying mechanism governing the fracture of metallic glasses, as well as other glassy systems. Up until now, however, scientists have been unable to directly observe the cavitation behavior of fractures, despite their intensive efforts.
Search for strange Skyrmion phenomenon fails but finds stranger magnetic beaded necklace
 Physicists on the hunt for a rarely seen magnetic spin texture have discovered another object that bears its hallmarks, hidden in the structure of ultra-thin magnetic films, that they have called an incommensurate spin crystal.
Physicists on the hunt for a rarely seen magnetic spin texture have discovered another object that bears its hallmarks, hidden in the structure of ultra-thin magnetic films, that they have called an incommensurate spin crystal.
From dinner to sustainable electronics, the surprising versatility of crabs
 Researchers report a sustainable nanocarbon material made from crab shells that are suitable for use in photosensing and energy storage devices.
Researchers report a sustainable nanocarbon material made from crab shells that are suitable for use in photosensing and energy storage devices.
Researchers develop third and final 'made-to-order' nanotube synthesis technique
 The typical 'top-down' method of producing carbon nanotubes does not allow for control over their diameter, length or which of three types will be produced. Control over two types has recently been demonstrated by producing their elementary 'nanobelt' molecules, and now researchers have developed a way to construct the third and last type, offering complete 'made-to-order' management of the synthesis of nanotube molecules.
The typical 'top-down' method of producing carbon nanotubes does not allow for control over their diameter, length or which of three types will be produced. Control over two types has recently been demonstrated by producing their elementary 'nanobelt' molecules, and now researchers have developed a way to construct the third and last type, offering complete 'made-to-order' management of the synthesis of nanotube molecules.
3D design leads to first stable and strong self-assembling 1D nanographene wires
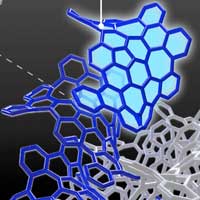 An international team of researchers has synthesized curved, infinitely stacking nanographenes -- like potato chips in a cardboard can -- that can assemble into nanowires.
An international team of researchers has synthesized curved, infinitely stacking nanographenes -- like potato chips in a cardboard can -- that can assemble into nanowires.
Novel nanocomposite developed for magnetic resonance tumor imaging
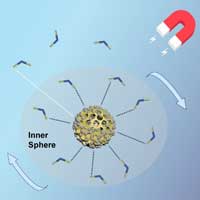 New nanocomposites pave the way for the practical clinical applications for manganese oxide nanosturctures in magnetic resonance imaging.
New nanocomposites pave the way for the practical clinical applications for manganese oxide nanosturctures in magnetic resonance imaging.
Why are optical refractive indices so small?
 An international team of scientists reports on a new theory that can explain why the refractive index of a disordered atomic medium only reaches a maximum value of 1.7.
An international team of scientists reports on a new theory that can explain why the refractive index of a disordered atomic medium only reaches a maximum value of 1.7.
Cohesive circuit protection for wearable electronics
 Researchers developed a cellulose nanofiber coating that counters bending damage, retains electrode function underwater, and thus offers unparalled water resistance for flexible electronic devices.
Researchers developed a cellulose nanofiber coating that counters bending damage, retains electrode function underwater, and thus offers unparalled water resistance for flexible electronic devices.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
