
Tuesday, August 28, 2018
All that is (nano)gold is not biochemically stable
Electric polarization in the macroscopic world and electrons moving at atomic scales
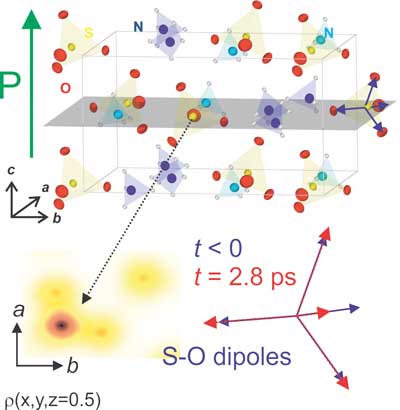
Nanocrystals pave the way for new design of digital devices
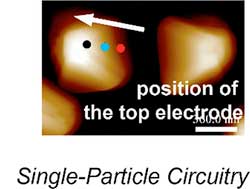
Researchers reveal the growth of graphene near polycrystalline substrate grain boundaries
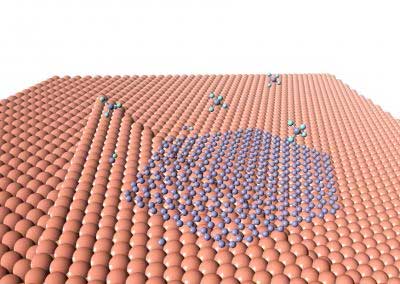
Researchers develop a method for cloaking nano-sensors for optics and biomedicine
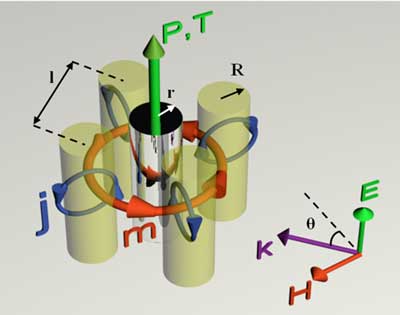
FeCo-selenide -- Next-generation material in energy storage devices?
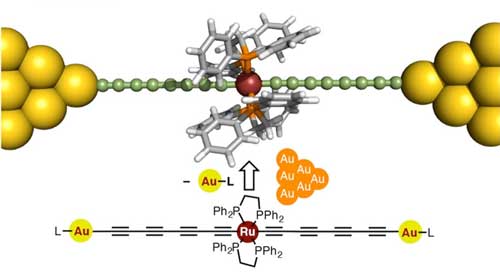
All wired up: New molecular wires for single-molecule electronic devices
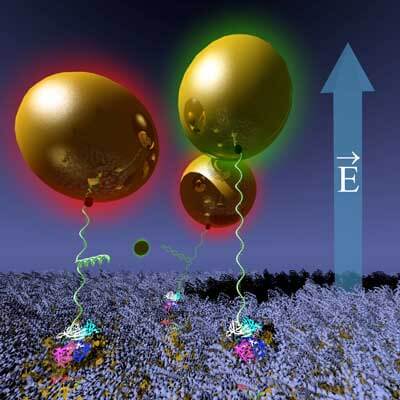
A novel DNA-nanoparticle actuator system
Carbon in color: First-ever colored thin films of nanotubes created

Levitating 2D semiconductor for better performance
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
