Thursday, May 31, 2018
Less is more when it comes to predicting molecules' conductivity
Scientists' model predicts more accurately by using two-electron interactions.

The straight path to absolute darkness
Scientists have obtained new insights in the control of light by nanostructures. They discovered for the first time ever how the amount of omnipresent light noise depends on the size of any nanostructure, and how fast the perfect limit of zero noise is reached.
Wednesday, May 30, 2018
A splash of detergent makes catalytic compounds more powerful
Instead of washing dishes, researchers put detergent to work molding nanoparticles into precise shapes to vastly improve their potency.

Building nanomaterials for next-generation computing
Scientists recently developed a blueprint to fabricate new nanoheterostructures using 2-D materials.
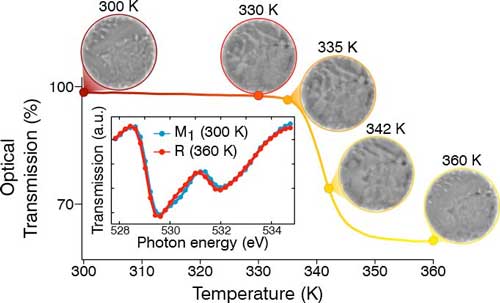
Insulator-metal transition at the nanoscale
By looking at the material with 50 nm resolution, the scientists were able to observe that defects in the material played an important role in initiating the phase transition from the insulator to the metal.
Tuesday, May 29, 2018
Plastic crystals hold key to record-breaking energy transport
Scientists have found a way to create plastic semiconductor nanostructures that absorb light and transport its energy 20 times further than has been previously observed, paving the way for more flexible and more efficient solar cells and photodetectors.
Engineers design color-changing compression bandage
Bandage is threaded with photonic fibers that change color to signal pressure level.

Nanoparticle combination pack battles cancer
Nanoparticles with multifunctional drug precursor for synergistic tumor therapy.
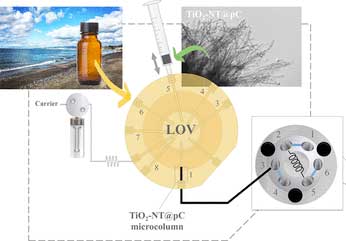
Nanotube analysis system is able to identify pollutants from cosmetics in seawater
Researchers have designed a method that detects the presence of pollutants in seawater in a faster and more efficient way and also at very low concentrations.
'Smart' material enables novel applications in autonomous driving and robotics
New research has shown the potential of liquid crystal shells as enabling material for a vast array of future applications, ranging from autonomous driving to anti-counterfeiting technology and a new class of sensors.

Better, faster, stronger: Building batteries that don't go boom
Understanding how lithium reacts to pressure developed from charging and discharging a battery could mean safer, better batteries.

Researchers predict materials to stabilize record-high capacity lithium-ion battery
Advancement could pave the way for less expensive, longer-lasting batteries for electric vehicles.
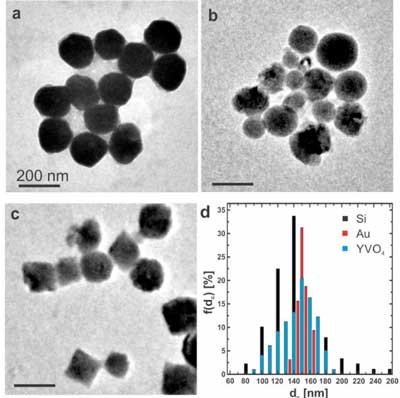
Researchers use silicon nanoparticles for bioimaging and drug delivery
An international research team has studied a new cell visualisation and drug delivery system based on nanoparticles coated with luminescent dye molecules.
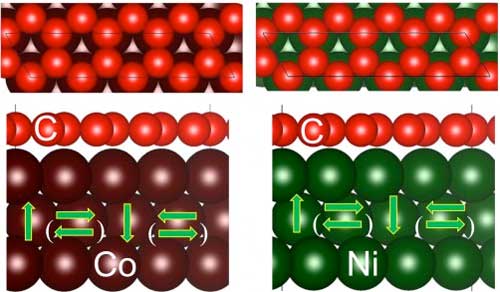
Graphene layered with magnetic materials could drive ultrathin spintronics
Measurements reveal exotic spin properties that could drive new form of data storage.
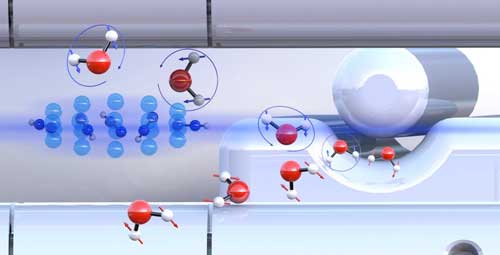
Water is not the same as water
Water molecules exist in two different forms with almost identical physical properties. For the first time, researchers have succeeded in separating the two forms to show that they can exhibit different chemical reactivities.
How to code a functional molecular machine?
An international team has developed a model that simulates protein evolution. Starting from stiff, unfunctional proteins, the computer model shows how evolving protein components can work together to give rise to dynamic and efficient molecular machines.
Switched on: a breakthrough for spintronics
Scientists have discovered a switch to control the spin current, a mechanism needed for information processing with full spin-based devices.
Monday, May 28, 2018
Simultaneous monitoring of surfaces and protein distribution in cells
The combination of two high-resolution methods produces new insights into the cells? mode of operation.

Deciphering the language of cells with a nanophotonic biosensor
Researchers have developed an innovative label-free method for studying the behavior of single cells continuously and in real time. By placing a cell in a small chamber containing nanosensors and observing it over many hours, it is possible to identify the cell's unique personality and understand how it communicates.
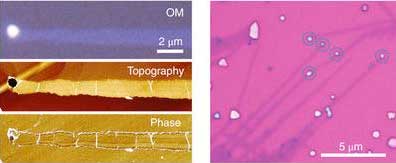
Novel method to fabricate nanoribbons from speeding nano droplets
An international team of researchers has discovered a novel method for the synthesis of ultrathin semiconductors. This is a unique growth mechanism, which yielded nanoscopic semiconductor ribbons that are only a few atoms thick.
Sunday, May 27, 2018
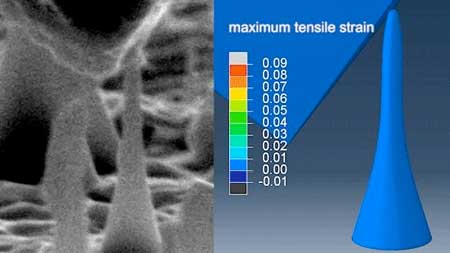
Researchers introduce novel method to grow elastic diamonds
A study has unveiled that brittle diamonds can be bent and stretched elastically when made into ultrafine needles.
Friday, May 25, 2018
Shine bright like a nanoaggregate
Highly luminescent inks made from copper-iodine hybrid clusters with aggregation-induced emission.

An elastic fiber filled with electrodes set to revolutionize smart clothes
The fibers can detect even the slightest pressure and strain and can withstand deformation of close to 500% before recovering their initial shape.

Thursday, May 24, 2018
Rare element to provide better material for high-speed electronics
Researchers have discovered a new two-dimensional material, derived from the rare element tellurium, to make transistors that carry a current better throughout a computer chip.
Battling brain cancer with nanotechnology
Nanoparticles carrying two drugs can cross the blood-brain barrier and shrink glioblastoma tumors.

Wood to supercapacitors
Sustainable highly conductive electrode materials from ultrathin carbon nanofiber aerogels derived from nanofibrillated cellulose.
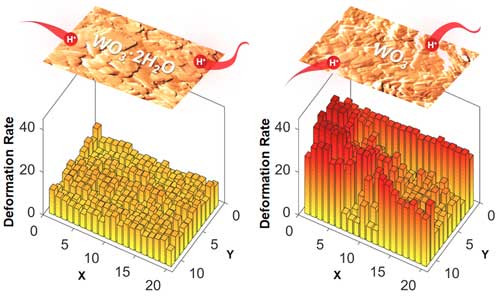
Microscopy advance reveals unexpected role for water in energy storage material
A material with atomically thin layers of water holds promise for energy storage technologies, and researchers have now discovered that the water is performing a different role than anyone anticipated.
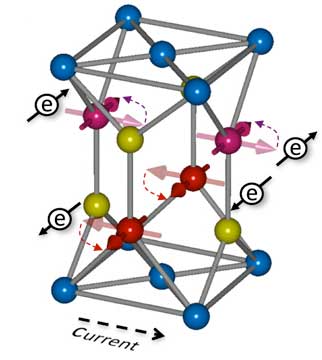
Antiferromagnetic materials allow for processing at terahertz speeds
Increased data volume and writing speed in a new antiferromagnetic-based memory.
A thermal diode based on nanoscale thermal radiation
Researchers explore rectification in the near-field, where heat fluxes are much larger than those in the far-field and can exceed the blackbody limit of far-field thermal radiation, and demonstrate that rectification coefficients between VO2 and doped Si can exceed 50% in the near-field for moderate temperature differences.

Could a particle accelerator using laser-driven implosion become a reality?
Scientists have discovered a novel particle acceleration mechanism called 'Micro-bubble implosion,' in which super-high energy hydrogen ions (relativistic protons) are emitted at the moment when bubbles shrink to atomic size through the irradiation of hydrides with micron-sized spherical bubbles by ultraintense laser pulses.
Recombinant E. coli as a biofactory for the biosynthesis of diverse nanomaterials
A metabolic research group has developed a recombinant E. coli strain that biosynthesizes 60 different nanomaterials covering 35 elements on the periodic table.

Electron tomography technique leads to 3-D reconstructions at the nanoscale
A new transmission electron microscopy technique determines three-dimensional position of individual atoms.
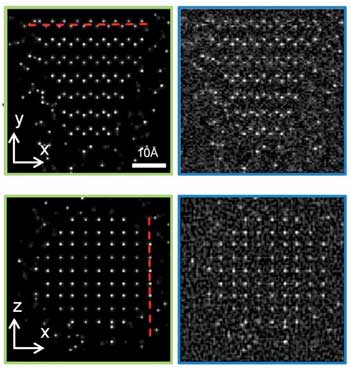
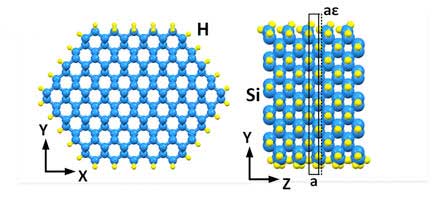
Silicon breakthrough could make key microwave technology much cheaper and better
Researchers using powerful supercomputers have found a way to generate microwaves with inexpensive silicon, a breakthrough that could dramatically cut costs and improve devices such as sensors in self-driving vehicles.
Switching with molecules
Molecular switch will facilitate the development of pioneering electro-optical devices.
Scientists crack code to cheap, small carbon nanotubes
Imagine a box you plug into the wall that cleans your toxic air and pays you cash. That's essentially what researchers produced after discovering the blueprint for turning the carbon dioxide into carbon nanotubes with small diameters.

Wednesday, May 23, 2018
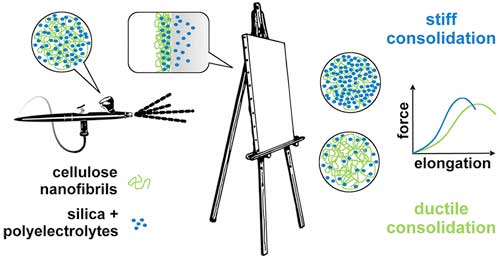
Preserving a painter's legacy with nanomaterials
In an effort to combat the aging process of paintings, researchers are reporting that nanomaterials can provide multiple layers of reinforcement.
A chip-scale broadband optical system that can sense molecules in the mid-infrared
This novel system could lead to a spectroscopy lab-on-a-chip for real-time sensing in the microseconds.
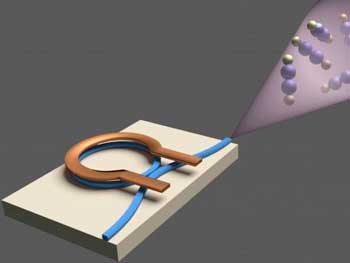
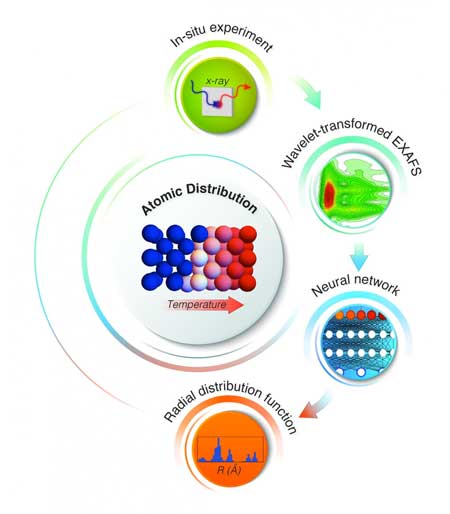
Atomic-scale manufacturing now a reality
Scientists have applied a machine learning technique using artificial intelligence to perfect and automate atomic-scale manufacturing, something which has never been done before.

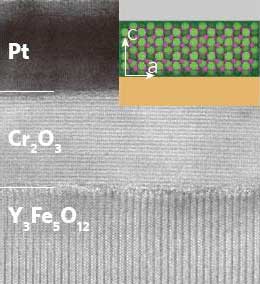
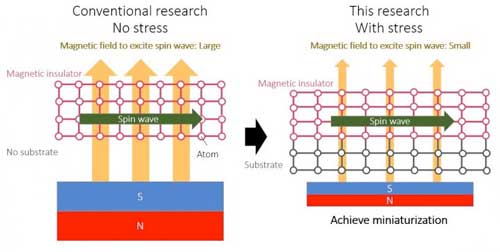
Strain directs spin waves
The relationship between magnetoelastic anisotropy and propagation properties of forward volume spin waves in single-crystalline yttrium iron garnet films grown on three garnet substrates was experimentally demonstrated. This facilitates the design of spin wave integrated circuits.
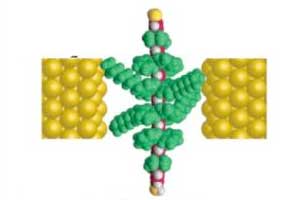
Beyond the limits of conventional electronics: stable organic molecular nanowires
Researchers have created the first thermally stable organic molecular nanowire devices using a single 4.5-nm-long molecule placed inside electroless gold-plated nanogap electrodes.
Understanding the generation of light-induced electrical current in atomically thin nanomaterials
Scientists demonstrated that scanning photocurrent microscopy could provide the optoelectronic information needed to improve the performance of devices for power generation, communications, data storage, and lighting.
Research reveals how order first appears in liquid crystals
Chemists have shown a technique that can identify regions in a liquid crystal system where molecular order begins to emerge just before the system fully transitions from disordered to ordered states.
Using 3D X-rays to measure particle movement inside lithium ion batteries
Researchers applied a technique using 3D X-ray tomography of an electrode to better understand what is happening on the inside of a lithium ion battery and ultimately build batteries with more storage capacity and longer life.

Scientists put the optical microscope under the microscope to achieve atomic accuracy
New research developments enable optical microscopes to measure these nanometer-scale details with a new level of accuracy.
Inorganic material database 'AtomWork-Adv' made available to the public
AtomWork-Adv markedly improves upon the amount of data available and the usability of the current web-based AtomWork database.

Tuesday, May 22, 2018
Mimicking biology to shape nanomaterials
Researchers utilize cellular proteins to shape silver nanoplates, suggesting an efficient strategy for controlling the nanostructure of inorganic materials.

Tunable diamond string may hold key to quantum memory
A process similar to guitar tuning improves storage time of quantum memory.
Remote control of transport through nanopores
New study outlines key factors affecting the transfer of molecules through biological channels.
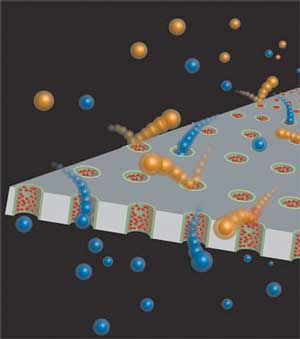
Magnesium magnificent for plasmonic applications
Researchers have synthesized and isolated plasmonic magnesium nanoparticles that show all the promise of their gold, silver and aluminum cousins with none of the drawbacks.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
