Thursday, January 17, 2019
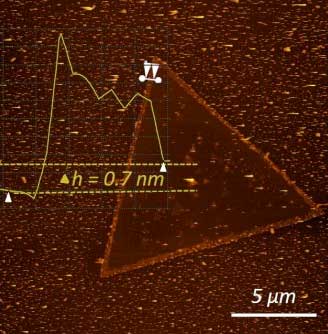
Open-source automated chemical vapor deposition system for the production of two-dimensional nanomaterials
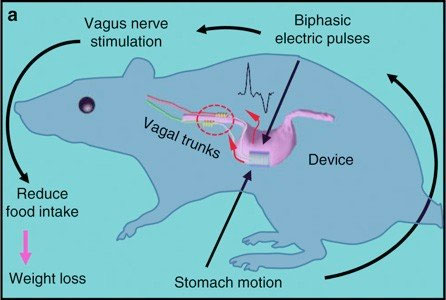
Nanogenerators turn body motion Into weight control and wound-healing therapies
How to rapidly image entire brains at nanoscale resolution
Nanoparticle breakthrough in the fight against cancer
New nanosensor to detect disease and infection
Light connects two worlds on a single chip
Creating a roadmap for 2D materials
MXene researchers find 2-D transition-metal carbides react with water, opening a door to their unknown chemistry
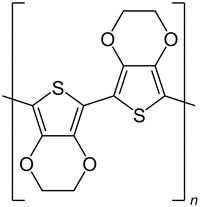
New light shed on organic polymer PEDOT
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
