 A University of Cordoba research project is able to incorporate luminescence into grpahene, paving a new way to continue expanding properties.
A University of Cordoba research project is able to incorporate luminescence into grpahene, paving a new way to continue expanding properties.
Tuesday, April 30, 2019
Researchers design a strategy to make graphene luminescent
 A University of Cordoba research project is able to incorporate luminescence into grpahene, paving a new way to continue expanding properties.
A University of Cordoba research project is able to incorporate luminescence into grpahene, paving a new way to continue expanding properties.
2D nanomaterials prolong growth factor release to mend cartilage
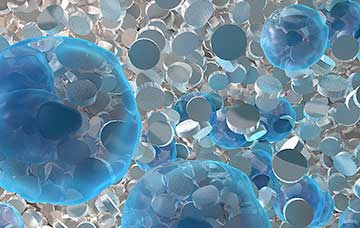 Researchers have designed a new class of two-dimensional (2D) nanomaterials that are disc-shaped and flat on the surface, similar to a coin, to aid in treatments for cartilage repair. The nanomaterials' unique charge arrangement allows them to trap proteins or growth factors, which can be slowly released over time.
Researchers have designed a new class of two-dimensional (2D) nanomaterials that are disc-shaped and flat on the surface, similar to a coin, to aid in treatments for cartilage repair. The nanomaterials' unique charge arrangement allows them to trap proteins or growth factors, which can be slowly released over time.
Inorganic perovskite absorbers for use in thin-film solar cells
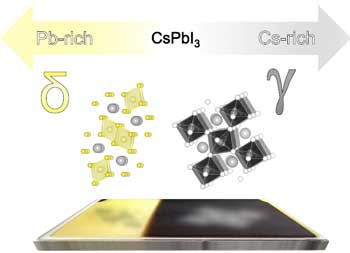 Researchers succeeded in producing inorganic perovskite thin films at moderate temperatures using co-evaporation - making post-tempering at high temperatures unnecessary. The process makes it much easier to produce thin-film solar cells from this material.
Researchers succeeded in producing inorganic perovskite thin films at moderate temperatures using co-evaporation - making post-tempering at high temperatures unnecessary. The process makes it much easier to produce thin-film solar cells from this material.
Heat-conducting nanostructured polymers
 Material may replace many metals as lightweight, flexible heat dissipators in cars, refrigerators, and electronics.
Material may replace many metals as lightweight, flexible heat dissipators in cars, refrigerators, and electronics.
Tracking small things in cells
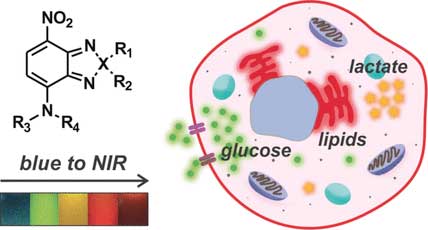 Small and tunable fluorophores for the imaging of metabolites in living cells.
Small and tunable fluorophores for the imaging of metabolites in living cells.
Partitioning of porous materials
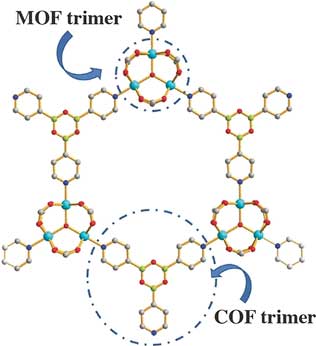 Highly resorptive metal?organic frameworks can be constructed by a foresighted combination of two different synthetic principles.
Highly resorptive metal?organic frameworks can be constructed by a foresighted combination of two different synthetic principles.
Nanomaterials mimicking natural enzymes with superior catalytic activity
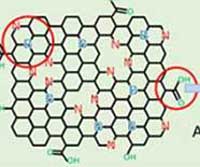 Researchers doped nitrogen and boron into graphene to selectively increase peroxidase-like activity and succeeded in synthesizing a peroxidase-mimicking nanozyme with a low cost and superior catalytic activity.
Researchers doped nitrogen and boron into graphene to selectively increase peroxidase-like activity and succeeded in synthesizing a peroxidase-mimicking nanozyme with a low cost and superior catalytic activity.
A shot in the arm for spintronics
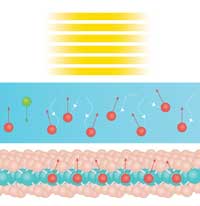 A spin injection technique that is more than 10,000 times more efficient than existing methods could allow for the development of ultrafast spintronic computers.
A spin injection technique that is more than 10,000 times more efficient than existing methods could allow for the development of ultrafast spintronic computers.
Monday, April 29, 2019
How to purify water with graphene
 Graphene is capable of purifying water, making it drinkable, without further chlorination. Capturing bacterial cells, it forms flakes that can be easily extracted from the water. Graphene separated by ultrasound can be reused.
Graphene is capable of purifying water, making it drinkable, without further chlorination. Capturing bacterial cells, it forms flakes that can be easily extracted from the water. Graphene separated by ultrasound can be reused.
Formation of honeycomb nanostructures finally explained
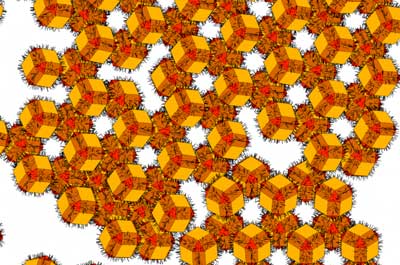 Scientists have developed a simulation model that reproduces the formation of these nanostructures in detail.
Scientists have developed a simulation model that reproduces the formation of these nanostructures in detail.
Water creates traps in organic electronics
 Scientists show that the motion of charges in organic electronic devices is dramatically slowed down by minute amounts of water.
Scientists show that the motion of charges in organic electronic devices is dramatically slowed down by minute amounts of water.
Squid skin inspires creation of next-generation space blanket
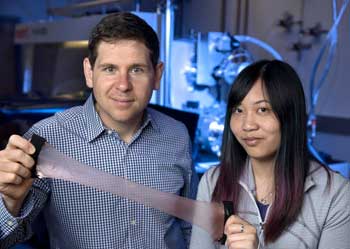 Engineers have developed a next-generation, adaptive space blanket that gives users the ability to control their temperature.
Engineers have developed a next-generation, adaptive space blanket that gives users the ability to control their temperature.
Novel 2D hybrid perovskite ferroelectric with high color rendering index
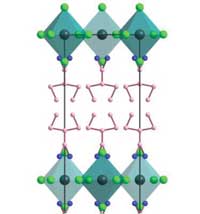 Researchers found that the orientation of organic cations and the significant structural distortion of PbCl6 synergistically induce the generation of large spontaneous polarizations.
Researchers found that the orientation of organic cations and the significant structural distortion of PbCl6 synergistically induce the generation of large spontaneous polarizations.
Nanomaterial-based artificial organelles protect normal cells against chemotherapy side effects
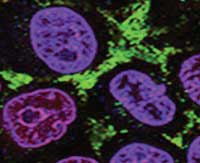 A novel strategy for capturing chemotherapeutics in normal cells rather than further optimizing tumor targeting, may reduce the cytotoxicity for normal cell and improve pharmacotherapy.
A novel strategy for capturing chemotherapeutics in normal cells rather than further optimizing tumor targeting, may reduce the cytotoxicity for normal cell and improve pharmacotherapy.
Decoupled graphene thanks to potassium bromide
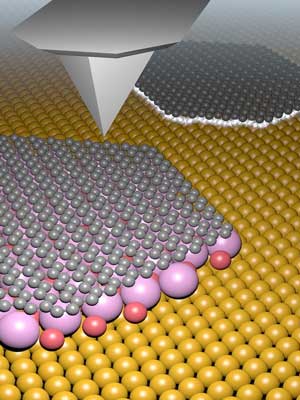 When potassium bromide molecules arrange themselves between graphene and copper, it results in electronic decoupling. This alters the electrical properties of the graphene produced, bringing them closer to pure graphene.
When potassium bromide molecules arrange themselves between graphene and copper, it results in electronic decoupling. This alters the electrical properties of the graphene produced, bringing them closer to pure graphene.
Sunday, April 28, 2019
Graphene sponge helps lithium sulphur batteries reach new potential
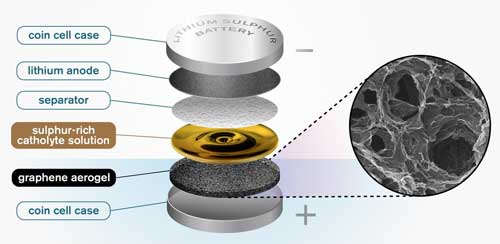 Researchers recently unveiled a promising breakthrough for lithium sulphur batteries, using a catholyte with the help of a graphene sponge.
Researchers recently unveiled a promising breakthrough for lithium sulphur batteries, using a catholyte with the help of a graphene sponge.
DNA folds into a smart nanocapsule for drug delivery
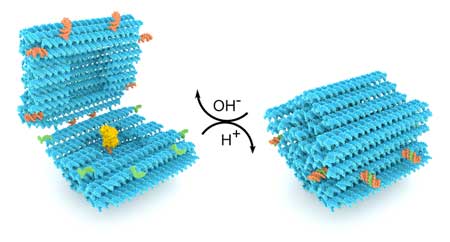 New study shows that nanostructures constructed of DNA molecules can be programmed to function as pH-responsive cargo carriers, paving the way towards functional drug-delivery vehicles.
New study shows that nanostructures constructed of DNA molecules can be programmed to function as pH-responsive cargo carriers, paving the way towards functional drug-delivery vehicles.
Saturday, April 27, 2019
Nanoparticles take a fantastic, magnetic voyage
 Tiny robots powered by magnetic fields could help drug-delivery nanoparticles reach their targets.
Tiny robots powered by magnetic fields could help drug-delivery nanoparticles reach their targets.
Friday, April 26, 2019
Chemists manipulate the quantum states of gold nanoclusters
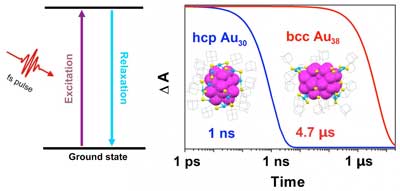 Scientists have found a way to control the lifetime of the quantum states of gold nanoclusters by three orders of magnitude, which could lead to improvements in solar cell and photocatalysis technologies.
Scientists have found a way to control the lifetime of the quantum states of gold nanoclusters by three orders of magnitude, which could lead to improvements in solar cell and photocatalysis technologies.
Flexible circuits for 3D printing
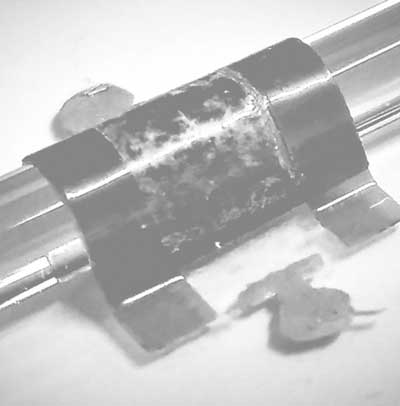 Researchers have developed a process suitable for 3D printing that can be used to produce transparent and mechanically flexible electronic circuits. The technique can enable new applications such as printable light-emitting diodes, solar cells or tools with integrated circuits.
Researchers have developed a process suitable for 3D printing that can be used to produce transparent and mechanically flexible electronic circuits. The technique can enable new applications such as printable light-emitting diodes, solar cells or tools with integrated circuits.
We accidentally created a new wonder material that could revolutionise batteries and electronics
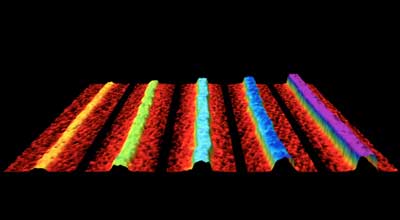 Researchers have created phosphorene nanoribbons by accident - a material made from one of the universe?s basic building blocks, but that has the potential to revolutionise a wide range of technologies.
Researchers have created phosphorene nanoribbons by accident - a material made from one of the universe?s basic building blocks, but that has the potential to revolutionise a wide range of technologies.
Mikado inside a nano box: Bertrand's paradox revisited
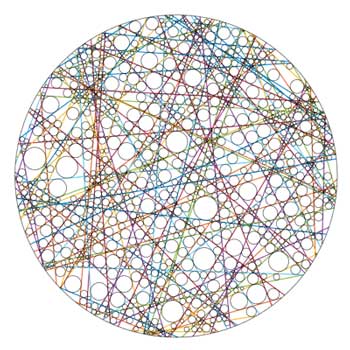 When you shake a box filled with Mikado sticks, will you get a uniform spreading of the sticks inside the box? This question touches Bertrands paradox, a classic in mathematics. For designing nano mikado boxes for photonics purposes, scientists wanted to be able to determine the free space between the sticks.
When you shake a box filled with Mikado sticks, will you get a uniform spreading of the sticks inside the box? This question touches Bertrands paradox, a classic in mathematics. For designing nano mikado boxes for photonics purposes, scientists wanted to be able to determine the free space between the sticks.
3D printing micro-electromechanical switches
 Researchers have demonstrated the facile fabrication of two-terminal micro-electromechanical (MEM) switches using a commercially available fused deposition modeling (FDM)-based 3D printer.
Researchers have demonstrated the facile fabrication of two-terminal micro-electromechanical (MEM) switches using a commercially available fused deposition modeling (FDM)-based 3D printer.
Thursday, April 25, 2019
Scientists propose new method for studying hydrodynamic behavior of electrons in graphene
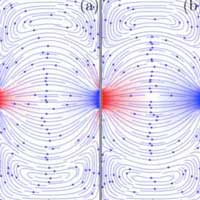 By studying how electrons in two-dimensional graphene can literally act like a liquid, researchers have paved the way for further research into a material that has the potential to enable future electronic computing devices that outpace silicon transistors.
By studying how electrons in two-dimensional graphene can literally act like a liquid, researchers have paved the way for further research into a material that has the potential to enable future electronic computing devices that outpace silicon transistors.
Crack propagation is asymmetric in polar materials
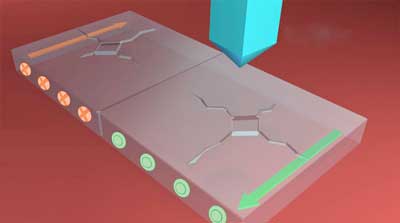 Researchers report how, due to flexoelectricity, cracks in ferroelectrics (switchable polar materials) propagate more easily in the polar direction than in the opposite.
Researchers report how, due to flexoelectricity, cracks in ferroelectrics (switchable polar materials) propagate more easily in the polar direction than in the opposite.
Capturing the behavior of single-atom catalysts on the move
 Scientists precisely control where single-atom catalysts sit on their support structures, and show how changing their position affects their reactivity.
Scientists precisely control where single-atom catalysts sit on their support structures, and show how changing their position affects their reactivity.
Unprecedented insight into two-dimensional magnets using diamond quantum sensors
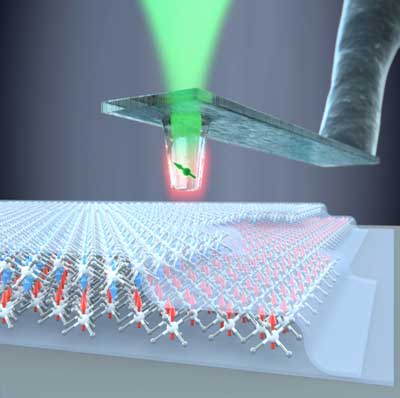 For the first time, physicists have succeeded in measuring the magnetic properties of atomically thin van der Waals materials on the nanoscale.
For the first time, physicists have succeeded in measuring the magnetic properties of atomically thin van der Waals materials on the nanoscale.
New lens system for brighter, sharper diffraction images
 Researchers designed, implemented, and applied a new and improved focusing system for electron diffraction measurements.
Researchers designed, implemented, and applied a new and improved focusing system for electron diffraction measurements.
DNA as you?ve never seen it before, thanks to a new nanotechnology imaging method
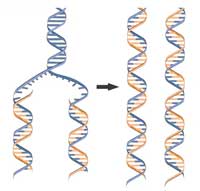 Nanochannel technology allows scientists to conduct an experiment never attempted before: map all the locations where DNA replication begins simultaneously on millions of single DNA fibers.
Nanochannel technology allows scientists to conduct an experiment never attempted before: map all the locations where DNA replication begins simultaneously on millions of single DNA fibers.
A close look at lithium batteries
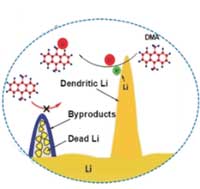 Fluorescence probe shows the distribution of active lithium species on lithium metal anodes.
Fluorescence probe shows the distribution of active lithium species on lithium metal anodes.
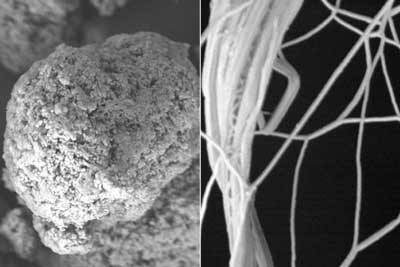
Nanostructures from hair to aid biomedical engineering
 Researchers have explored the hierarchical micro-/nanostructures from human hair and isolated these structures as a new kind of biomaterial.
Researchers have explored the hierarchical micro-/nanostructures from human hair and isolated these structures as a new kind of biomaterial.
Wednesday, April 24, 2019
Graphene nanomaterial to replace mercury in LEDs
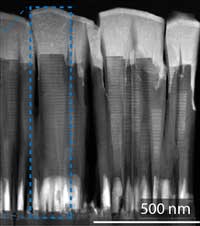 Researchers succeeded in creating light-emitting diodes, or LEDs, from a graphene nanomaterial that emits ultraviolet light.
Researchers succeeded in creating light-emitting diodes, or LEDs, from a graphene nanomaterial that emits ultraviolet light.
Graphene quantum dots could yield treatment for traumatic injuries
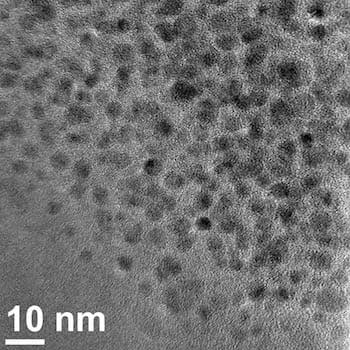 Graphene quantum dots drawn from common coal may be the basis for an effective antioxidant for people who suffer traumatic brain injuries, strokes or heart attacks.
Graphene quantum dots drawn from common coal may be the basis for an effective antioxidant for people who suffer traumatic brain injuries, strokes or heart attacks.
Nano-imaging system helps surgeons remove tiny ovarian tumors
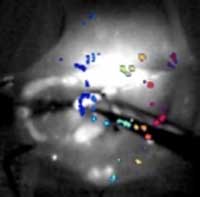 Real-time carbon nanotube based fluorescent imaging could boost survival rates for ovarian cancer.
Real-time carbon nanotube based fluorescent imaging could boost survival rates for ovarian cancer.
Study shows the potential of carbon nanotubes to cool electronic circuits
 Mechanically stretched carbon nanotubes extract heat efficiently and could be used to cool flexible electronic devices.
Mechanically stretched carbon nanotubes extract heat efficiently and could be used to cool flexible electronic devices.
Polymers to give early warning signs
 Scientists have developed a method to tailor the properties of stress-indicating molecules that can be integrated into polymers and signal damages or excessive mechanical loads with an optical signal.
Scientists have developed a method to tailor the properties of stress-indicating molecules that can be integrated into polymers and signal damages or excessive mechanical loads with an optical signal.
Nanosized container with photoswitches: release of cargo upon irradiation in water
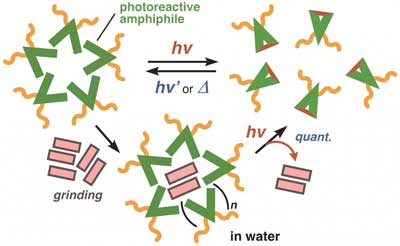 A versatile system with potential application for non-invasive drug delivery.
A versatile system with potential application for non-invasive drug delivery.
'Nanofiber yarn' makes for stretchy, protective artificial tissue
 Twisted fibers coated with living cells could assist healing of injured muscles and tendons.
Twisted fibers coated with living cells could assist healing of injured muscles and tendons.
Printed organic electronics you can eat
 Researchers report that organic transistors composed mainly of ingestible materials can be easily transferred on edible substrates by means of untreated commercial tattoo-paper.
Researchers report that organic transistors composed mainly of ingestible materials can be easily transferred on edible substrates by means of untreated commercial tattoo-paper.
Quantum distillery for light
 The distillation of spirits increases the content of alcohol relative to the water content. A similar method works on light quanta - photons. It extracts individual photons from a light source, reduces the unwanted vacuum component, and heralds this event.
The distillation of spirits increases the content of alcohol relative to the water content. A similar method works on light quanta - photons. It extracts individual photons from a light source, reduces the unwanted vacuum component, and heralds this event.
New nanomedicine slips through the cracks
 Nanomachines aim to deliver cancer drugs to hard-to-reach areas like the brain.
Nanomachines aim to deliver cancer drugs to hard-to-reach areas like the brain.
Highly fire retardant coating developed from nanocellulose
 A spray- or brush-applied fire retardant coating made from nanocellulose is well suited for improving the fire properties of wood-based materials. It reduces the access of oxygen to the surface, thus significantly inhibiting combustion.
A spray- or brush-applied fire retardant coating made from nanocellulose is well suited for improving the fire properties of wood-based materials. It reduces the access of oxygen to the surface, thus significantly inhibiting combustion.
Tuesday, April 23, 2019
Watching molecules split in real time
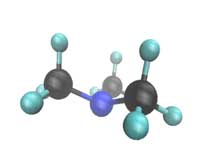 A new method could be used to look at chemical reactions that other techniques can?t catch, for instance in catalysis, photovoltaics, peptide and combustion research.
A new method could be used to look at chemical reactions that other techniques can?t catch, for instance in catalysis, photovoltaics, peptide and combustion research.
Scientists explore the unknown behaviour of gold nanoparticles with neutrons
 Scientists investigated the physical and chemical influences when gold nanoparticles interact with a model biological membrane, in order to identify the behavioural mechanisms taking place.
Scientists investigated the physical and chemical influences when gold nanoparticles interact with a model biological membrane, in order to identify the behavioural mechanisms taking place.
Nanomechanical router is a quantum leap for physicists
 Physicists have developed a nanocomponent that emits light particles carrying quantum information.
Physicists have developed a nanocomponent that emits light particles carrying quantum information.
New thirty-minute blood test to reduce sepsis deaths
 A new detector using photonics to identify E. coli bacteria from a tiny drop of blood, and produce a while-you-wait diagnosis in less than thirty minutes is making a bold bid to reduce the mortality rate from sepsis by more than 70%.
A new detector using photonics to identify E. coli bacteria from a tiny drop of blood, and produce a while-you-wait diagnosis in less than thirty minutes is making a bold bid to reduce the mortality rate from sepsis by more than 70%.
Nanocasting platinum in MOFs
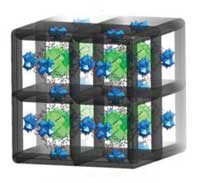 Researchers demonstrate that metallic platinum structures can be effectively casted into zirconium-based MOFs by a two-step infiltration/reduction process.
Researchers demonstrate that metallic platinum structures can be effectively casted into zirconium-based MOFs by a two-step infiltration/reduction process.
Atomic beams shoot straighter via cascading silicon peashooters
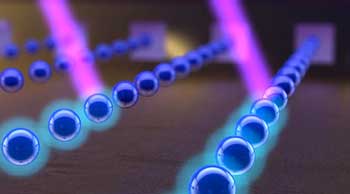 To a non-physicist, an 'atomic beam collimator' may sound like a phaser firing mystical particles. That might not be the worst metaphor to introduce a technology that researchers have now miniaturized, making it more likely to someday land in handheld devices.
To a non-physicist, an 'atomic beam collimator' may sound like a phaser firing mystical particles. That might not be the worst metaphor to introduce a technology that researchers have now miniaturized, making it more likely to someday land in handheld devices.
Researchers discover perfectly imperfect twist on nanowire growth
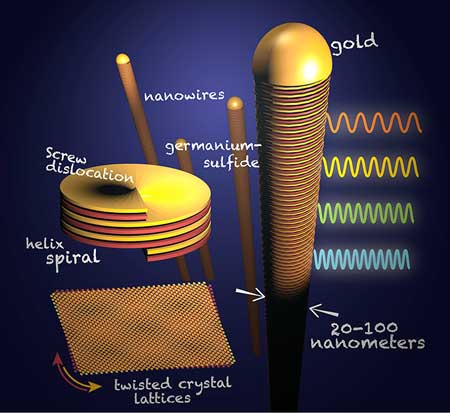 For years, researchers have been trying to find ways to grow an optimal nanowire, using crystals with perfectly aligned layers all along the wire. A team of engineering researchers sees an advantage to natural imperfection.
For years, researchers have been trying to find ways to grow an optimal nanowire, using crystals with perfectly aligned layers all along the wire. A team of engineering researchers sees an advantage to natural imperfection.
How slippery surfaces allow sticky pastes and gels to slide
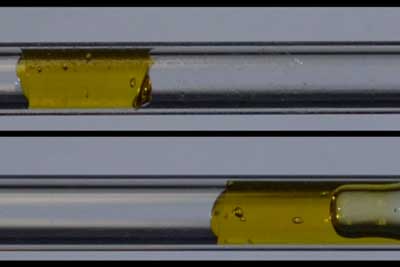 Engineered surface treatment can reduce waste and improve efficiency in many processes.
Engineered surface treatment can reduce waste and improve efficiency in many processes.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
