 Researchers have found a way to grow a single crystalline layer of alpha-aluminum gallium oxide that has the widest energy bandgap to date - a discovery that clears the way for new semiconductors that will handle higher voltages, higher power densities and higher frequencies than previously seen.
Researchers have found a way to grow a single crystalline layer of alpha-aluminum gallium oxide that has the widest energy bandgap to date - a discovery that clears the way for new semiconductors that will handle higher voltages, higher power densities and higher frequencies than previously seen.
Wednesday, January 20, 2021
Ultrawide bandgap gives material high-power potential
 Researchers have found a way to grow a single crystalline layer of alpha-aluminum gallium oxide that has the widest energy bandgap to date - a discovery that clears the way for new semiconductors that will handle higher voltages, higher power densities and higher frequencies than previously seen.
Researchers have found a way to grow a single crystalline layer of alpha-aluminum gallium oxide that has the widest energy bandgap to date - a discovery that clears the way for new semiconductors that will handle higher voltages, higher power densities and higher frequencies than previously seen.
Researchers develop hydrogen-bonded organic frameworks based electrochromic film
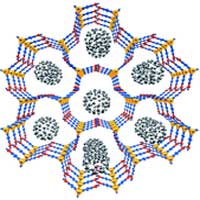 Researchers have developed an electrochromic hydrogen-bonded organic frameworks film with long cycle life, facile modification, easy recycling and regeneration prepared via electrophoretic deposition rapidly and facile.
Researchers have developed an electrochromic hydrogen-bonded organic frameworks film with long cycle life, facile modification, easy recycling and regeneration prepared via electrophoretic deposition rapidly and facile.
A sharp new eye to view atoms and molecules
 A new X-ray laser oscillator generates types of pulses that were never before possible. The pulses are stable, intense, and of ultrashort duration and have a well-defined wavelength. This ability opens new possibilities in experiments and research.
A new X-ray laser oscillator generates types of pulses that were never before possible. The pulses are stable, intense, and of ultrashort duration and have a well-defined wavelength. This ability opens new possibilities in experiments and research.
New metamaterial offers reprogrammable properties
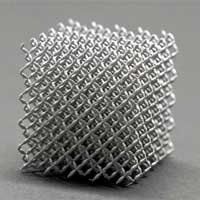 Scientists have developed a metamaterial whose mechanical properties can be reprogrammed on demand and whose internal structure can be modified by applying a magnetic field.
Scientists have developed a metamaterial whose mechanical properties can be reprogrammed on demand and whose internal structure can be modified by applying a magnetic field.
New metamaterial offers reprogrammable properties
 Scientists have developed a metamaterial whose mechanical properties can be reprogrammed on demand and whose internal structure can be modified by applying a magnetic field.
Scientists have developed a metamaterial whose mechanical properties can be reprogrammed on demand and whose internal structure can be modified by applying a magnetic field.
Nanocarbon nucleation layer allows an anode-free zinc battery
 Researchers report a prototype of an anode-free, zinc-based battery that uses low-cost, naturally abundant materials.
Researchers report a prototype of an anode-free, zinc-based battery that uses low-cost, naturally abundant materials.
Lasers create miniature robots from bubbles (w/video)
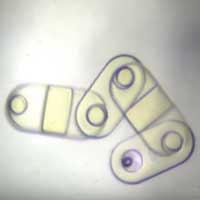 Researchers have used lasers to create miniature robots from bubbles that lift, drop and manipulate small pieces into interconnected structures.
Researchers have used lasers to create miniature robots from bubbles that lift, drop and manipulate small pieces into interconnected structures.
Novel nanomaterial generates powerful beams for enhanced optical imaging
 Using DNA as a scaffold, engineers create a synthetic nanomaterial that could pave the way for rapid and more accurate diagnostic testing from a single molecule.
Using DNA as a scaffold, engineers create a synthetic nanomaterial that could pave the way for rapid and more accurate diagnostic testing from a single molecule.
Researchers guide a single ion through a Bose Einstein condensate
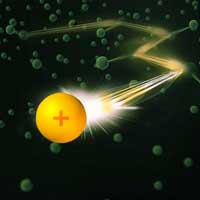 Transport processes are ubiquitous in nature but still raise many questions. Scientists have now developed a new method that allows them to observe a single charged particle on its path through a dense cloud of ultracold atoms.
Transport processes are ubiquitous in nature but still raise many questions. Scientists have now developed a new method that allows them to observe a single charged particle on its path through a dense cloud of ultracold atoms.
Storing information with light: photo-ferroelectric materials
 New photo-ferroelectric materials allow to store information in a non-volatile way using light stimulus. The idea is to create energy efficient memory devices with high performance and versatility to face the challenges of the current society.
New photo-ferroelectric materials allow to store information in a non-volatile way using light stimulus. The idea is to create energy efficient memory devices with high performance and versatility to face the challenges of the current society.
Do simulations represent the real world at the atomic scale?
 Researchers have developed a groundbreaking validation protocol for simulations of the atomic structure of the interface between a solid (a metal oxide) and liquid water.
Researchers have developed a groundbreaking validation protocol for simulations of the atomic structure of the interface between a solid (a metal oxide) and liquid water.
Gold nanoparticles more stable by putting rings on them
 Scientists have found a way to prevent gold nanoparticles from clumping, which could help towards their use as an anti-cancer therapy.
Scientists have found a way to prevent gold nanoparticles from clumping, which could help towards their use as an anti-cancer therapy.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
