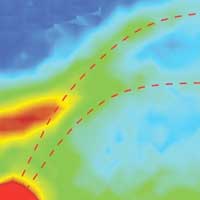
 Scientists examined a highly efficient thermoelectric material in a new way - by using light.
Scientists examined a highly efficient thermoelectric material in a new way - by using light.
Monday, November 9, 2020
Researchers decode thermal conductivity with light
 Scientists examined a highly efficient thermoelectric material in a new way - by using light.
Scientists examined a highly efficient thermoelectric material in a new way - by using light.
3D model shows bacterial motor in action
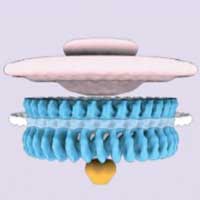 Scientists have uncovered details of how the bacterial propeller, known as the flagellum, switches between counterclockwise and clockwise rotation, allowing it to control its movement. The findings include a model that shows structural changes happening within portions of the flagellar motor.
Scientists have uncovered details of how the bacterial propeller, known as the flagellum, switches between counterclockwise and clockwise rotation, allowing it to control its movement. The findings include a model that shows structural changes happening within portions of the flagellar motor.
Tiny device enables new record in super-fast quantum light detection
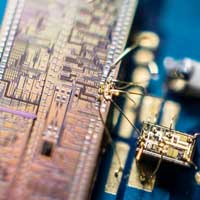 Researchers have developed a tiny device that paves the way for higher performance quantum computers and quantum communications, making them significantly faster than the current state-of-the-art.
Researchers have developed a tiny device that paves the way for higher performance quantum computers and quantum communications, making them significantly faster than the current state-of-the-art.
Plant inspired: Printing self-folding paper structures for future mechatronics
 Scientists develop a simple method that mimics plant motion to get paper to 'fold itself' after printing.
Scientists develop a simple method that mimics plant motion to get paper to 'fold itself' after printing.
Water predictions: Telling when a nanolithography mold will break through droplets
 Scientists formulate a novel strategy to predict the lifetime of nanolithography molds through changes in the contact angle of water on the mold surface.
Scientists formulate a novel strategy to predict the lifetime of nanolithography molds through changes in the contact angle of water on the mold surface.
Bringing drugs to the brain with nanoparticles to treat neurodegenerative diseases
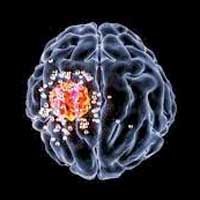 Nanoparticles could cross the blood-brain barrier to deliver drugs to the brain.
Nanoparticles could cross the blood-brain barrier to deliver drugs to the brain.
Electrified magnets: researchers uncover a new way to handle data
 Researchers report on how magnets and magnetic signals can be coupled more effectively and steered by electric fields. This could result in new, environmentally friendly concepts for efficient communication and data processing.
Researchers report on how magnets and magnetic signals can be coupled more effectively and steered by electric fields. This could result in new, environmentally friendly concepts for efficient communication and data processing.
Antiferromagnets are suitable for dissipationless nanoelectronics, contrary to current theories
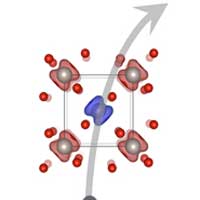 A physicist discovers the Hall effect in an antiferromagnet, which - according to current theories - is impossible.
A physicist discovers the Hall effect in an antiferromagnet, which - according to current theories - is impossible.
Infection diagnostics 3.0: Faster thanks to nanopore sequencing
 To ensure that sepsis patients receive appropriate antibiotics as quickly as possible, researchers have developed a diagnostic procedure that uses high-throughput sequencing of blood samples and delivers results much faster than conventional culture-based techniques. Thanks to the latest single-molecule sequencing techniques, this process has now been further improved so that pathogens can be identified after just a few hours.
To ensure that sepsis patients receive appropriate antibiotics as quickly as possible, researchers have developed a diagnostic procedure that uses high-throughput sequencing of blood samples and delivers results much faster than conventional culture-based techniques. Thanks to the latest single-molecule sequencing techniques, this process has now been further improved so that pathogens can be identified after just a few hours.
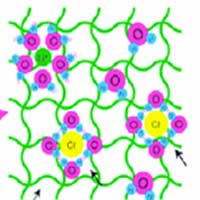
Coating plastics with porous MOF nanofilms
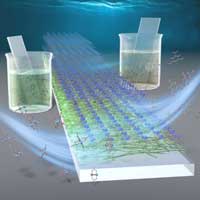 A research team has developed a new method for creating metal-organic framework (MOF) thin films that can be applied to sensors and electric devices.
A research team has developed a new method for creating metal-organic framework (MOF) thin films that can be applied to sensors and electric devices.
Hollow porphyrinic nanospheres
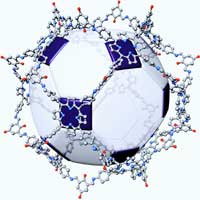 Making such purely organic, atomically precise hollow molecular spheres or cages is synthetically challenging. Now, researchers have successfully developed a template-free, one-pot synthesis of a porphyrin-based gigantic organic cages composed of multi-porphyrin units.
Making such purely organic, atomically precise hollow molecular spheres or cages is synthetically challenging. Now, researchers have successfully developed a template-free, one-pot synthesis of a porphyrin-based gigantic organic cages composed of multi-porphyrin units.
New insights into the production and dissociation of atomic clusters
 Atomic clusters are composed of several atoms of the same or very few different elements. Which conditions lead to the formation of atomic clusters? When and how do they fragment? These questions have been investigated by researchers.
Atomic clusters are composed of several atoms of the same or very few different elements. Which conditions lead to the formation of atomic clusters? When and how do they fragment? These questions have been investigated by researchers.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
