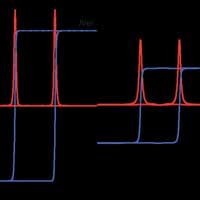
 Researchers have experimentally realized the quantum anomalous Hall effect in a multilayered insulator, essentially producing a multilane highway for the transport of electrons that could increase the speed and efficiency of information transfer without energy loss.
Researchers have experimentally realized the quantum anomalous Hall effect in a multilayered insulator, essentially producing a multilane highway for the transport of electrons that could increase the speed and efficiency of information transfer without energy loss.
Wednesday, December 16, 2020
Quantum insulators create multilane highways for electrons
 Researchers have experimentally realized the quantum anomalous Hall effect in a multilayered insulator, essentially producing a multilane highway for the transport of electrons that could increase the speed and efficiency of information transfer without energy loss.
Researchers have experimentally realized the quantum anomalous Hall effect in a multilayered insulator, essentially producing a multilane highway for the transport of electrons that could increase the speed and efficiency of information transfer without energy loss.
Colorful, magnetic Janus balls could help foil counterfeiters (w/video)
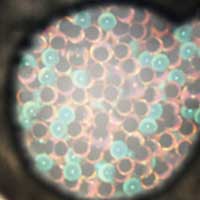 Researchers have developed tiny 'Janus balls' that show their colored side under a magnetic field. These microparticles could be useful in inks for anti-counterfeiting tags, which could be verified with an ordinary magnet, the researchers say.
Researchers have developed tiny 'Janus balls' that show their colored side under a magnetic field. These microparticles could be useful in inks for anti-counterfeiting tags, which could be verified with an ordinary magnet, the researchers say.
Exploring the flow of polymers through nanopores
 Printing with an ink-jet printer is part of daily life, but the same technology finds more complex applications in electronics and in protein separation. These applications rely on the quality of the printing process which depends on the flow of the 'ink' through narrow pores.
Printing with an ink-jet printer is part of daily life, but the same technology finds more complex applications in electronics and in protein separation. These applications rely on the quality of the printing process which depends on the flow of the 'ink' through narrow pores.
Physicists solve geometrical puzzle in electromagnetism
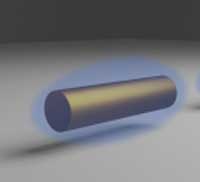 A team of scientists have solved the longstanding problem of how electrons move together as a group inside cylindrical nanoparticles.
A team of scientists have solved the longstanding problem of how electrons move together as a group inside cylindrical nanoparticles.
Novel ionic gel conductor may form the basis of flexible electronics and efficient photovoltaics
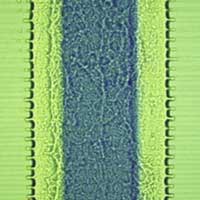 Researchers have created a new carbon-based electrical device by using an ionic gel made of a conductive polymer. This work may lead to cheaper and more reliable flexible printable electronics.
Researchers have created a new carbon-based electrical device by using an ionic gel made of a conductive polymer. This work may lead to cheaper and more reliable flexible printable electronics.
Semiconductor material analysis made possible with artificial intelligence
 Instant analysis of magnetic Hamiltonian parameters through electron microscopy.
Instant analysis of magnetic Hamiltonian parameters through electron microscopy.
Changing graphene properties one bond at a time
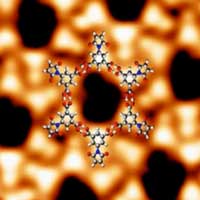 An international research team has demonstrated a novel process to modify the structure and properties of graphene. This chemical reaction, known as photocycloaddition, modifies the bonds between atoms using ultraviolet (UV) light.
An international research team has demonstrated a novel process to modify the structure and properties of graphene. This chemical reaction, known as photocycloaddition, modifies the bonds between atoms using ultraviolet (UV) light.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
