 Chemical engineers have developed a new way to manufacture zeolitic membranes, state-of-the-art materials used for gas separation in harsh conditions.
Chemical engineers have developed a new way to manufacture zeolitic membranes, state-of-the-art materials used for gas separation in harsh conditions.
Monday, October 5, 2020
Lego-like assembly of zeolitic membranes improves carbon capture
 Chemical engineers have developed a new way to manufacture zeolitic membranes, state-of-the-art materials used for gas separation in harsh conditions.
Chemical engineers have developed a new way to manufacture zeolitic membranes, state-of-the-art materials used for gas separation in harsh conditions.
Scientists teach old spectroscope new tricks
 Researchers have improved a method for probing semiconducting crystals with light to detect defects and impurities. The details of their 'omnidirectional photoluminescence (ODPL) spectroscopy' set-up could help improve the fabrication of materials for electric cars and solar cells.
Researchers have improved a method for probing semiconducting crystals with light to detect defects and impurities. The details of their 'omnidirectional photoluminescence (ODPL) spectroscopy' set-up could help improve the fabrication of materials for electric cars and solar cells.
Twisting magnetization with light - Laser pulses enable faster creation of skyrmions in magnets
 Scientists have demonstrated how tiny magnetization patterns known as skyrmions can be written into a ferromagnetic material faster than previously thought possible.
Scientists have demonstrated how tiny magnetization patterns known as skyrmions can be written into a ferromagnetic material faster than previously thought possible.
New shortcut enables faster creation of spin pattern in magnet
 Physicists have discovered a much faster approach to create a pattern of spins in a magnet. This 'shortcut' opens a new chapter in topology research. Interestingly, this discovery also offers an additional method to achieve more efficient magnetic data storage.
Physicists have discovered a much faster approach to create a pattern of spins in a magnet. This 'shortcut' opens a new chapter in topology research. Interestingly, this discovery also offers an additional method to achieve more efficient magnetic data storage.
Nanoparticles can turn off genes in bone marrow cells
 Using these new particles, researchers could develop treatments for heart disease and other conditions.
Using these new particles, researchers could develop treatments for heart disease and other conditions.
Carbon nanosheets derived from spinach could power fuel cells
 Spinach, when converted from its leafy, edible form into carbon nanosheets, acts as a catalyst for an oxygen reduction reaction in fuel cells and metal-air batteries.
Spinach, when converted from its leafy, edible form into carbon nanosheets, acts as a catalyst for an oxygen reduction reaction in fuel cells and metal-air batteries.
Blocking vibrations that remove heat could boost efficiency of next-gen solar cells
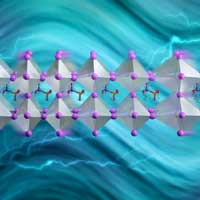 A study of a solar-energy material with a bright future revealed a way to slow phonons, the waves that transport heat. The discovery could improve novel hot-carrier solar cells, which convert sunlight to electricity more efficiently than conventional solar cells by harnessing photogenerated charge carriers before they lose energy to heat.
A study of a solar-energy material with a bright future revealed a way to slow phonons, the waves that transport heat. The discovery could improve novel hot-carrier solar cells, which convert sunlight to electricity more efficiently than conventional solar cells by harnessing photogenerated charge carriers before they lose energy to heat.
Two-dimensional MXene as a novel electrode material for next-generation display
 Interface engineered 2D titanium carbide MXene film serves as efficient flexible electrodes for light-emitting diodes.
Interface engineered 2D titanium carbide MXene film serves as efficient flexible electrodes for light-emitting diodes.
Millimetre-precision drug delivery to the brain
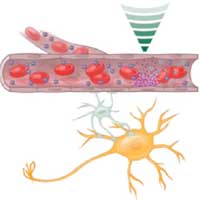 Researchers have developed a method for concentrating and releasing drugs in the brain with pinpoint accuracy. This could make it possible in the future to deliver psychiatric and cancer drugs and other medications only to those regions of the brain where this is medically desirable.
Researchers have developed a method for concentrating and releasing drugs in the brain with pinpoint accuracy. This could make it possible in the future to deliver psychiatric and cancer drugs and other medications only to those regions of the brain where this is medically desirable.
Solar-battery effect enables a new light-driven organic microswimmer to operate in the dark
 Researchers have developed a biocompatible microswimmer made of carbon nitride, which they can propel forward through light. The particle can also store solar energy similar to miniature solar cells equipped with batteries, and can thus also swim in the dark using the stored energy.
Researchers have developed a biocompatible microswimmer made of carbon nitride, which they can propel forward through light. The particle can also store solar energy similar to miniature solar cells equipped with batteries, and can thus also swim in the dark using the stored energy.
Exploiting molecular vibrations to synthesize conducting polymers
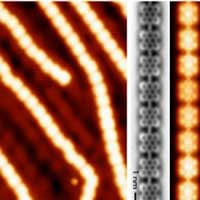 Researchers study a novel strategy to synthesize low bandgap polymers on a gold surface taking advantage of their molecular vibrations. The work combines the chemical synthesis with STM and AFM studies of the electronic properties of bisanthene polymers, whose synthesis is not feasible by conventional methods.
Researchers study a novel strategy to synthesize low bandgap polymers on a gold surface taking advantage of their molecular vibrations. The work combines the chemical synthesis with STM and AFM studies of the electronic properties of bisanthene polymers, whose synthesis is not feasible by conventional methods.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
