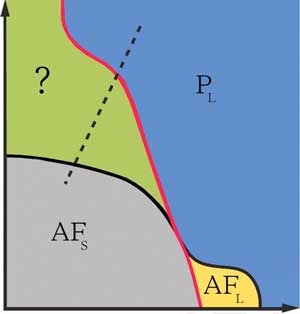
 Alloy behaves strangely while traversing potential 'spin liquid' state.
Alloy behaves strangely while traversing potential 'spin liquid' state.
Monday, September 30, 2019
Quantum material goes where none have gone before
 Alloy behaves strangely while traversing potential 'spin liquid' state.
Alloy behaves strangely while traversing potential 'spin liquid' state.
Millions of parabolic nanoantennas for a high-precision sensor
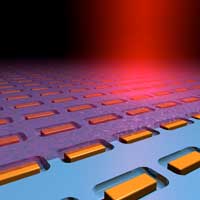 Researchers have developed a multi-purpose sensor based on a specially designed gold film which surface contains millions of parabolic nanoantennas produced by femtosecond laser printing.
Researchers have developed a multi-purpose sensor based on a specially designed gold film which surface contains millions of parabolic nanoantennas produced by femtosecond laser printing.
Curved nanochannels allow independent tuning of charge and spin currents
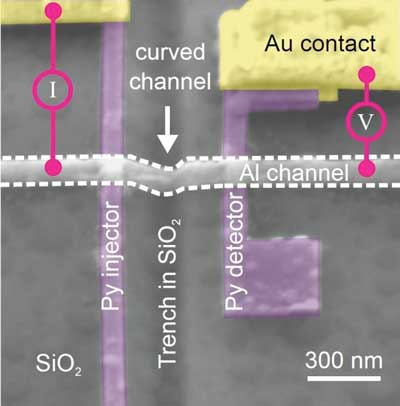 Scientists discovered that this new curved geometry makes it possible to independently tune charge and spin currents. \
Scientists discovered that this new curved geometry makes it possible to independently tune charge and spin currents. \
Silicon technology boost with graphene and 2D materials
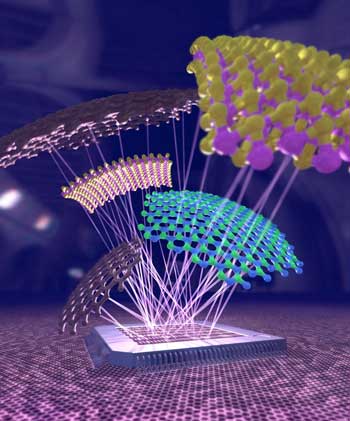 Researchers and collaborators report on the current state, challenges, opportunities of graphene and 2D material integration in silicon technology.
Researchers and collaborators report on the current state, challenges, opportunities of graphene and 2D material integration in silicon technology.
Borophene on silver grows freely into an atomic 'skin'
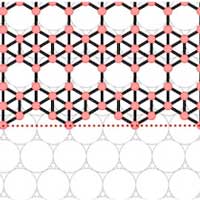 By using a silver substrate and through careful manipulation of temperature and deposition rate, scientists have discovered they can grow elongated hexagon-shaped flakes of borophene.
By using a silver substrate and through careful manipulation of temperature and deposition rate, scientists have discovered they can grow elongated hexagon-shaped flakes of borophene.
Towards safer, more effective cancer radiation therapy using X-rays and nanoparticles
 X-rays could be tuned to deliver a more effective punch that destroys cancer cells and not harm the body.
X-rays could be tuned to deliver a more effective punch that destroys cancer cells and not harm the body.
Saturday, September 28, 2019
Physicists found weak spots in ceramic/graphene composites
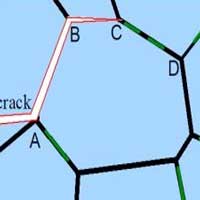 Physicists found out the structures in nanomaterials made of ceramic and graphene plates, in which cracks appear most frequently.
Physicists found out the structures in nanomaterials made of ceramic and graphene plates, in which cracks appear most frequently.
Light in a new light
 Researchers describe a noteworthy step forward in the quantum manipulation and control of light.
Researchers describe a noteworthy step forward in the quantum manipulation and control of light.
Physicists score double hit in LED research
 In two breakthroughs in the realm of photonics, researchers are reporting the successful demonstration of an LED based on half-light half-matter quasiparticles in atomically thin materials. This is also the first successful test of an electrically driven light emitter using atomically thin semiconductors embedded in a light trapping structure (optical cavity).
In two breakthroughs in the realm of photonics, researchers are reporting the successful demonstration of an LED based on half-light half-matter quasiparticles in atomically thin materials. This is also the first successful test of an electrically driven light emitter using atomically thin semiconductors embedded in a light trapping structure (optical cavity).
Novel nanogels hold promise for improved drug delivery to cancer patients
 Engineers developed multifunctional nanoscale gels for more precise delivery of therapeutic cancer treatments. The nanogels can deliver drugs, target malignant cells (or biomarkers), degrade into nontoxic components and execute multiple clinical functions.
Engineers developed multifunctional nanoscale gels for more precise delivery of therapeutic cancer treatments. The nanogels can deliver drugs, target malignant cells (or biomarkers), degrade into nontoxic components and execute multiple clinical functions.
New lattice designs defy conventional wisdom on metamaterials
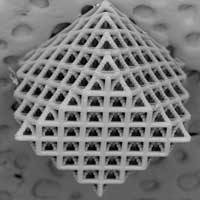 Researchers have designed a new class of 3D-printed lattice structures that combine light weight and high stiffness, despite breaking a rule previously thought to be required to exhibit such properties. One of the new structures additionally displays perfectly uniform response to forces in all directions.
Researchers have designed a new class of 3D-printed lattice structures that combine light weight and high stiffness, despite breaking a rule previously thought to be required to exhibit such properties. One of the new structures additionally displays perfectly uniform response to forces in all directions.
Researchers unveil the dynamic nature of single fission
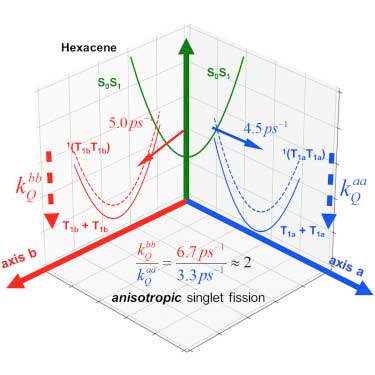 Chemists have unveiled the dynamic nature of single fission, a novel photophysical phenomenon that bears an unprecedented potential to drastically improve the solar cell efficiency.
Chemists have unveiled the dynamic nature of single fission, a novel photophysical phenomenon that bears an unprecedented potential to drastically improve the solar cell efficiency.
Friday, September 27, 2019
New design of bioactive peptide nanofibers keeping both temperature reversibility and stiffness control
 Researchers have developed a new method of molecular design to control both temperature reversibility and stiffness of nanofibers that are gel-forming peptides. The peptide nanofiber hydrogel can be used as biomedical materials. This method will allow the peptide nanofibers more biomedical applicable.
Researchers have developed a new method of molecular design to control both temperature reversibility and stiffness of nanofibers that are gel-forming peptides. The peptide nanofiber hydrogel can be used as biomedical materials. This method will allow the peptide nanofibers more biomedical applicable.
Use of nanopores could lead to cleaner water
 Scientists have reviewed recent Single Digit Nanopore experiments and identified critical gaps in understanding nanoscale hydrodynamics, molecular sieving, fluidic structure and thermodynamics.
Scientists have reviewed recent Single Digit Nanopore experiments and identified critical gaps in understanding nanoscale hydrodynamics, molecular sieving, fluidic structure and thermodynamics.
A laser, a crystal and molecular structures
 Researchers have built a new tool to study molecules using a laser, a crystal and light detectors. This new technology will reveal nature's smallest sculptures -- the structures of molecules -- with increased detail and specificity.
Researchers have built a new tool to study molecules using a laser, a crystal and light detectors. This new technology will reveal nature's smallest sculptures -- the structures of molecules -- with increased detail and specificity.
Liquid crystals and chirality explored
 In a newly funded research project, scientists are trying to create what amounts to a chiral dipole.
In a newly funded research project, scientists are trying to create what amounts to a chiral dipole.
Discovery in gallium nitride a key enabler of energy efficient electronics
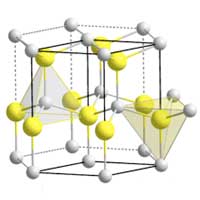 Gallium nitride, a semiconductor that revolutionized energy-efficient LED lighting, could also transform electronics and wireless communication, thanks to a recent discovery.
Gallium nitride, a semiconductor that revolutionized energy-efficient LED lighting, could also transform electronics and wireless communication, thanks to a recent discovery.
Converting carbon dioxide to valuable resources with the help of nanoparticles
 Researchers have adopted the principle from enzymes that produce complex molecules in multi-step reactions. The team transferred this mechanism to metallic nanoparticles.
Researchers have adopted the principle from enzymes that produce complex molecules in multi-step reactions. The team transferred this mechanism to metallic nanoparticles.
An artificial skin that can help rehabilitation and enhance virtual reality
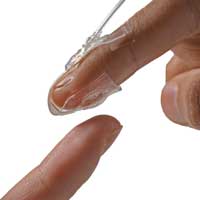 Scientists have developed a soft artificial skin that provides haptic feedback and -- thanks to a sophisticated self-sensing mechanism -- has the potential to instantaneously adapt to a wearer's movements. Applications for the new technology range from medical rehabilitation to virtual reality.
Scientists have developed a soft artificial skin that provides haptic feedback and -- thanks to a sophisticated self-sensing mechanism -- has the potential to instantaneously adapt to a wearer's movements. Applications for the new technology range from medical rehabilitation to virtual reality.
Thursday, September 26, 2019
Shocking heat waves stabilize single atoms
 Single atoms work great as catalysts, but they usually don't stay single for long. Scientists use high-temperature shock waves to keep them in their place.
Single atoms work great as catalysts, but they usually don't stay single for long. Scientists use high-temperature shock waves to keep them in their place.
'Safe-by-Design' - On the road to safe nanomedicine
 An international research consortium has developed guidelines that should enable the safe development of nanoparticles for medical use.
An international research consortium has developed guidelines that should enable the safe development of nanoparticles for medical use.
Compute at the speed of light
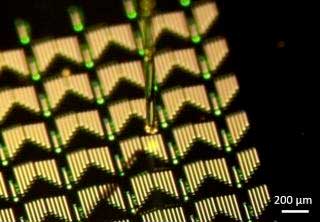 A new way to achieve integrated photonics could have applications in imaging, sensing and quantum information processing, such as on-chip transformation optics, mathematical operations and spectrometers.
A new way to achieve integrated photonics could have applications in imaging, sensing and quantum information processing, such as on-chip transformation optics, mathematical operations and spectrometers.
Study finds EU regulatory framework ready for the next generation of nanomaterials
 A study commissioned by the EU nanomaterials observatory has found that the current EU regulatory framework for characterising and identifying 'next generation' nanomaterials is able to address the majority of them and that no significant changes will be needed in the near future.
A study commissioned by the EU nanomaterials observatory has found that the current EU regulatory framework for characterising and identifying 'next generation' nanomaterials is able to address the majority of them and that no significant changes will be needed in the near future.
Wednesday, September 25, 2019
Nanotechnology improves chemotherapy delivery
 Scientists have invented a new way to monitor chemotherapy concentrations, which is more effective in keeping patients' treatments within the crucial therapeutic window.
Scientists have invented a new way to monitor chemotherapy concentrations, which is more effective in keeping patients' treatments within the crucial therapeutic window.
Quantum sensing on a chip
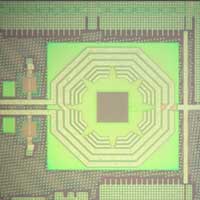 Researchers integrate diamond-based sensing components onto a chip to enable low-cost, high-performance quantum hardware.
Researchers integrate diamond-based sensing components onto a chip to enable low-cost, high-performance quantum hardware.
Machine learning finds new metamaterial designs for energy harvesting
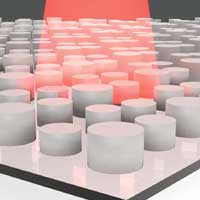 Design would enable thermophotovoltaic devices that convert waste heat to electricity.
Design would enable thermophotovoltaic devices that convert waste heat to electricity.
Researchers report a new way to produce curvy electronics
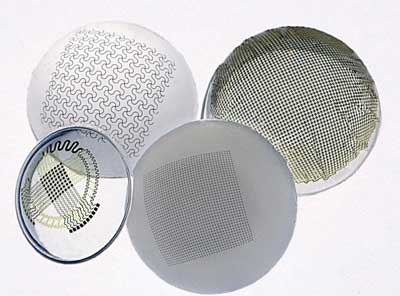 New method fills a need in emerging applications for electronic devices.
New method fills a need in emerging applications for electronic devices.
A stretchable and flexible buckypaper-based biofuel cell that runs on sweat
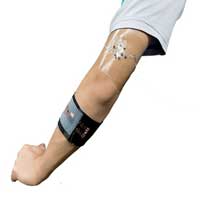 Researchers have developed a unique new flexible and stretchable device, worn against the skin and capable of producing electrical energy by transforming the compounds present in sweat.
Researchers have developed a unique new flexible and stretchable device, worn against the skin and capable of producing electrical energy by transforming the compounds present in sweat.
Bottom-up synthesis of crystalline 2D polymers: A dream finally comes true
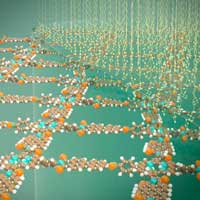 The 2D polymers consist of only a few single atomic layers and, due to their very special properties, are a promising material for use in electronic components and systems of a new generation.
The 2D polymers consist of only a few single atomic layers and, due to their very special properties, are a promising material for use in electronic components and systems of a new generation.
Engineered protein crystals make cells magnetic
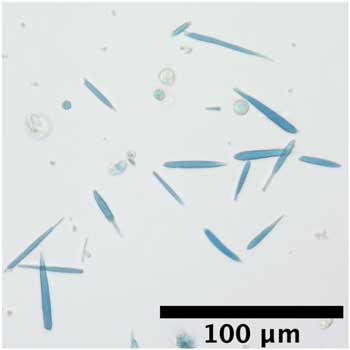 Researchers have engineered genetically encoded protein crystals that can generate magnetic forces many times stronger than those already reported.
Researchers have engineered genetically encoded protein crystals that can generate magnetic forces many times stronger than those already reported.
Scientists create sensors with traps for free radicals
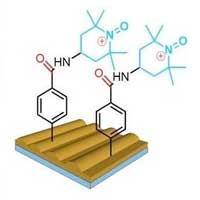 Scientists have designed extremely sensitive sensors for free oxygen-containing radicals that are able to disrupt cell function. These sensors are an alternative to traditional analytical chemical methods of analysis.
Scientists have designed extremely sensitive sensors for free oxygen-containing radicals that are able to disrupt cell function. These sensors are an alternative to traditional analytical chemical methods of analysis.
Nanocatalyst makes heavy work of formic acid
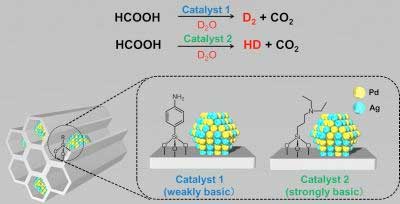 Researchers report an inexpensive and scalable route to hydrogen isotope compounds.
Researchers report an inexpensive and scalable route to hydrogen isotope compounds.
Tuesday, September 24, 2019
Iridium 'loses its identity' when interfaced with nickel
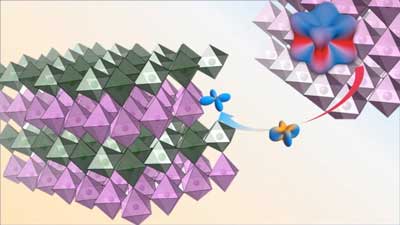 Study could lead to greater manipulation of quantum materials and deeper understanding of the quantum state for novel electronics.
Study could lead to greater manipulation of quantum materials and deeper understanding of the quantum state for novel electronics.
Quantum destabilization of a water sandwich
 When a thin layer of water is squeezed between two hydrophobic surfaces, the laws of classical physics break down.
When a thin layer of water is squeezed between two hydrophobic surfaces, the laws of classical physics break down.
Research could help flexible technology last longer, avoid critical failures
 A new study uses the topography of human skin as a model not for preventing cracks but for directing them in the best way possible to avoid critical components and make repairs easy.
A new study uses the topography of human skin as a model not for preventing cracks but for directing them in the best way possible to avoid critical components and make repairs easy.
How molecular footballs burst in an X-ray laser beam
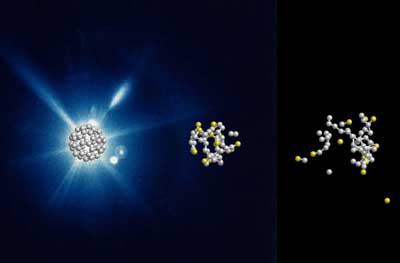 Study shows effect of X-ray flashes on sensitive biomolecules.
Study shows effect of X-ray flashes on sensitive biomolecules.
Highly sensitive nanowire diode converts microwaves to electricity
 The new technology is expected to play a role in harvesting energy from radio waves in the environment, in which electricity is generated from ambient radio waves, such as those emitted from mobile phone base stations.
The new technology is expected to play a role in harvesting energy from radio waves in the environment, in which electricity is generated from ambient radio waves, such as those emitted from mobile phone base stations.
Researchers can now place single ions into solids
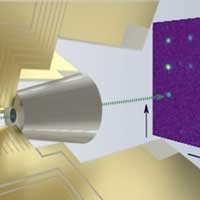 New technique enables implantation of individual ions into crystals with an accuracy of 35 nanometers.
New technique enables implantation of individual ions into crystals with an accuracy of 35 nanometers.
Seeing sound: Scientists observe how acoustic interactions change materials at the atomic level
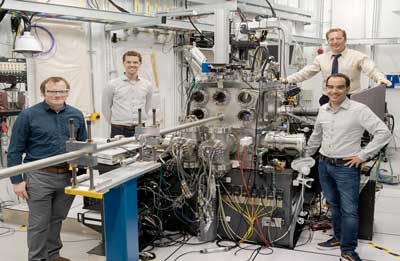 Scientists used X-rays to observe spatial changes in a silicon carbide crystal when using sound waves to strain buried defects inside it.
Scientists used X-rays to observe spatial changes in a silicon carbide crystal when using sound waves to strain buried defects inside it.
Converting absorbed photons into twice as many excitons: successful high-efficiency energy conversion with organic monolayer on gold nanocluster surface
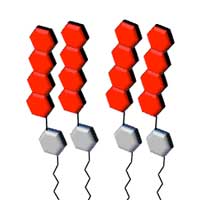 Scientists have found that when light was exposed to the surface of a tetracene alkanethiol-modified gold nanocluster, which they developed themselves, twice as many excitons could be converted compared to the number of photons absorbed by the tetracene molecules.
Scientists have found that when light was exposed to the surface of a tetracene alkanethiol-modified gold nanocluster, which they developed themselves, twice as many excitons could be converted compared to the number of photons absorbed by the tetracene molecules.
Monday, September 23, 2019
Researchers recreate living 3D displays (w/video)
 Researchers are developing a smart skin inspired by the cephalopod which can be used in 3D displays, as interfaces for the visually impaired, and to help reduce drag on marine vehicles.
Researchers are developing a smart skin inspired by the cephalopod which can be used in 3D displays, as interfaces for the visually impaired, and to help reduce drag on marine vehicles.
How to design efficient materials for OLED displays
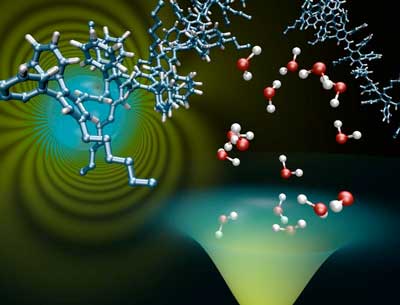 A major problem is that in many organic semiconductors the flow of electricity is hampered by microscopic defects. Scientists have now investigated how organic semiconductors can be designed such that the electric conduction is not influenced by these defects.
A major problem is that in many organic semiconductors the flow of electricity is hampered by microscopic defects. Scientists have now investigated how organic semiconductors can be designed such that the electric conduction is not influenced by these defects.
Wearable brain-machine interface could control a wheelchair, vehicle or computer
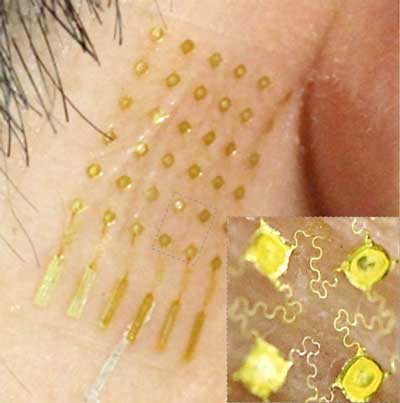 Combining new classes of nanomembrane electrodes with flexible electronics and a deep learning algorithm could help disabled people wirelessly control an electric wheelchair, interact with a computer or operate a small robotic vehicle without donning a bulky hair-electrode cap or contending with wires.
Combining new classes of nanomembrane electrodes with flexible electronics and a deep learning algorithm could help disabled people wirelessly control an electric wheelchair, interact with a computer or operate a small robotic vehicle without donning a bulky hair-electrode cap or contending with wires.
A process for making ductile glass
 Numerous applications for special glass may include tougher smart phone screens and transparent structural materials.
Numerous applications for special glass may include tougher smart phone screens and transparent structural materials.
Researchers develop new framework for nanoantenna light absorption
 Researchers have developed nanoantennas that pack the energy captured from light sources, such as LEDs, into particles with nanometer-scale diameters, making it possible to detect individual biomolecules, catalyze chemical reactions, and generate photons with desirable properties for quantum computing.
Researchers have developed nanoantennas that pack the energy captured from light sources, such as LEDs, into particles with nanometer-scale diameters, making it possible to detect individual biomolecules, catalyze chemical reactions, and generate photons with desirable properties for quantum computing.
Tiny, biocompatible nanolaser could function inside living tissues
 Nanolaser has potential to treat neurological disorders or sense disease biomarkers.
Nanolaser has potential to treat neurological disorders or sense disease biomarkers.
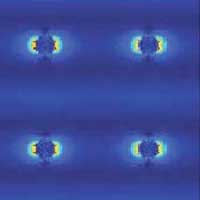
'Valley states' in this 2D material could potentially be used for quantum computing
 Physicists manipulate energy valleys in tungsten disulfide, with potential applications in quantum computing.
Physicists manipulate energy valleys in tungsten disulfide, with potential applications in quantum computing.
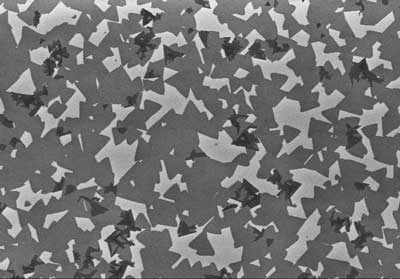
Graphene is actually a 3D material as well as a 2D material
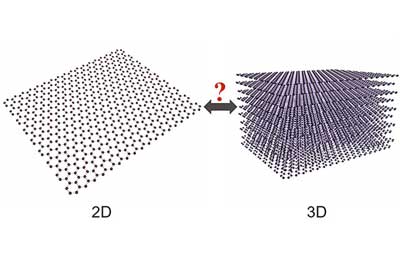 Researchers found that 2D graphene has many of the same mechanical properties as 3D graphite, which is a naturally occurring form of carbon made up from a very weak stack of many layers of graphene.
Researchers found that 2D graphene has many of the same mechanical properties as 3D graphite, which is a naturally occurring form of carbon made up from a very weak stack of many layers of graphene.
A new way to turn heat into energy
 The discovery could create more efficient energy generation from heat in things like car exhaust, interplanetary space probes and industrial processes.
The discovery could create more efficient energy generation from heat in things like car exhaust, interplanetary space probes and industrial processes.
Saturday, September 21, 2019
New sensors could lead to earlier lymphoma diagnosis
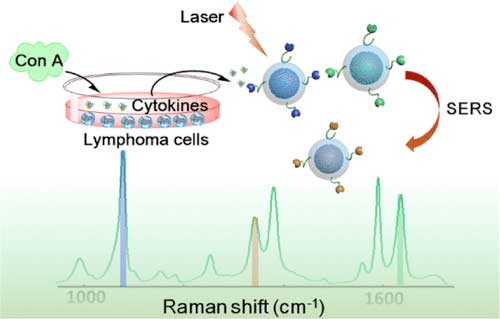 Researchers have developed a new method of detecting multiple cytokines - the body's messenger proteins - in very small volume samples, which could lead to earlier diagnosis of diseases such as lymphoma.
Researchers have developed a new method of detecting multiple cytokines - the body's messenger proteins - in very small volume samples, which could lead to earlier diagnosis of diseases such as lymphoma.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
