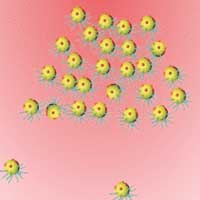
 Chemotactic movement on the macroscale by a swarm of bacteria-mimicking nanoswimmers.
Chemotactic movement on the macroscale by a swarm of bacteria-mimicking nanoswimmers.
Wednesday, July 31, 2019
Actively swimming gold nanoparticles
 Chemotactic movement on the macroscale by a swarm of bacteria-mimicking nanoswimmers.
Chemotactic movement on the macroscale by a swarm of bacteria-mimicking nanoswimmers.
Researchers produce electricity by flowing water over nanolayers of metal
 Oxide layer atop nanometal layer results in electron shuttle, not corrosion.
Oxide layer atop nanometal layer results in electron shuttle, not corrosion.
Magnetic nanosprings break down marine microplastic pollution
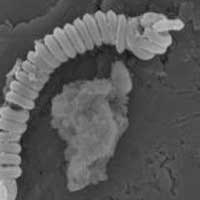 Using tiny coil-shaped carbon-based magnets, researchers in have developed a new approach to purging water sources of the microplastics that pollute them without harming nearby microorganisms.
Using tiny coil-shaped carbon-based magnets, researchers in have developed a new approach to purging water sources of the microplastics that pollute them without harming nearby microorganisms.
Nanobubbles hold clue to improved industrial structures
 Insights into how minute, yet powerful, bubbles form and collapse on underwater surfaces could help make industrial structures such as ship propellers more hardwearing, research suggests.
Insights into how minute, yet powerful, bubbles form and collapse on underwater surfaces could help make industrial structures such as ship propellers more hardwearing, research suggests.
New way to make 3D carbon nanotube components
 Researchers used a 3D printer to make lightweight, strong, highly porous pure carbon nanotube structures using a 3D printer.
Researchers used a 3D printer to make lightweight, strong, highly porous pure carbon nanotube structures using a 3D printer.
Experimental observation of a new class of materials: excitonic insulators
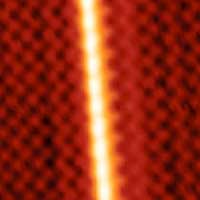 Scientists have found evidence of a new phase of matter predicted in the 1960s: the excitonic insulator.
Scientists have found evidence of a new phase of matter predicted in the 1960s: the excitonic insulator.
Lights out: Putting the ambient air oxidation of monolayer WS2 to bed
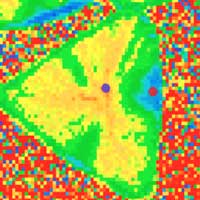 New research shows that the oxidation of monolayers of tungsten disulphide (WS2) in ambient conditions is due to the absorption of visible wavelengths of light.
New research shows that the oxidation of monolayers of tungsten disulphide (WS2) in ambient conditions is due to the absorption of visible wavelengths of light.
Tuesday, July 30, 2019
Treating solar cell materials reveals formation of unexpected microstructures
 Hybrid organic-inorganic perovskite crystals are more efficient after solution-treating, but there are mechanisms doing more than just removing defects.
Hybrid organic-inorganic perovskite crystals are more efficient after solution-treating, but there are mechanisms doing more than just removing defects.
3D printable 2D materials based inks show promise to improve energy storage devices
 For the first time, researchers have formulated inks using the 2D material MXene, to produce 3D printed interdigitated electrodes.
For the first time, researchers have formulated inks using the 2D material MXene, to produce 3D printed interdigitated electrodes.
Researchers develop novel process for structuring quantum materials
 To build high-performance quantum computers, for example, topological insulators have to be combined with superconductors. This fabrication step is associated with a number of challenges that have now been solved by researchers.
To build high-performance quantum computers, for example, topological insulators have to be combined with superconductors. This fabrication step is associated with a number of challenges that have now been solved by researchers.
Researchers repair faulty brain circuits using nanotechnology
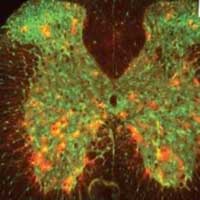 Possible new drug targets for dementia and intellectual disability.
Possible new drug targets for dementia and intellectual disability.
New nanoparticle combination therapy shows effective resuscitation for massive hemorrhage
 Scientists successfully resuscitated rabbits with coagulopathy from severe hemorrhagic shock using hemostatic nanoparticles and oxygen-carrying nanoparticles, which respectively stopped bleeding and delivered oxygen to the systemic tissues and organs. There are no effective therapies for such massive hemorrhage so far, thereby the combination therapy using two kinds of functional nanoparticles maybe desirable in future emergency trauma care.
Scientists successfully resuscitated rabbits with coagulopathy from severe hemorrhagic shock using hemostatic nanoparticles and oxygen-carrying nanoparticles, which respectively stopped bleeding and delivered oxygen to the systemic tissues and organs. There are no effective therapies for such massive hemorrhage so far, thereby the combination therapy using two kinds of functional nanoparticles maybe desirable in future emergency trauma care.
Monday, July 29, 2019
Expanding functions of conducting microbial nanowires for chemical, biological sensors
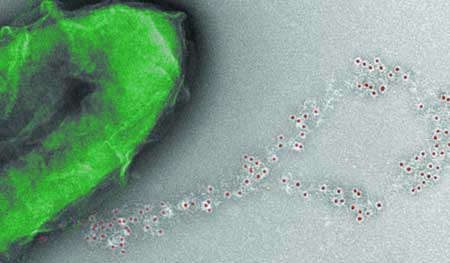 Scientists report 'a major advance' in the quest to develop electrically conductive protein nanowires in the bacterium Geobacter sulfurreducens for use as chemical and biological sensors.
Scientists report 'a major advance' in the quest to develop electrically conductive protein nanowires in the bacterium Geobacter sulfurreducens for use as chemical and biological sensors.
Oddball edge wins nanotube faceoff
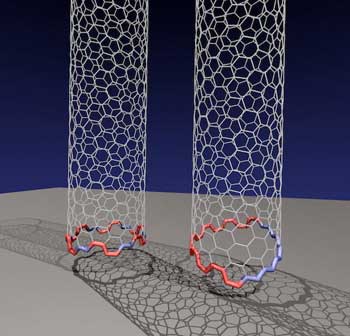 Theory shows peculiar ?Janus? interface a common mechanism in carbon nanotube growth.
Theory shows peculiar ?Janus? interface a common mechanism in carbon nanotube growth.
Engineers use heat-free tech for flexible electronics; print metal on flowers, gelatin
 Researchers are using liquid-metal particles to print electronic lines and traces on rose petals, leaves, paper, gelatin - on all kinds of materials. The technology creates flexible electronics that could have many applications such as monitoring crops, tracking a building's structural integrity or collecting biological data.
Researchers are using liquid-metal particles to print electronic lines and traces on rose petals, leaves, paper, gelatin - on all kinds of materials. The technology creates flexible electronics that could have many applications such as monitoring crops, tracking a building's structural integrity or collecting biological data.
Dynamics in quantum dots: Smallest measurable processes recorded individually
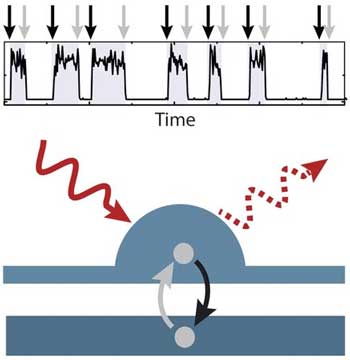 Colloquially, the term 'quantum jump' is used to describe a tremendous development. In fact, it is the smallest change of state that can still be traced. Physicists have now succeeded in measuring every single jump by optical means and drawing conclusions about the dynamics of the electrons inside a quantum dot.
Colloquially, the term 'quantum jump' is used to describe a tremendous development. In fact, it is the smallest change of state that can still be traced. Physicists have now succeeded in measuring every single jump by optical means and drawing conclusions about the dynamics of the electrons inside a quantum dot.
Transforming advanced nanoscience data into interactive art
 Scientists and a multimedia artist generated novel representations of experimental nanoscience data through 3-D printing, sound, and virtual reality.
Scientists and a multimedia artist generated novel representations of experimental nanoscience data through 3-D printing, sound, and virtual reality.
Travelling towards a quantum internet at light speed
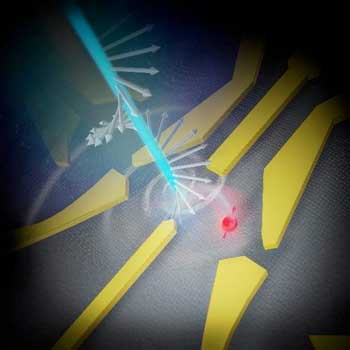 Scientists successfully transferred and verified the angular momentum basis of quantum information from laser light to an electron trapped on a quantum dot. This work is a major step towards realizing hacker-proof interconnected quantum computers.
Scientists successfully transferred and verified the angular momentum basis of quantum information from laser light to an electron trapped on a quantum dot. This work is a major step towards realizing hacker-proof interconnected quantum computers.
Scientists film molecular rotation
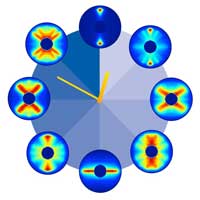 Quantum movie displays probability density distribution of rotating carbonyl sulphide molecules.
Quantum movie displays probability density distribution of rotating carbonyl sulphide molecules.
Sunday, July 28, 2019
Transformative Carbon XPrize technological advance in CO2 utilization
 Rather than carbon taxes or extended debates on the international path to combat global warming, transforming the greenhouse carbon dioxide to a valuable product incentivizes its 'mining' and removal, either from industrial flue gas or directly from the air.
Rather than carbon taxes or extended debates on the international path to combat global warming, transforming the greenhouse carbon dioxide to a valuable product incentivizes its 'mining' and removal, either from industrial flue gas or directly from the air.
Plasmonic magnetism - Light may magnetise non-magnetic metals, propose physicists
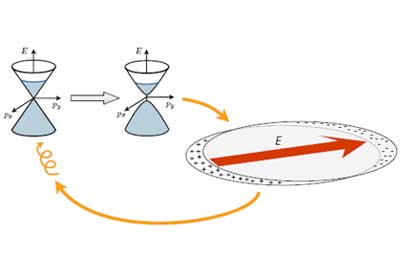 Physicists have devised a method to turn a non-magnetic metal into a magnet using laser light.
Physicists have devised a method to turn a non-magnetic metal into a magnet using laser light.
Trandfer-printing technology for creating flexible sensors on topographic surfaces
 A esearch team developed a transfer-printing technology that uses hydrogel and nano ink to easily create high-performance sensors on flexible substrates of diverse shapes and structures.
A esearch team developed a transfer-printing technology that uses hydrogel and nano ink to easily create high-performance sensors on flexible substrates of diverse shapes and structures.
Saturday, July 27, 2019
A good first step toward nontoxic solar cells
 Engineers discover lead-free perovskite semiconductor for solar cells using data analytics, supercomputers.
Engineers discover lead-free perovskite semiconductor for solar cells using data analytics, supercomputers.
Friday, July 26, 2019
Bioinspired nanoparticles remodel tumor stroma to enhance nanoparticle accessibility to cancer cells
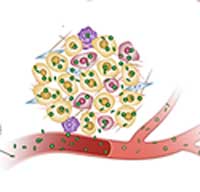 Scientists propose a bioinspired lipoproteins (bLP)-mediated strategy, aiming at inducing photothermia to disrupt the tumor stromal microenvironments (TSM) barriers and augmenting the accessibility of second-wave nanoparticles to cancer cells to suppress tumor relapse and metastasis.
Scientists propose a bioinspired lipoproteins (bLP)-mediated strategy, aiming at inducing photothermia to disrupt the tumor stromal microenvironments (TSM) barriers and augmenting the accessibility of second-wave nanoparticles to cancer cells to suppress tumor relapse and metastasis.
Yellow is not the new black: Discovery paves way for new generation of solar cells
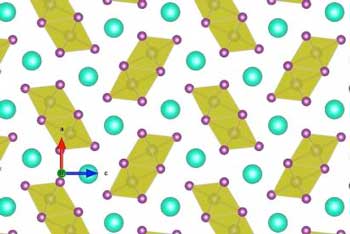 A study for the first time explains how a promising type of perovskites - man-made crystals that can convert sunlight into electricity - can be stabilized. As a result, the crystals turn black, enabling them to absorb sunlight.
A study for the first time explains how a promising type of perovskites - man-made crystals that can convert sunlight into electricity - can be stabilized. As a result, the crystals turn black, enabling them to absorb sunlight.
Shaping light with a smartlens
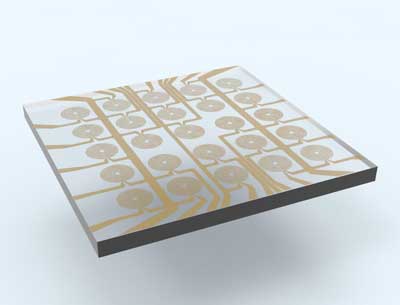 A team of researchers reports on a dynamically tuneable lens capable of achieving almost any complex optical function.
A team of researchers reports on a dynamically tuneable lens capable of achieving almost any complex optical function.
New quantum phenomenon helps to understand fundamental limits of graphene electronics
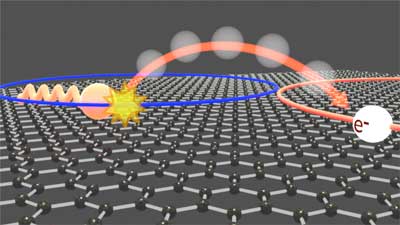 A new study describes how electrons in a single atomically-thin sheet of graphene scatter off the vibrating carbon atoms which make up the hexagonal crystal lattice.
A new study describes how electrons in a single atomically-thin sheet of graphene scatter off the vibrating carbon atoms which make up the hexagonal crystal lattice.
Next-generation graphene membranes for carbon capture
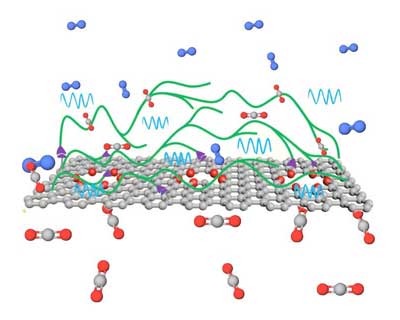 Chemical engineers have developed a new class of high-performance membranes for carbon capture that greatly exceed current targets.
Chemical engineers have developed a new class of high-performance membranes for carbon capture that greatly exceed current targets.
Listening to the whispers of individual cells
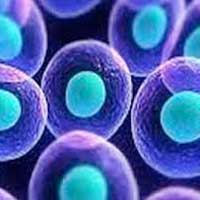 A new method developed by biophysicists has made it possible for the first time to detect and analyse signals between individual cells.
A new method developed by biophysicists has made it possible for the first time to detect and analyse signals between individual cells.
Synthetic biology enables protein origami
 Engineers find new way to create single-chain protein nanostructures using synthetic biology and protein-assembly techniques.
Engineers find new way to create single-chain protein nanostructures using synthetic biology and protein-assembly techniques.
Physicists discover new quantum trick for graphene: magnetism
 Physicists were stunned when two twisted sheets of graphene showed signs of superconductivity. Now scientists have shown that the material also generates a type of magnetism once only dreamed of theoretically.
Physicists were stunned when two twisted sheets of graphene showed signs of superconductivity. Now scientists have shown that the material also generates a type of magnetism once only dreamed of theoretically.
Designed switch allows unprecedented control over living cells
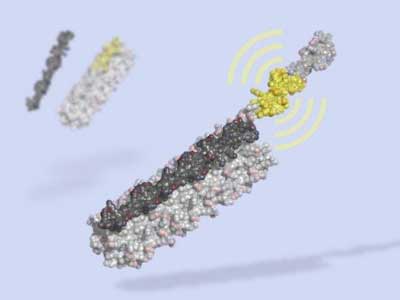 From modifying gene expression to cell signaling, dynamic designer proteins may usher in a new era of synthetic biology.
From modifying gene expression to cell signaling, dynamic designer proteins may usher in a new era of synthetic biology.
Mimicking lizard skin to save energy on an industrial scale
 The LABIONICS project is set to drive the commercial development of breakthrough laser-engineered products inspired by the unique skin and scale textures of animals and insects, potentially leading to entirely new applications across industry, energy and medicine.
The LABIONICS project is set to drive the commercial development of breakthrough laser-engineered products inspired by the unique skin and scale textures of animals and insects, potentially leading to entirely new applications across industry, energy and medicine.
Thursday, July 25, 2019
Researchers construct an artificial olfactory system based on self-powered nano-generator
 This device can sense different odor molecules and recognize different odors. It has been demonstrated in vivo in animal models.
This device can sense different odor molecules and recognize different odors. It has been demonstrated in vivo in animal models.
Transforming biology to design next-generation computers, using a surprise ingredient
 Researchers have found ways of transforming structures that occur naturally in cell membranes to create other architectures, like parallel 1nm-wide line segments, more applicable to computing.
Researchers have found ways of transforming structures that occur naturally in cell membranes to create other architectures, like parallel 1nm-wide line segments, more applicable to computing.
Molecular mayhem at root of battery breakdown
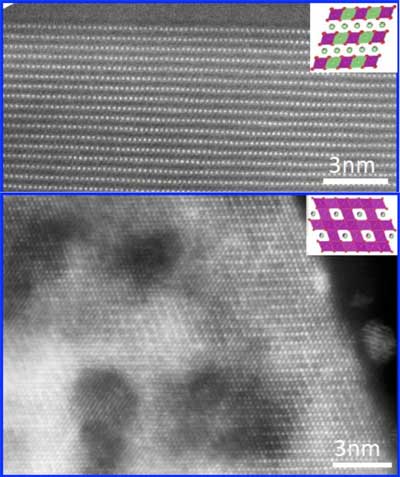 Overly active oxygen atoms escape with ease, leading to battery failure.
Overly active oxygen atoms escape with ease, leading to battery failure.
Chemists close gap in making nanomedicines safer, more efficient
 A new study describes how one of the liver's natural toxin-removal processes can improve the delivery of nanomedicines.
A new study describes how one of the liver's natural toxin-removal processes can improve the delivery of nanomedicines.
Soft micro-monitors keep tabs on oxygen in new tissues
 Scientists develop fluorescent sensors to track nutrients in hydrogel-based healing.
Scientists develop fluorescent sensors to track nutrients in hydrogel-based healing.
Wednesday, July 24, 2019
Microrobots show promise for treating tumors
 Researchers demonstrate a robotic platform for delivering drugs in the human body.
Researchers demonstrate a robotic platform for delivering drugs in the human body.
Nanoparticles promote functional healing following spinal cord injury
 Paralyzing damage in spinal cord injury is often caused by the zealous immune response to the injury. Scientists have developed nanoparticles that lure immune cells away from the spinal cord, allowing regeneration that restored spinal cord function in mice.
Paralyzing damage in spinal cord injury is often caused by the zealous immune response to the injury. Scientists have developed nanoparticles that lure immune cells away from the spinal cord, allowing regeneration that restored spinal cord function in mice.
A novel method to fine-tune the properties of carbon nanotubes
 Scientists have developed a novel method to fine-tune the optoelectrical properties of single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNT) by applying an aerosolized dopant solution on their surface, thus opening up new avenues for SWCNT application in optoelectronics.
Scientists have developed a novel method to fine-tune the optoelectrical properties of single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNT) by applying an aerosolized dopant solution on their surface, thus opening up new avenues for SWCNT application in optoelectronics.
Developing technologies that run on light
 Researchers are designing a nanoscale photon diode - a necessary component that could bring us closer to faster, more energy-efficient computers and communications that replace electricity with light.
Researchers are designing a nanoscale photon diode - a necessary component that could bring us closer to faster, more energy-efficient computers and communications that replace electricity with light.
Tiny changes, big impact
 As the use of nanoparticles in products grows ever more common, scientists are exploring ways to keep them from harming our freshwater ecosystems.
As the use of nanoparticles in products grows ever more common, scientists are exploring ways to keep them from harming our freshwater ecosystems.
Does one size does fit all? A new model for organic semiconductors
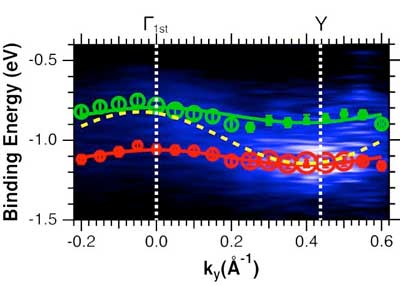 Researchers report new observations for organic single crystals that derive from their flexibility, opening the door for new organic electronics.
Researchers report new observations for organic single crystals that derive from their flexibility, opening the door for new organic electronics.
Valleytronics core theory for future high-efficiency semiconductor technology
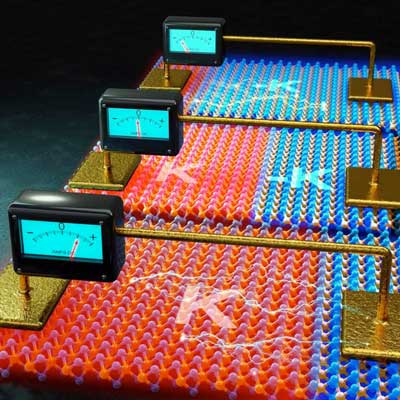 Scientists discovered a theory that can expand the development of valleytronics technology, which has been drawing attention as a next generation semiconductor technology. This is expected to advance the development of valleytronics technology one level further, a new magnetic technology of next generation that surpasses the existing data processing speed.
Scientists discovered a theory that can expand the development of valleytronics technology, which has been drawing attention as a next generation semiconductor technology. This is expected to advance the development of valleytronics technology one level further, a new magnetic technology of next generation that surpasses the existing data processing speed.
Using 2D materials to make ultrathin transistors for faster computer chips
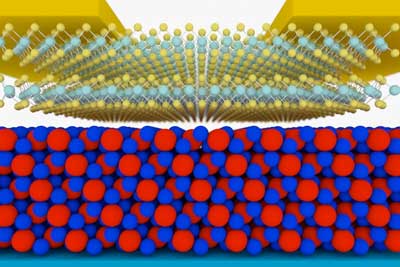 An important breakthrough in transistor technology has been achieved: With the help of novel insulators, high-quality transistors can be produced using two-dimensional materials.
An important breakthrough in transistor technology has been achieved: With the help of novel insulators, high-quality transistors can be produced using two-dimensional materials.
Artificial graphene throat could someday help mute people 'speak'
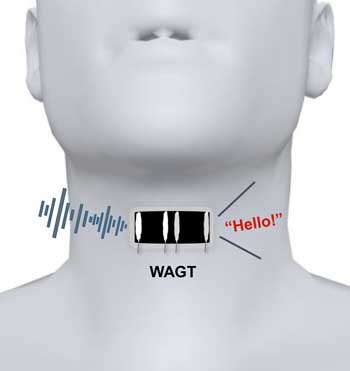 Researchers have developed a wearable artificial throat that, when attached to the neck like a temporary tattoo, can transform throat movements into sounds.
Researchers have developed a wearable artificial throat that, when attached to the neck like a temporary tattoo, can transform throat movements into sounds.
Tuesday, July 23, 2019
New nanocomposite material for wearable devices able to restore conductivity
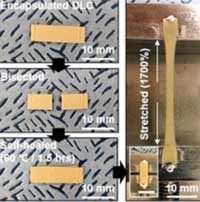 New material for wearable devices can self-heal and recover its original electrical conductivity even after being significantly stretched or completely cut.
New material for wearable devices can self-heal and recover its original electrical conductivity even after being significantly stretched or completely cut.
Unconventional phenomena triggered by acoustic waves in 2D materials
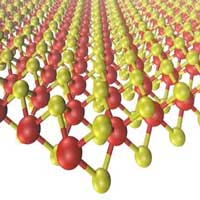 Researchers report a novel phenomenon, called Valley Acoustoelectric Effect, which takes place in 2D materials, similar to graphene.
Researchers report a novel phenomenon, called Valley Acoustoelectric Effect, which takes place in 2D materials, similar to graphene.
Self-organizing molecules: Nanorings with two sides
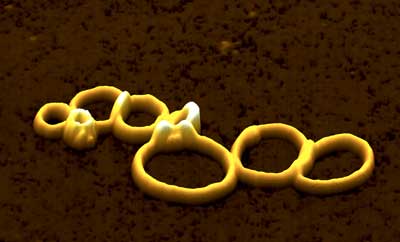 Scientists succeeded in producing Janus nanorings with two different sides for the first time.
Scientists succeeded in producing Janus nanorings with two different sides for the first time.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
