 A team of physicists and chemists have jointly succeeded in developing a so-called nano-tomographic technique which is able to detect the typically invisible properties of nanostructured fields in the focus of a lens. Such a method may help to establish nano-structured light landscapes as a tool for material machining, optical tweezers, or high-resolution imaging.
A team of physicists and chemists have jointly succeeded in developing a so-called nano-tomographic technique which is able to detect the typically invisible properties of nanostructured fields in the focus of a lens. Such a method may help to establish nano-structured light landscapes as a tool for material machining, optical tweezers, or high-resolution imaging.
Friday, September 20, 2019
New method for the measurement of nano-structured light fields
 A team of physicists and chemists have jointly succeeded in developing a so-called nano-tomographic technique which is able to detect the typically invisible properties of nanostructured fields in the focus of a lens. Such a method may help to establish nano-structured light landscapes as a tool for material machining, optical tweezers, or high-resolution imaging.
A team of physicists and chemists have jointly succeeded in developing a so-called nano-tomographic technique which is able to detect the typically invisible properties of nanostructured fields in the focus of a lens. Such a method may help to establish nano-structured light landscapes as a tool for material machining, optical tweezers, or high-resolution imaging.
The best of two worlds: Magnetism and Weyl semimetals
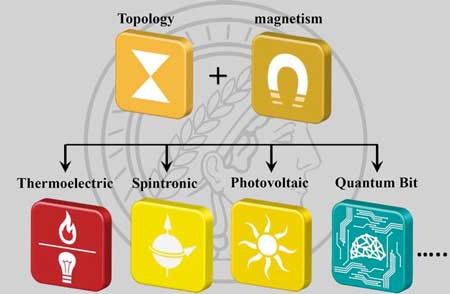 Imagine a world in which electricity could flow through the grid without any losses or where all the data in the world could be stored in the cloud without the need for power stations. This seems unimaginable but a path towards such a dream has opened with the discovery of a new family of materials with magical properties.
Imagine a world in which electricity could flow through the grid without any losses or where all the data in the world could be stored in the cloud without the need for power stations. This seems unimaginable but a path towards such a dream has opened with the discovery of a new family of materials with magical properties.
Highly sensitive sensors to measure the heart and brain activity
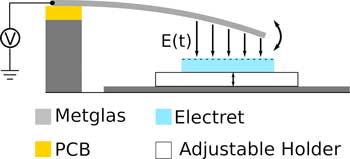 Research team develops energy-efficient sensors for extremely low frequencies.
Research team develops energy-efficient sensors for extremely low frequencies.
Researchers find way to study proteins moving (relatively) slowly
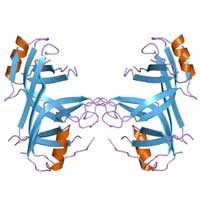 Biophysical chemists found a way to measure the ways proteins move at slower speeds - hundreds of nanoseconds to microseconds. The discovery, a fundamental breakthrough, could open a new line of research for scientists trying to understand how proteins behave in the body.
Biophysical chemists found a way to measure the ways proteins move at slower speeds - hundreds of nanoseconds to microseconds. The discovery, a fundamental breakthrough, could open a new line of research for scientists trying to understand how proteins behave in the body.
Clarification of a new synthesis mechanism of semiconductor atomic sheet
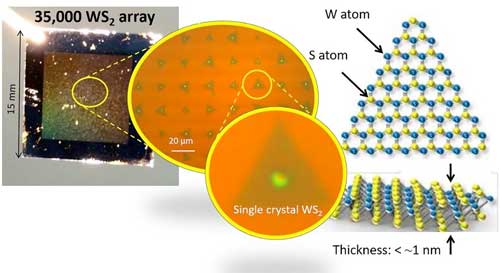 Researchers succeeded in clarifying a new synthesis mechanism regarding transition metal dichalcogenides (TMD), which are semiconductor atomic sheets having thickness in atomic order. Because it is difficult to directly observe the aspect of the growing process of TMD in a special environment, the initial growth process remained unclear.
Researchers succeeded in clarifying a new synthesis mechanism regarding transition metal dichalcogenides (TMD), which are semiconductor atomic sheets having thickness in atomic order. Because it is difficult to directly observe the aspect of the growing process of TMD in a special environment, the initial growth process remained unclear.
Nanogenerator-powered bandages could help reverse baldness
 Reversing baldness could someday be as easy as wearing a hat, thanks to a noninvasive, low-cost hair-growth-stimulating technology developed by engineers.
Reversing baldness could someday be as easy as wearing a hat, thanks to a noninvasive, low-cost hair-growth-stimulating technology developed by engineers.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
