Thursday, February 1, 2018
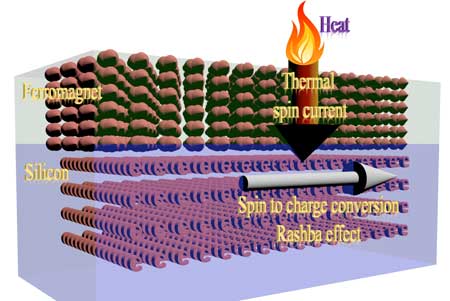
Engineers report advances in spintronic devices that will help lead to a new technology for computing and data storage
Discoveries will help realize the promise of faster, energy-efficient spintronic computers and ultra-high-capacity data storage.
Researchers observe electrons zipping around in crystals
Scientists have tracked electrons moving through exotic materials that may make up the next generation of computing hardware.

Future of semiconductor lasing: Topological insulator lasers
Applying topological physics to lasing creates more highly efficient and robust lasers.
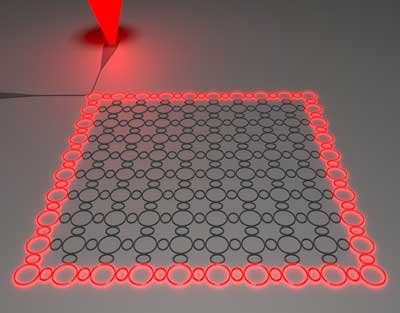
Zero gravity graphene promises success in space (w/video)
In a series of experiments, researchers experienced weightlessness testing graphene?s application in space.
A biological approach to precision medicine targets endless number of diseases
Self-assembling platform effectively delivers inhibitory RNA molecules to targeted cell populations.
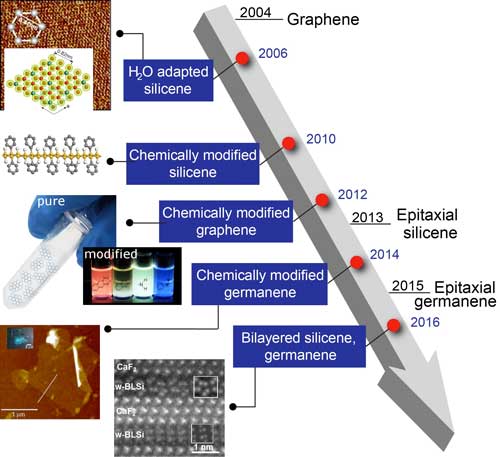
Moving beyond graphene
Developing 2D materials similar to graphene remains a challenge, but chemists are making progress - moving closer to smaller and faster electronics and photonics.
Friction found where there should be none: In superfluids near absolute zero
Physicists have discovered unexpected friction while rotating superfluid helium.

New, safe zinc oxide quantum dots
Chemists have shown that ZnO nanoparticles produced by a new self-supporting organometallic method are safe for human cells. Now it's only one step towards innovative applications.

Splashdown: Supersonic cold metal bonding in 3-D
A highly versatile deposition process already used to manufacture aircraft parts and other expensive, delicate surfaces is now 3-D modeled to show the effects of temperature for the first time.
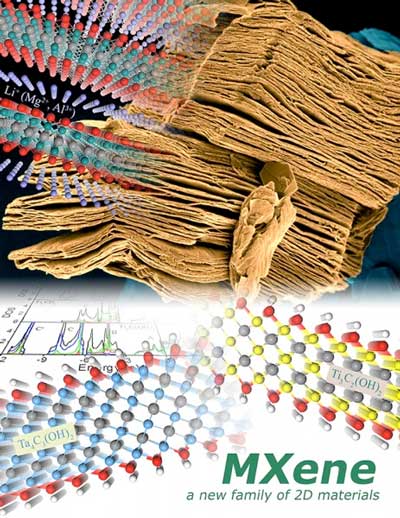
New MXene materials could capture wasted frictional energy from smartphones
New research describes how a new family of two-dimensional transition metal carbides, known as MXenes, could be used to harvest wasted frictional energy, for example, from muscle contractions during typing or walking.
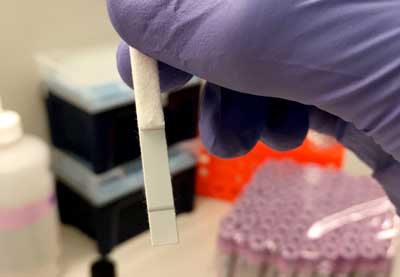
Quick HIV detection method could diagnose early disease
Scientists have develped a test capable of detecting HIV early using more efficient, robust methods.
Engineering research gives optical switches the 'contrast' of electronic transistors
Engineers have taken an important step toward the creation of a working optical transistor: precisely controlling the mixing of optical signals via tailored electric fields, and obtaining outputs with a near perfect contrast and extremely large on/off ratios.
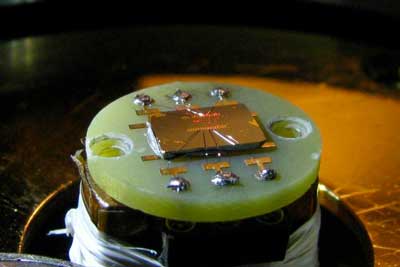
Nanofoam catalysts efficiently generates hydrogen from water
Researchers have found a way to more efficiently generate hydrogen from water - an important key to making clean energy more viable.

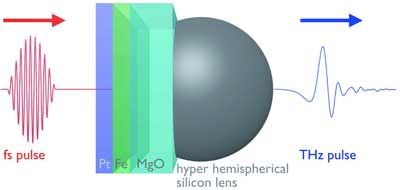
Physicists generate terahertz waves with spin current flow
Physicists use a quantum magnetic current flow, so-called spin current, in magnetic metal nanostructures. The cost-effective and material-saving technology has the potential for industry applications.
Engineers develop flexible lithium battery for wearable electronics
Shaped like a spine, new design enables remarkable flexibility, high energy density, and stable voltage, no matter how it is flexed or twisted.

New magnet-based drug delivery system shows promise for cancer treatment
A team of researchers has developed a non-invasive method of delivering drugs directly to cancerous tissue using magnetic forces, a form of treatment that could significantly reduce the toxic side effects of chemotherapy.

Self-sssembled 'hairy' nanoparticles could give a double punch to cancer
'Hairy nanoparticles made with light-sensitive materials that assemble themselves could one day become nano-carriers providing doctors a new way to simultaneously introduce both therapeutic drugs and cancer-fighting heat into tumors.

Macromolecular order in the plastic kingdom
Researchers have found out how the regularity of polypropylene molecules and thermal treatment affect the mechanical properties of the end product. Their new insights make it possible to synthesize a material with predetermined properties, such as elasticity or hardness.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)

