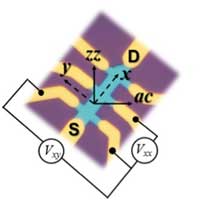
 A new study shows how impurities affect the electrical properties in anisotropic germanium arsenide (GeAs).
A new study shows how impurities affect the electrical properties in anisotropic germanium arsenide (GeAs).
Monday, April 27, 2020
New study reveals how impurities affect the electrical properties in anisotropic 2D materials
 A new study shows how impurities affect the electrical properties in anisotropic germanium arsenide (GeAs).
A new study shows how impurities affect the electrical properties in anisotropic germanium arsenide (GeAs).
Abundant element to power small devices
 A thin, iron-based generator uses waste heat to provide small amounts of power.
A thin, iron-based generator uses waste heat to provide small amounts of power.
Two steps closer to flexible, powerful, fast bioelectronic devices
 Researchers design biocompatible ion-driven soft transistors that can perform real-time neurologically relevant computation and a mixed-conducting particulate composite that allows creation of electronic components out of a single material.
Researchers design biocompatible ion-driven soft transistors that can perform real-time neurologically relevant computation and a mixed-conducting particulate composite that allows creation of electronic components out of a single material.
Electronics for high-altitude use can get smaller and sturdier with new nanomaterials
 Scientists are creating new metal-based nanomaterials for circuit boards that could be resistant to the high-altitude radiation encountered by electronics in aerospace equipment, fighter jets and weapon systems.
Scientists are creating new metal-based nanomaterials for circuit boards that could be resistant to the high-altitude radiation encountered by electronics in aerospace equipment, fighter jets and weapon systems.
New metasurface laser produces world's first super-chiral light
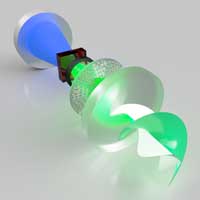 Researchers have demonstrated the world's first metasurface laser that produces 'super-chiral light': light with ultra-high angular momentum. The light from this laser can be used as a type of "optical spanner" to or for encoding information in optical communications.
Researchers have demonstrated the world's first metasurface laser that produces 'super-chiral light': light with ultra-high angular momentum. The light from this laser can be used as a type of "optical spanner" to or for encoding information in optical communications.
Scientists develop stable luminescent composite material based on perovskite nanocrystals
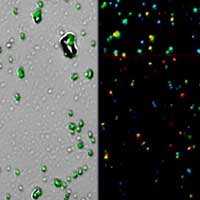 Scientists develop light-emitting composite material based on perovskite nanocrystals with air- and water resilient optical characteristics.
Scientists develop light-emitting composite material based on perovskite nanocrystals with air- and water resilient optical characteristics.
Ultra-fast vector microscopy is a breakthrough in nano-optics
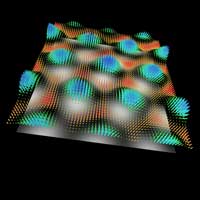 The duration of their snapshot relates to a second as this second does to the age of the universe: Physicists have developed ultra-fast vector microscopy as a means of determining electric fields on surfaces with high temporal and spatial resolution.
The duration of their snapshot relates to a second as this second does to the age of the universe: Physicists have developed ultra-fast vector microscopy as a means of determining electric fields on surfaces with high temporal and spatial resolution.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
