 Researchers developed a new class of broadband solid state light emitter in the short-wave infrared that could be miniaturized, integrated with CMOS technology and used for many applications including food inspection, health or safety.
Researchers developed a new class of broadband solid state light emitter in the short-wave infrared that could be miniaturized, integrated with CMOS technology and used for many applications including food inspection, health or safety.
Wednesday, September 30, 2020
Colloidal quantum dot light emitters go broadband in the infrared
 Researchers developed a new class of broadband solid state light emitter in the short-wave infrared that could be miniaturized, integrated with CMOS technology and used for many applications including food inspection, health or safety.
Researchers developed a new class of broadband solid state light emitter in the short-wave infrared that could be miniaturized, integrated with CMOS technology and used for many applications including food inspection, health or safety.
The most sensitive and fastest graphene microwave bolometer
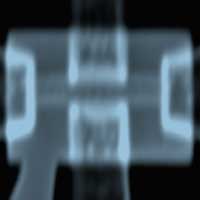 Researchers have developed a graphene-based bolometer that can detect microwave photons at extremely high sensitivities and with fast time responses.
Researchers have developed a graphene-based bolometer that can detect microwave photons at extremely high sensitivities and with fast time responses.
Zebrafish embryos help prove what happens to nanoparticles in the blood
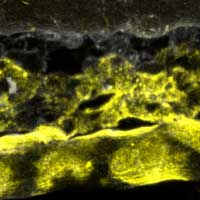 What happens to the nanoparticles when they are injected into the bloodstream, for example, to destroy solid tumours? Researchers are now ready to tackle such a challenging question using zebrafish embryos as a new study model in nanomedicine and nanotoxicology.
What happens to the nanoparticles when they are injected into the bloodstream, for example, to destroy solid tumours? Researchers are now ready to tackle such a challenging question using zebrafish embryos as a new study model in nanomedicine and nanotoxicology.
New detector breakthrough pushes boundaries of quantum computing
 New research findings show potential for graphene bolometers to become a game-changer for quantum technology.
New research findings show potential for graphene bolometers to become a game-changer for quantum technology.
A peek inside a cellular antenna
 Scientists developed a new method and discover new features of primary cilia - little understood antenna-like structures protruding from cells.
Scientists developed a new method and discover new features of primary cilia - little understood antenna-like structures protruding from cells.
Scientists synthesise a MOF capable of degrading nerve agents in water
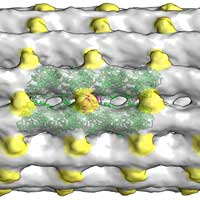
 Researchers have synthesized a new porous material that enables and guides the degradation of compounds analogous to nerve agents used in chemical warfare. This material will make it possible to capture and degrade this type of compounds that until now could not be eliminated.
Researchers have synthesized a new porous material that enables and guides the degradation of compounds analogous to nerve agents used in chemical warfare. This material will make it possible to capture and degrade this type of compounds that until now could not be eliminated.
This message will self-destruct in seven days... (w/video)
 A self-erasing chip for security and anti-counterfeit technologies.
A self-erasing chip for security and anti-counterfeit technologies.
Hot Stuff: Unusual thermal diode rectifies heat in both directions
 Dual-mode thermal rectification could be a game changer for a range of industrial and medical applications.
Dual-mode thermal rectification could be a game changer for a range of industrial and medical applications.
Graphite instead of gold: Nanolayers for better hydrogen cars
 Researchers devlop innovative coating for bipolar plates in fuel cells.
Researchers devlop innovative coating for bipolar plates in fuel cells.
Researchers use amino acids to grow high-performance copper thin films
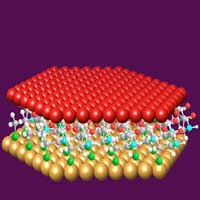 For the first time, researchers have shown that highly ordered copper thin films can be crystallized directly on a one-molecule-thick layer of organic material rather than on the inorganic substrates that have been used for years.
For the first time, researchers have shown that highly ordered copper thin films can be crystallized directly on a one-molecule-thick layer of organic material rather than on the inorganic substrates that have been used for years.
Tuesday, September 29, 2020
Nanotechnology filter coating offers promise against COVID-19
 A nanocoating designed to allow air filters to capture airborne or aerosolized droplets of the virus that causes COVID-19.
A nanocoating designed to allow air filters to capture airborne or aerosolized droplets of the virus that causes COVID-19.
Nanotechnology filter coating offers promise against COVID-19
 A nanocoating designed to allow air filters to capture airborne or aerosolized droplets of the virus that causes COVID-19.
A nanocoating designed to allow air filters to capture airborne or aerosolized droplets of the virus that causes COVID-19.
Why disordered light-harvesting systems produce ordered outcomes
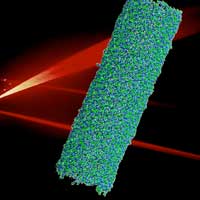 Scientists typically prefer to work with ordered systems. However, a diverse team of physicists and biophysicists found that individual light-harvesting nanotubes with disordered molecular structures still transport light energy in the same way.
Scientists typically prefer to work with ordered systems. However, a diverse team of physicists and biophysicists found that individual light-harvesting nanotubes with disordered molecular structures still transport light energy in the same way.
Researchers solve decades-old problem of how to uniformly switch memristors
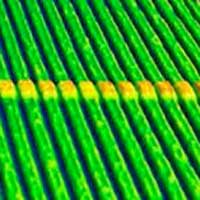 A uniform switching mechanism in memristors is something researchers have been looking in the last several decades.
A uniform switching mechanism in memristors is something researchers have been looking in the last several decades.
Researchers develop a new membraneless fuel cell
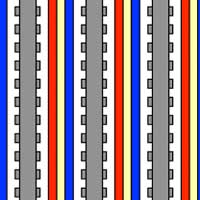 Researchers have designed a green membraneless fuel cell that uses oxygen from the air.
Researchers have designed a green membraneless fuel cell that uses oxygen from the air.
Monday, September 28, 2020
Spinal carbon nanotube implants restore motor functions
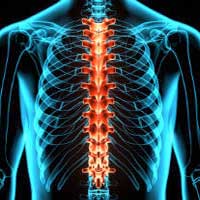 A new study shows the efficacy of carbon nanotube implants to restore motor functions and paves the way for a new therapeutic approach for spinal cord injuries.
A new study shows the efficacy of carbon nanotube implants to restore motor functions and paves the way for a new therapeutic approach for spinal cord injuries.
Cooling clothing stays flexible even when frozen
 Researchers develop cooling clothing to improve human performance when exerting energy in warm environments.
Researchers develop cooling clothing to improve human performance when exerting energy in warm environments.
Discovery of large family of two-dimensional ferroelectric metals
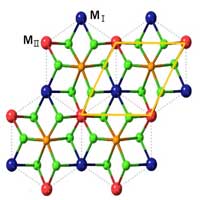 Scientists have discovered 16 novel ferroelectric metals from a large family (2,964) of 2D bimetal phosphates via data-driven machine learning and high-throughput first-principle calculations.
Scientists have discovered 16 novel ferroelectric metals from a large family (2,964) of 2D bimetal phosphates via data-driven machine learning and high-throughput first-principle calculations.
Borate-based passivation layers enable reversible calcium batteries
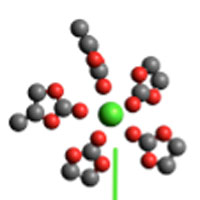 A new study has combined experimental and theoretical approaches to study the passivation layers formed on calcium metal electrodes and their influence on the reversible operation of calcium-based batteries.
A new study has combined experimental and theoretical approaches to study the passivation layers formed on calcium metal electrodes and their influence on the reversible operation of calcium-based batteries.
Avoiding environmental losses in quantum information systems
 New research has revealed how robust initial states can be prepared in quantum information systems, minimising any unwanted transitions which lead to losses in quantum information.
New research has revealed how robust initial states can be prepared in quantum information systems, minimising any unwanted transitions which lead to losses in quantum information.
New nanochannels make lithium batteries charge faster
 Researchers found out that by nanostructuring graphite, new 'paths' will be created for lithium ions. This makes the battery charge faster.
Researchers found out that by nanostructuring graphite, new 'paths' will be created for lithium ions. This makes the battery charge faster.
Speaking with neurons through nanostructured neural electrodes
 Researchers have designed improved flexible thin metal electrodes with nanotopography for a more intimate interfacing with neurons.
Researchers have designed improved flexible thin metal electrodes with nanotopography for a more intimate interfacing with neurons.
Noble metal clusters can enhance performance of catalysts and save resources
 Lower-cost production thanks to optimized distribution of atoms.
Lower-cost production thanks to optimized distribution of atoms.
Terraced graphene for ultrasensitive magnetic field sensor
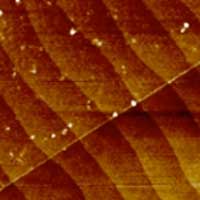 Physicists have developed a sensitive two-dimensional (2-D) magnetic field sensor, which can potentially improve the detection of nanoscale magnetic domains for data storage applications.
Physicists have developed a sensitive two-dimensional (2-D) magnetic field sensor, which can potentially improve the detection of nanoscale magnetic domains for data storage applications.
Saturday, September 26, 2020
Roadmap points out the directions for quantum materials
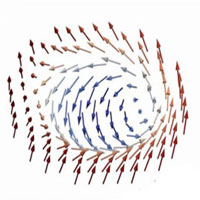 Twenty-nine leading experts of materials science, quantum information, condensed-matter physics and related areas review the diverse materials and challenges in the field. The roadmap points out the directions in which new research is necessary, combining both fundamental and applied interests, such as quantum computing.
Twenty-nine leading experts of materials science, quantum information, condensed-matter physics and related areas review the diverse materials and challenges in the field. The roadmap points out the directions in which new research is necessary, combining both fundamental and applied interests, such as quantum computing.
Friday, September 25, 2020
Researchers develop method to create colloidal diamonds
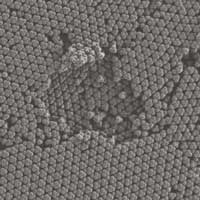 The long-awaited photonic technique could change the way optical technologies are developed and used over the next decade.
The long-awaited photonic technique could change the way optical technologies are developed and used over the next decade.
Pest control with biosynthesized silver nanoparticles
 In a new study, researchers provide evidence for the novel future application of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles based nanoformulation for pest management.
In a new study, researchers provide evidence for the novel future application of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles based nanoformulation for pest management.
Secure nano-carrier delivers medications directly to cells
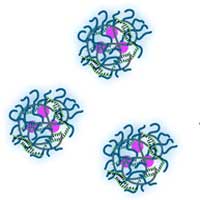 A stable nano-carrier for medications with a special mechanism that makes sure the drugs are only released in diseased cells.
A stable nano-carrier for medications with a special mechanism that makes sure the drugs are only released in diseased cells.
Thursday, September 24, 2020
Nanosecond laser-induced amplification of a photochromic reaction in a diarylethene nanoparticle
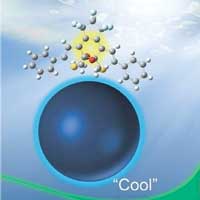 Researchers have found a drastically amplified ring-opening reaction yield in aqueous nanoparticle colloids of a photochromic diarylethene when induced by an intense nanosecond laser pulse, and clarified its amplification mechanism.
Researchers have found a drastically amplified ring-opening reaction yield in aqueous nanoparticle colloids of a photochromic diarylethene when induced by an intense nanosecond laser pulse, and clarified its amplification mechanism.
High-performance single-atom catalysts for high-temperature fuel cells
 Individual platinum atoms participate in catalytic reaction to faciitate the electrode process by up to 10 times. Single-atom platinum catalysts are stable at 700 degrees Celsius and expected to stimulate the commercialization of next-gen reversible fuel cells.
Individual platinum atoms participate in catalytic reaction to faciitate the electrode process by up to 10 times. Single-atom platinum catalysts are stable at 700 degrees Celsius and expected to stimulate the commercialization of next-gen reversible fuel cells.
Metal wires of carbon complete toolbox for carbon-based computers
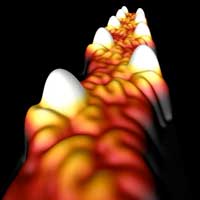 Metallic carbon circuit element enables work on faster, efficient carbon-based transistors.
Metallic carbon circuit element enables work on faster, efficient carbon-based transistors.
Bridging the gap between the magnetic and electronic properties of topological insulators
 Scientists shed light on the relationship between the magnetic properties of topological insulators and their electronic band structure. Their experimental results shed new insights into recent debates regarding the evolution of the band structure with temperature in these materials, which exhibit unusual quantum phenomena and are envisioned to be crucial in next-generation electronics, spintronics, and quantum computers.
Scientists shed light on the relationship between the magnetic properties of topological insulators and their electronic band structure. Their experimental results shed new insights into recent debates regarding the evolution of the band structure with temperature in these materials, which exhibit unusual quantum phenomena and are envisioned to be crucial in next-generation electronics, spintronics, and quantum computers.
Dynamic tattoos promise to warn wearers of health threats
 You can't walk into a doctor's office and get a dynamic tattoo yet, but they are on the way. Early proof-of-concept studies provide convincing evidence that tattoos can be engineered, not only to change color, but to sense and convey biomedical information, including the onset of cancer.
You can't walk into a doctor's office and get a dynamic tattoo yet, but they are on the way. Early proof-of-concept studies provide convincing evidence that tattoos can be engineered, not only to change color, but to sense and convey biomedical information, including the onset of cancer.
The groove of the self-organized active nematic ribbon
 Researchers report the creation of a 3D active nematic. The material passes through several spatial patterns, from collapsing into a ribbon to wrinkling in 3D.
Researchers report the creation of a 3D active nematic. The material passes through several spatial patterns, from collapsing into a ribbon to wrinkling in 3D.
Scientists take a 'spin' onto magnetoresistive RAM
 Magnetoresistive random access memory (MRAM) is the forerunning candidate for the next generation digital technology. However, manipulating MRAM efficiently and effectively has been challenging. A revolutionary breakthrough generates spin current to switch the pinned magnetic moments at will.
Magnetoresistive random access memory (MRAM) is the forerunning candidate for the next generation digital technology. However, manipulating MRAM efficiently and effectively has been challenging. A revolutionary breakthrough generates spin current to switch the pinned magnetic moments at will.
'Stretching rack' for cells
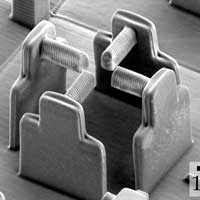 An ingenious device, only a few micrometers in size, enables to study the reaction of individual biological cells to mechanical stress.
An ingenious device, only a few micrometers in size, enables to study the reaction of individual biological cells to mechanical stress.
The return of the spin echo
 Multiple echoes as a result of a strong link between spins and microwave photons - this effect presents exciting, new opportunities for working with quantum information.
Multiple echoes as a result of a strong link between spins and microwave photons - this effect presents exciting, new opportunities for working with quantum information.
White graphene: high defect tolerance and elasticity unveiled by nanomechanics experts
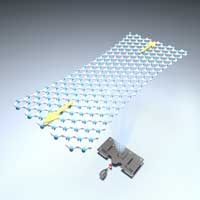 After revealing the realistic strength and stretchability of graphene, researchers have carried forward the success by unveiling the high defect tolerance and elasticity of hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN), another 2D material known as 'white graphene'. This follow-up study will promote future development and applications of strain engineering, piezoelectronics and flexible electronics.
After revealing the realistic strength and stretchability of graphene, researchers have carried forward the success by unveiling the high defect tolerance and elasticity of hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN), another 2D material known as 'white graphene'. This follow-up study will promote future development and applications of strain engineering, piezoelectronics and flexible electronics.
Researchers develop smallest particle sensor in the world
 With this innovation, smartphones, smart watches or fitness wristbands can for the first time measure the quality of the ambient air in real time and sound the alarm in the event of increased fine dust values.
With this innovation, smartphones, smart watches or fitness wristbands can for the first time measure the quality of the ambient air in real time and sound the alarm in the event of increased fine dust values.
New brain cell-like nanodevices work together to identify mutations in viruses
 These systems could potentially overcome computational hurdles faced by current digital technologies.
These systems could potentially overcome computational hurdles faced by current digital technologies.
Wednesday, September 23, 2020
Magnetic 'T-Budbots' made from tea plants kill and clean biofilms (w/video)
 Researchers have made magnetically propelled microbots derived from tea buds, which they call 'T-Budbots', that can dislodge biofilms, release an antibiotic to kill bacteria, and clean away the debris.
Researchers have made magnetically propelled microbots derived from tea buds, which they call 'T-Budbots', that can dislodge biofilms, release an antibiotic to kill bacteria, and clean away the debris.
Nanoscale vortices with a unique property
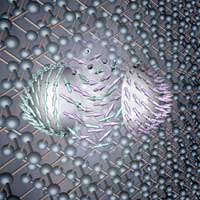 For the first time, researchers have managed to create and identify antiferromagnetic skyrmions with a unique property: critical elements inside them are arranged in opposing directions. Scientists have succeeded in visualising this phenomenon using neutron scattering.
For the first time, researchers have managed to create and identify antiferromagnetic skyrmions with a unique property: critical elements inside them are arranged in opposing directions. Scientists have succeeded in visualising this phenomenon using neutron scattering.
A multishot lensless camera in development could aid disease diagnosis
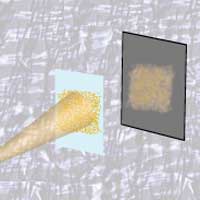 Researchers are developing a new type of imaging that does not require a lens and uses reconfigurable particle-based masks to take multiple shots of an object.
Researchers are developing a new type of imaging that does not require a lens and uses reconfigurable particle-based masks to take multiple shots of an object.
The world's smallest 'refrigerator' can only be seen through an electron microscope
 Researchers have succeeded in creating thermoelectric coolers that are only 100 nanometers thick and have developed an innovative new technique for measuring their cooling performance.
Researchers have succeeded in creating thermoelectric coolers that are only 100 nanometers thick and have developed an innovative new technique for measuring their cooling performance.
New materials: A toggle switch for catalysis
 Researchers showed that a special material made of lanthanum, strontium, iron and oxygen can be switched back and forth between two different states: In one state the material is catalytically extremely active, in the other less so. The reason for this is the behavior of iron nanoparticles on the surface.
Researchers showed that a special material made of lanthanum, strontium, iron and oxygen can be switched back and forth between two different states: In one state the material is catalytically extremely active, in the other less so. The reason for this is the behavior of iron nanoparticles on the surface.
Ambient vibration energy harvester with automatic resonance tuning mechanism
 Energy harvesting technology with automatic resonance tuning mechanism. Possible application for an stand-alone power source for IoT or small electronics.
Energy harvesting technology with automatic resonance tuning mechanism. Possible application for an stand-alone power source for IoT or small electronics.
Scientists turn nanoparticle into Trojan horse to kill cancer cells without using drugs
 Cancer cells are killed in lab experiments and tumour growth reduced in mice, using a new approach that turns a nanoparticle into a 'Trojan horse' that causes cancer cells to self-destruct.
Cancer cells are killed in lab experiments and tumour growth reduced in mice, using a new approach that turns a nanoparticle into a 'Trojan horse' that causes cancer cells to self-destruct.
Tuesday, September 22, 2020
Controlling ultrastrong light-matter coupling at room temperature
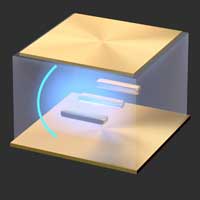 Physicists have managed to achieve ultrastrong coupling between light and matter at room temperature. The discovery is of importance for fundamental research and might pave the way for advances within, for example, light sources, nanomachinery, and quantum technology.
Physicists have managed to achieve ultrastrong coupling between light and matter at room temperature. The discovery is of importance for fundamental research and might pave the way for advances within, for example, light sources, nanomachinery, and quantum technology.
Scientists get soft on 3D nanoprinting
 New method could jump-start creation of tiny medical devices for the body.
New method could jump-start creation of tiny medical devices for the body.
Physicists develop printable organic transistors
 Scientists have come a step closer to the vision of a broad application of flexible, printable electronics. They succeeded for the first time in developing powerful vertical organic transistors with two independent control electrodes.
Scientists have come a step closer to the vision of a broad application of flexible, printable electronics. They succeeded for the first time in developing powerful vertical organic transistors with two independent control electrodes.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
