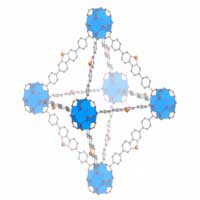
 New nanoscale metal-organic framework design leverages radiation treatment and the adaptive immune response to deliver multipronged cancer therapy.
New nanoscale metal-organic framework design leverages radiation treatment and the adaptive immune response to deliver multipronged cancer therapy.
Friday, October 2, 2020
New nanotechology design provides hope for personalized vaccination for treating cancer
 New nanoscale metal-organic framework design leverages radiation treatment and the adaptive immune response to deliver multipronged cancer therapy.
New nanoscale metal-organic framework design leverages radiation treatment and the adaptive immune response to deliver multipronged cancer therapy.
3D-printed 'invisible' fibres can sense breath, sound, and biological cells
 From capturing your breath to guiding biological cell movements, 3D printing of tiny, transparent conducting fibres could be used to make devices which can 'smell, hear and touch' - making it particularly useful for health monitoring, Internet of Things and biosensing applications.
From capturing your breath to guiding biological cell movements, 3D printing of tiny, transparent conducting fibres could be used to make devices which can 'smell, hear and touch' - making it particularly useful for health monitoring, Internet of Things and biosensing applications.
Research shows cell perturbation system could have medical applications
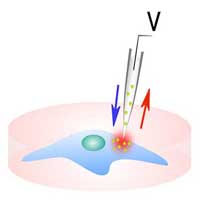 Nanofountain Probe Electroporation system may lead to quicker and more customized treatment plans.
Nanofountain Probe Electroporation system may lead to quicker and more customized treatment plans.
Physicists build circuit that generates clean, limitless power from graphene
 Researchers harnessed the atomic motion of graphene to generate an electrical current that could lead to a chip to replace batteries.
Researchers harnessed the atomic motion of graphene to generate an electrical current that could lead to a chip to replace batteries.
Visualizing defects in crystal solids revolutionized by Artificial Intelligence
 A new study challenges the ways in which defects in crystal structures are described, proposing a novel approach to characterizing and modeling crystal defects at the atomic scale based on machine learning techniques.
A new study challenges the ways in which defects in crystal structures are described, proposing a novel approach to characterizing and modeling crystal defects at the atomic scale based on machine learning techniques.
Silicon flexes its muscles: How nature is inspiring completely new material concepts for the technology of tomorrow
 Researchers have given silicon muscle power. This new property enables the material to convert electrical signals into mechanical movements for the first time. The new hybrid material thus offers completely new perspectives for the chip-based technologies of tomorrow.
Researchers have given silicon muscle power. This new property enables the material to convert electrical signals into mechanical movements for the first time. The new hybrid material thus offers completely new perspectives for the chip-based technologies of tomorrow.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
