Wednesday, March 14, 2018
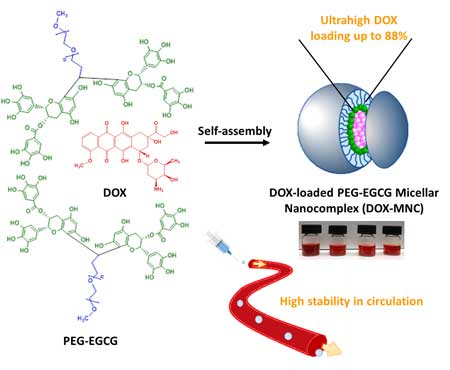
Green tea-based drug nanocarriers improve cancer treatment
Scientists have reported superior results using new green tea-based nanocarriers to kill liver cancer cells, compared to existing drug delivery systems.
The element of surprise
In a new study, chemists have explored protactinium's multiple resemblances to more completely understand the relationship between the transition metals and the complex chemistry of the early actinide elements.

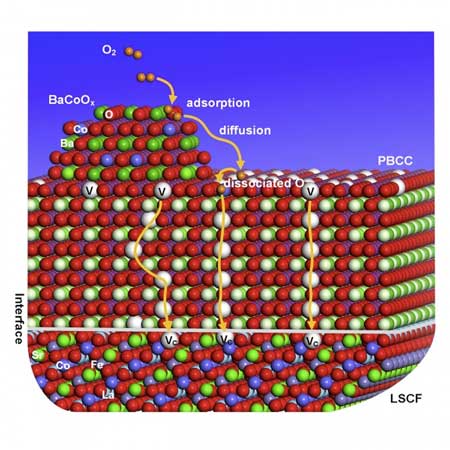
Turbocharging fuel cells with a multifunctional nanotechnology catalyst
The new catalyst, a nanotechnology material developed by engineers, markedly speeds up oxygen processing and is the subject of a new study.
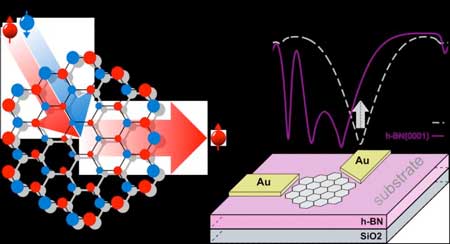
Chemists use abundant, low-cost and non-toxic elements to synthesize semiconductors
Scientists have focused on sodium-based alternatives and started an 18-month search for a new kind of semiconductor.

Researchers demonstrate existence of new form of electronic matter
Researchers have produced a 'human scale' demonstration of a new phase of matter called quadrupole topological insulators that was recently predicted using theoretical physics. These are the first experimental findings to validate this theory.
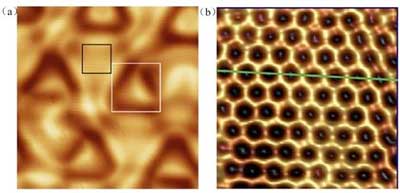
Boron can form a purely honeycomb, graphene-like 2-D structure
Researchers report the successful preparation of a purely honeycomb, graphene-like borophene, by using an Al(111) surface as the substrate and molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) growth in ultrahigh vacuum.
Graphene flakes for future transistors
These nanostructures could open new prospects for the development of innovative devices thanks to quantum effects and unique magnetic properties.
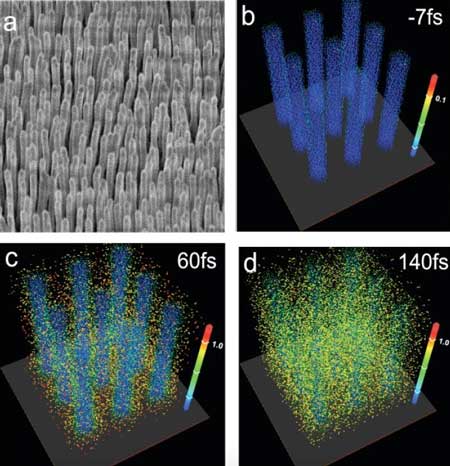
Laser-heated nanowires produce micro-scale nuclear fusion
Using a compact but powerful laser to heat arrays of ordered nanowires, scientists have demonstrated micro-scale nuclear fusion in the lab.
Nanostructures could make gene therapies safer, faster and more affordable
Scientists have developed a new method that utilizes microscopic splinter-like structures for the targeted delivery of biomolecules such as genes straight to patient cells. These magnetically guided nanostructures could enable gene therapies that are safer, faster and more cost-effective.
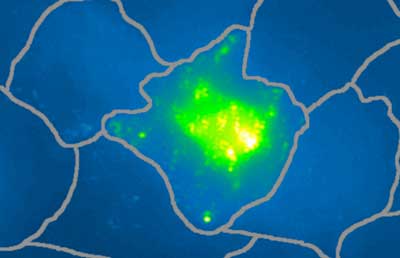
Hybrid nanoprobe can detect live cancer cells
Using nano-probes to amplify biochemical signals could lead to targeted, noninvasive treatment of cancer.
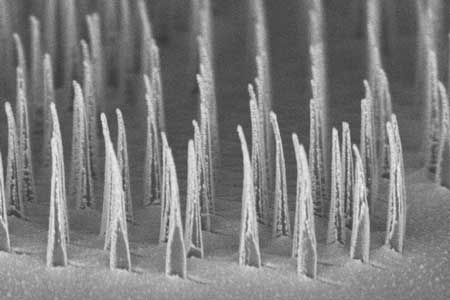
Nanospears deliver genetic material to cells with pinpoint accuracy
In a step toward accelerating the production of new gene therapies, scientists report that they have developed remote-controlled, needle-like nanospears capable of piercing membrane walls and delivering DNA into selected cells.
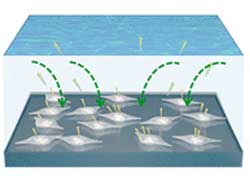
Removing heavy metals from water with MOFs
Their unprecedented internal surface areas and easy chemical tunability allow MOFs to 'pull' water vapor and other gases from air. These same features make them promising materials also for selectively removing heavy metals from water.

Graphene-based water filter removes more than 99% of natural organic matter
A world-first graphene-based filter that can remove more than 99% of the natural organic matter in treated drinking water is being scaled up for possible use in conventional plants.
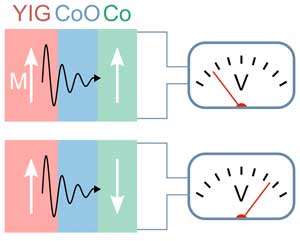
Construction set of magnon logic extended: Magnon spin currents controlled via spin valve structure
Magnon spintronics employs magnons instead of electrical charges for information processing.
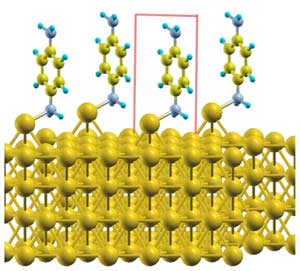
Energy level alignment for molecular electronics
Physicists have found that complex electron-electron interactions change the energy levels at molecule-metal interfaces, affecting the performance of molecular electronic devices.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
