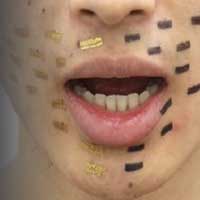
 Researchers demonstrate a novel type of sensor which is applied directly to the skin to capture certain biometric information.
Researchers demonstrate a novel type of sensor which is applied directly to the skin to capture certain biometric information.
Tuesday, September 8, 2020
Soft durable skin sensors can take the strain
 Researchers demonstrate a novel type of sensor which is applied directly to the skin to capture certain biometric information.
Researchers demonstrate a novel type of sensor which is applied directly to the skin to capture certain biometric information.
Scientists develop low-cost chip for detecting presence and quantity of COVID-19 antibodies
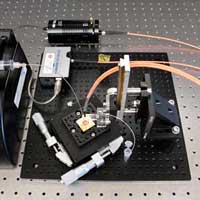 The device uses portable lab-on-a-chip technology to accurately measure the concentration of antibodies present in diluted blood plasma.
The device uses portable lab-on-a-chip technology to accurately measure the concentration of antibodies present in diluted blood plasma.
An environmentally friendly way to transform silicon into nanoparticles
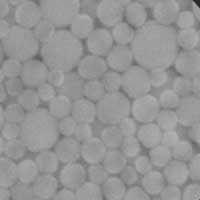 Scientists have developed a new method of silicon recycling. Converting silicon into silicon oxide nanoparticles answers to silicon waste recycling issues and providing a new source of nanoparticles for various uses in science and industry.
Scientists have developed a new method of silicon recycling. Converting silicon into silicon oxide nanoparticles answers to silicon waste recycling issues and providing a new source of nanoparticles for various uses in science and industry.
Boundaries no barrier for thermoelectricity
 Researchers find potentially useful electrical phenomenon in gold nanowires.
Researchers find potentially useful electrical phenomenon in gold nanowires.
Extracting order from a quantum measurement finally shown experimentally
 For more than a hundred years, physicists have been aware of the link between the concepts of disorder in a system, and information obtained by measurement. However, a clean experimental assessment of this link in common monitored systems, that is systems which are continuously measured over time, was missing so far.
For more than a hundred years, physicists have been aware of the link between the concepts of disorder in a system, and information obtained by measurement. However, a clean experimental assessment of this link in common monitored systems, that is systems which are continuously measured over time, was missing so far.
Producing technicolor through brain-like electronic devices
 Researchers have successfully obtained vivid colors by using semiconductor chips - not dyes - made by mimicking the human brain structure.
Researchers have successfully obtained vivid colors by using semiconductor chips - not dyes - made by mimicking the human brain structure.
Quantum light squeezes the noise out of microscopy signals
 Researchers used quantum optics to advance state-of-the-art microscopy and illuminate a path to detecting material properties with greater sensitivity than is possible with traditional tools.
Researchers used quantum optics to advance state-of-the-art microscopy and illuminate a path to detecting material properties with greater sensitivity than is possible with traditional tools.
Physicists achieve tunable spin wave excitation
 Scientists excite magnons in nanostructures with laser pulses.
Scientists excite magnons in nanostructures with laser pulses.
Coronavirus nanoscience: the tiny technologies tackling a global pandemic
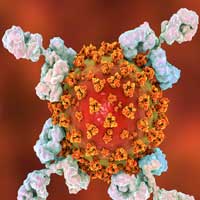 Nanotechnology has an impressive record against viruses and has been used since the late 1880s to separate and identify them. More recently, nanomedicine has been used to develop treatments for flu, Zika and HIV. And now it's joining the fight against the COVID-19 virus, SARS-CoV-2.
Nanotechnology has an impressive record against viruses and has been used since the late 1880s to separate and identify them. More recently, nanomedicine has been used to develop treatments for flu, Zika and HIV. And now it's joining the fight against the COVID-19 virus, SARS-CoV-2.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
