 Researchers describe how the ability of twisted bilayer graphene to conduct electrical current changes in response to mid-infrared light.
Researchers describe how the ability of twisted bilayer graphene to conduct electrical current changes in response to mid-infrared light.
Friday, July 31, 2020
Physicists find misaligned carbon sheets yield unparalleled properties
 Researchers describe how the ability of twisted bilayer graphene to conduct electrical current changes in response to mid-infrared light.
Researchers describe how the ability of twisted bilayer graphene to conduct electrical current changes in response to mid-infrared light.
Way, shape and form: Synthesis conditions define the nanostructure of manganese dioxide
 A new study sheds light on how different synthesis conditions can produce manganese dioxide with distinct porous structures, hinting at a strategy for the development of highly tuned MnO2 nanomaterials that could serve as catalysts in the fabrication of bioplastics.
A new study sheds light on how different synthesis conditions can produce manganese dioxide with distinct porous structures, hinting at a strategy for the development of highly tuned MnO2 nanomaterials that could serve as catalysts in the fabrication of bioplastics.
A new synthesis method for three-dimensional nanocarbons
 Connecting carbon by catalysis to create octagonal structures.
Connecting carbon by catalysis to create octagonal structures.
Nano-sponges of solid acid transform carbon dioxide to fuel and plastic waste to chemicals
 In this work, researchers dealt with both these problems at one stroke, by developing nano solid acids that transform carbon dioxide directly to fuel (dimethyl ether) and plastic waste to chemicals (hydrocarbons).
In this work, researchers dealt with both these problems at one stroke, by developing nano solid acids that transform carbon dioxide directly to fuel (dimethyl ether) and plastic waste to chemicals (hydrocarbons).
Unusual electron sharing found in cool crystal
 These findings suggest further studies could reveal compounds with interesting electronic properties.
These findings suggest further studies could reveal compounds with interesting electronic properties.
Efficient and durable overall CO2 photoreduction achieved by rationally designed MOFs
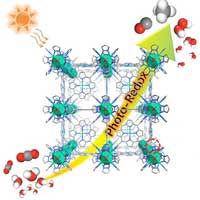 Scientists selected a MOF composed of reactive NiOx cluster nodes and light-harvesting metalloporphyrin ligands connected via pyrazolyl groups as a sole photocatalyst and achieved efficient and durable gas-phase overall CO2 photoreduction with H2O vapor.
Scientists selected a MOF composed of reactive NiOx cluster nodes and light-harvesting metalloporphyrin ligands connected via pyrazolyl groups as a sole photocatalyst and achieved efficient and durable gas-phase overall CO2 photoreduction with H2O vapor.
Nanoreactor strategy generates superior supported bimetallic catalysts
 To improve the performance and efficiency of the supported bimetallic nanoparticles, researchers recently proposed a nanoreactor strategy for their scalable synthesis.
To improve the performance and efficiency of the supported bimetallic nanoparticles, researchers recently proposed a nanoreactor strategy for their scalable synthesis.
Thursday, July 30, 2020
Researchers synthesize nanoparticles tailored for special applications
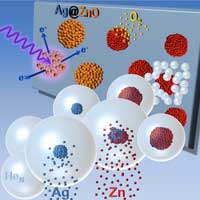 Core-shell clusters pave the way for new efficient nanomaterials that make catalysts, magnetic and laser sensors or measuring devices for detecting electromagnetic radiation more efficient.
Core-shell clusters pave the way for new efficient nanomaterials that make catalysts, magnetic and laser sensors or measuring devices for detecting electromagnetic radiation more efficient.
Machine learning model may perfect 3D nanoprinting
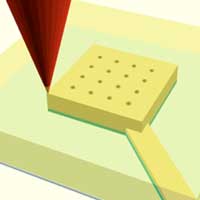 Two-photon lithography (TPL) has shown promise in research applications but has yet to achieve widespread industry acceptance due to limitations on large-scale part production and time-intensive setup. Scientists turned to machine learning to address two key barriers to industrialization of TPL.
Two-photon lithography (TPL) has shown promise in research applications but has yet to achieve widespread industry acceptance due to limitations on large-scale part production and time-intensive setup. Scientists turned to machine learning to address two key barriers to industrialization of TPL.
3D nanometer-thin membrane borrows from biology
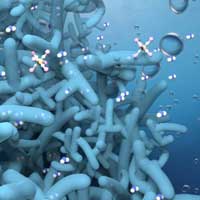 Mimicking the structure of the kidney, a team of scientists has created a three-dimensional nanometer (nm)-thin membrane that breaks the permeance-selectivity trade-off of artificial membranes.
Mimicking the structure of the kidney, a team of scientists has created a three-dimensional nanometer (nm)-thin membrane that breaks the permeance-selectivity trade-off of artificial membranes.
Incorporating ferromagnetism and superconductivity together in a single layer of molecular superlattice
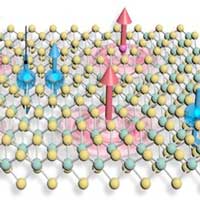 Scientists have demonstrated an interlayer-space confined chemical design method for the synthesis of single-atom doped tantalum disulfide (TaS2) molecular superlattice, where ferromagnetism was successfully introduced in the superconducting TaS2 layers.
Scientists have demonstrated an interlayer-space confined chemical design method for the synthesis of single-atom doped tantalum disulfide (TaS2) molecular superlattice, where ferromagnetism was successfully introduced in the superconducting TaS2 layers.
A crazier crazy straw for science
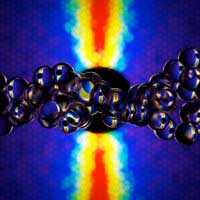 Curlicued research tool propels fast-moving fluids for study by neutrons.
Curlicued research tool propels fast-moving fluids for study by neutrons.
Researchers follow the charging and discharging of silicon electrodes live
 Scientists have now succeeded for the first time in observing the charging and discharging process directly on crystalline silicon electrodes in detail.
Scientists have now succeeded for the first time in observing the charging and discharging process directly on crystalline silicon electrodes in detail.
Researchers enhance electron spin longevity
 Researchers developed a way to extend and stabilize the lifetime of the electron's spin to more effectively carry information.
Researchers developed a way to extend and stabilize the lifetime of the electron's spin to more effectively carry information.
Wednesday, July 29, 2020
New fabrication method brings single-crystal perovskite devices closer to viability
 Nanoengineers developed a new method to fabricate perovskites as single-crystal thin films, which are more efficient for use in solar cells and optical devices than the current state-of-the-art polycrystalline forms of the material.
Nanoengineers developed a new method to fabricate perovskites as single-crystal thin films, which are more efficient for use in solar cells and optical devices than the current state-of-the-art polycrystalline forms of the material.
Tailored light inspired by nature
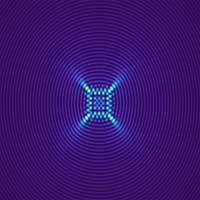 Researchers develop for the first time light fields using caustics that do not change during propagation.
Researchers develop for the first time light fields using caustics that do not change during propagation.
Electrochemical doping: researchers improve carbon nanotube transparent conductors
 Researchers have discovered that electrochemical doping with ionic liquid can significantly enhance the optical and electrical properties of transparent conductors made of single-walled carbon nanotube films.
Researchers have discovered that electrochemical doping with ionic liquid can significantly enhance the optical and electrical properties of transparent conductors made of single-walled carbon nanotube films.
Trying to listen to the signal from neurons
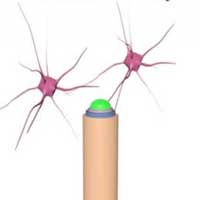 Improved quality of neural recording using a 'coaxial' microneedle-electrode.
Improved quality of neural recording using a 'coaxial' microneedle-electrode.
Gold nanosensor spots difference between dengue, Zika
 A new class of nanosensor could more accurately identify dengue and Zika infections, a task that is complicated by their genetic similarities and which can result in misdiagnosis.
A new class of nanosensor could more accurately identify dengue and Zika infections, a task that is complicated by their genetic similarities and which can result in misdiagnosis.
'Quantum negativity' can power ultra-precise measurements
 Scientists have found that a physical property called 'quantum negativity' can be used to take more precise measurements of everything from molecular distances to gravitational waves.
Scientists have found that a physical property called 'quantum negativity' can be used to take more precise measurements of everything from molecular distances to gravitational waves.
How plantains and carbon nanotubes can improve cars
 The natural plantain fibres are combined with carbon nanotubes and epoxy resin to form a natural fibre-reinforced polymer hybrid nanocomposite material.
The natural plantain fibres are combined with carbon nanotubes and epoxy resin to form a natural fibre-reinforced polymer hybrid nanocomposite material.
Using light to tune interlayer forces in van-der-Waals materials
 Scientists demonstrated for the first time that interlayer coupling in a van der Waals (vdW) material can be largely modulated by a protonic gate, which inject protons to devices from an ionic solid.
Scientists demonstrated for the first time that interlayer coupling in a van der Waals (vdW) material can be largely modulated by a protonic gate, which inject protons to devices from an ionic solid.
Tuesday, July 28, 2020
Discovery will allow more sophisticated work at nanoscale
 New method of fluid gating has implications for drug delivery, power generation and other uses.
New method of fluid gating has implications for drug delivery, power generation and other uses.
Probing the properties of magnetic quasi-particles
 Researchers have for the first time measured a fundamental property of magnets called magnon polarisation - and in the process, are making progress towards building low-energy devices.
Researchers have for the first time measured a fundamental property of magnets called magnon polarisation - and in the process, are making progress towards building low-energy devices.
Metal-breathing bacteria could transform electronics, biosensors, and more
 The ability of Shewanella oneidensis to produce molybdenum disulfide nanoparticle - a material that is able to transfer electrons easily, like graphene - is the focus of research.
The ability of Shewanella oneidensis to produce molybdenum disulfide nanoparticle - a material that is able to transfer electrons easily, like graphene - is the focus of research.
Research on metallic nanoparticles may lead to improved solar cells
 In a new study, a research group explain their outstanding success in harvesting 'hot electron holes'. The results of their work can be used to improve solar cells, photochemical reactions and photosensors.
In a new study, a research group explain their outstanding success in harvesting 'hot electron holes'. The results of their work can be used to improve solar cells, photochemical reactions and photosensors.
Solving materials problems with a quantum computer
 Scientists have developed a method paving the way to using quantum computers to simulate realistic molecules and complex materials, whose description requires hundreds of atoms.
Scientists have developed a method paving the way to using quantum computers to simulate realistic molecules and complex materials, whose description requires hundreds of atoms.
Monday, July 27, 2020
Rare glassy metal discovered during quest to improve battery performance
 Materials scientists studying recharging fundamentals made an astonishing discovery that could open the door to better batteries, faster catalysts and other materials science leaps.
Materials scientists studying recharging fundamentals made an astonishing discovery that could open the door to better batteries, faster catalysts and other materials science leaps.
Ferried across: Figuring out unconventional spin transport in quantum spin liquids
 Scientists uncover the peculiar mechanism by which spin perturbations travel through a seemingly unpassable region of a quantum spin liquid system. This new insight may represent another building block in next-generation electronics and even quantum computers.
Scientists uncover the peculiar mechanism by which spin perturbations travel through a seemingly unpassable region of a quantum spin liquid system. This new insight may represent another building block in next-generation electronics and even quantum computers.
Origami metamaterials show reversible auxeticity combined with deformation recoverability
 Findings open up possibilities for mechanical metamaterials to be used in soft robotics and medical devices.
Findings open up possibilities for mechanical metamaterials to be used in soft robotics and medical devices.
Study: Mapping crystal shapes could fast-track 2D materials
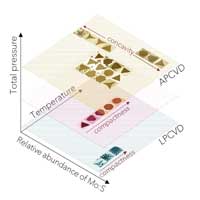 Materials scientists are calling for a collective, global effort to fast-track the mass production of 2D materials like graphene and molybdenum disulfide.
Materials scientists are calling for a collective, global effort to fast-track the mass production of 2D materials like graphene and molybdenum disulfide.
Self-healing soft material outsmarts nature
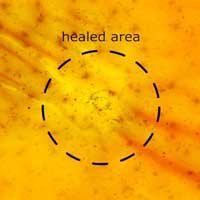 A soft material that heals itself instantaneously is now reality. A team of scientists tune the nanostructure of a new stretchable material in such a way that it now entirely recovers its structure and properties at the blink of an eye after being cut or poked.
A soft material that heals itself instantaneously is now reality. A team of scientists tune the nanostructure of a new stretchable material in such a way that it now entirely recovers its structure and properties at the blink of an eye after being cut or poked.
Small but self-imposing: Titanium alters behavior of host lattice atoms
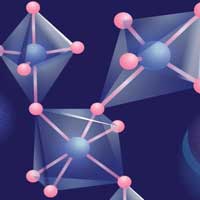 Researchers have combined optical and acoustic approaches and found that incorporating titanium atoms into barium hexaferrite leads to an unexpected substructure forming in the crystal lattice. The resulting material is promising for ultrafast computer memory applications.
Researchers have combined optical and acoustic approaches and found that incorporating titanium atoms into barium hexaferrite leads to an unexpected substructure forming in the crystal lattice. The resulting material is promising for ultrafast computer memory applications.
Novel drug delivery nanoparticles use neurotransmitters as a 'passport' into the brain
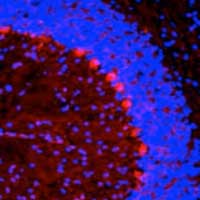 Researchers create neurotransmitter-lipid hybrids that help ferry therapeutic drugs and gene editing proteins across the blood-brain barrier in mice.
Researchers create neurotransmitter-lipid hybrids that help ferry therapeutic drugs and gene editing proteins across the blood-brain barrier in mice.
Scientists publish seminal study into impact of nanoparticles on living species
 The study assessed how the guts of species could protect against the bioaccumulation and toxicological effects of engineered nanomaterials.
The study assessed how the guts of species could protect against the bioaccumulation and toxicological effects of engineered nanomaterials.
Taking the guesswork out of twistronics
 New model explores the design space of twisted 2D materials.
New model explores the design space of twisted 2D materials.
Water molecules are gold for nanocatalysis
 Water molecules play an active role in facilitating the oxygen dissociation needed for the oxidation reaction.
Water molecules play an active role in facilitating the oxygen dissociation needed for the oxidation reaction.
Novel technique moves microparticles using electric fields
 Theoretical studies have suggested that 'particle density', or the number of particles in an area, can be utilized to develop a novel ratchet transportation with a 'static' electrical field.
Theoretical studies have suggested that 'particle density', or the number of particles in an area, can be utilized to develop a novel ratchet transportation with a 'static' electrical field.
Heat smarter, not harder - how microwaves make catalytic reactions more efficient
 Scientists demonstrate a synchrotron X-ray spectroscopy-based method by which the local temperatures of metal nanoparticles can be measured under microwaves.
Scientists demonstrate a synchrotron X-ray spectroscopy-based method by which the local temperatures of metal nanoparticles can be measured under microwaves.
Magnetic nanoparticles change their magnetic structure in a magnetic field
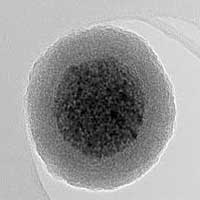 When ultrafine magnetic particles are exposed to an external magnetic field, their magnetic core grows in a previously unexpected way.
When ultrafine magnetic particles are exposed to an external magnetic field, their magnetic core grows in a previously unexpected way.
Trapping tiny particles: A versatile tool for nanomanipulation
 Researchers overcame the natural restrictions by developing optical tweezers based on metamaterials - a synthetic material with specific properties that do not occur naturally. This was the first time that this kind of metamaterial had been used for single nanoparticle trapping.
Researchers overcame the natural restrictions by developing optical tweezers based on metamaterials - a synthetic material with specific properties that do not occur naturally. This was the first time that this kind of metamaterial had been used for single nanoparticle trapping.
Friday, July 24, 2020
Manipulating non-magnetic atoms in a chromium halide enables tuning of magnetic properties
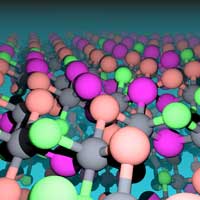 New approach creates synthetic layered magnets with unprecedented level of control over their magnetic properties.
New approach creates synthetic layered magnets with unprecedented level of control over their magnetic properties.
Discovery of disordered nanolayers in intermetallic alloys
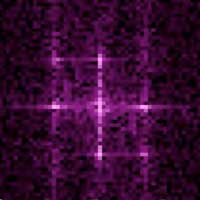 Resolving alloys' strength-ductility trade-off and thermal instability.
Resolving alloys' strength-ductility trade-off and thermal instability.
A nanotechnology-based system that can transport methane at lower pressure and cost
 Researchers have created an optimal, low-cost methane storage system. In the pores of this MOF material (highly porous metal-organic framework) it is possible to create the conditions required to replicate gas structures under the sea.
Researchers have created an optimal, low-cost methane storage system. In the pores of this MOF material (highly porous metal-organic framework) it is possible to create the conditions required to replicate gas structures under the sea.
Mucus-penetrating nanocarriers for efficient therapy of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
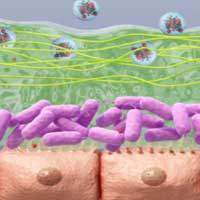 The researchers combined PEGylated chitosan nanoparticles and biodegradable black phosphorus quantum dots to deliver amikacin for efficient therapy of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
The researchers combined PEGylated chitosan nanoparticles and biodegradable black phosphorus quantum dots to deliver amikacin for efficient therapy of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Thursday, July 23, 2020
Getting a grip on near-field light
 Scientists have developed a system to mold near-field light - opening the door to unprecedented control over this powerful, largely unexplored type of light.
Scientists have developed a system to mold near-field light - opening the door to unprecedented control over this powerful, largely unexplored type of light.
Combatting COVID-19 at the nano level
 Copper, a metal commonly used throughout history for its antibacterial properties, is being utilized by researchers to solve a problem very relevant today: making reusable face masks safer and more comfortable for daily use.
Copper, a metal commonly used throughout history for its antibacterial properties, is being utilized by researchers to solve a problem very relevant today: making reusable face masks safer and more comfortable for daily use.
Nature provides inspiration for researchers developing selective membranes
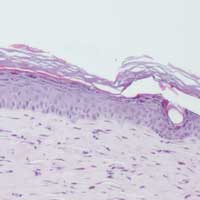 Current synthetic membranes are effectively microscopic sieves, but researchers hope that in the future they will be able to choose which molecules to let through.
Current synthetic membranes are effectively microscopic sieves, but researchers hope that in the future they will be able to choose which molecules to let through.
Electrons obey social distancing in 'strange' metals
 Scientists used state-of-the-art computational tools to model the chaotic behavior of Planckian, or 'strange', metals. This behavior has long intrigued physicists, but they have not been able to simulate it down to the lowest possible temperature until now.
Scientists used state-of-the-art computational tools to model the chaotic behavior of Planckian, or 'strange', metals. This behavior has long intrigued physicists, but they have not been able to simulate it down to the lowest possible temperature until now.
Scientists discover a topological magnet that exhibits exotic quantum effects
 Researchers uncovered a new class of magnet that exhibits novel quantum effects that extend to room temperature.
Researchers uncovered a new class of magnet that exhibits novel quantum effects that extend to room temperature.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
