 Researchers have used ultra-fast extreme ultraviolet lasers to measure the properties of materials more than 100 times thinner than a human red blood cell.
Researchers have used ultra-fast extreme ultraviolet lasers to measure the properties of materials more than 100 times thinner than a human red blood cell.
Wednesday, July 15, 2020
Ultra-fast extreme ultraviolet lasers open window into the nanoworld
 Researchers have used ultra-fast extreme ultraviolet lasers to measure the properties of materials more than 100 times thinner than a human red blood cell.
Researchers have used ultra-fast extreme ultraviolet lasers to measure the properties of materials more than 100 times thinner than a human red blood cell.
New technology prolongs blood circulation for virtually any nanomedicine, boosting therapeutic efficiency
 Scientists have developed a breakthrough technology to resolve a key problem that has prevented the introduction of novel drugs into clinical practice for decades.
Scientists have developed a breakthrough technology to resolve a key problem that has prevented the introduction of novel drugs into clinical practice for decades.
Higher-order topology found in 2D crystal
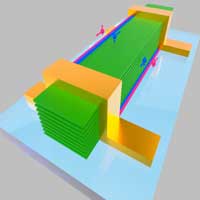 The research team took a new approach by using the Josephson junctions to spatially resolve the supercurrent flow and to show that WTe2 does indeed appear to have hinge states and be a higher-order topological insulator.
The research team took a new approach by using the Josephson junctions to spatially resolve the supercurrent flow and to show that WTe2 does indeed appear to have hinge states and be a higher-order topological insulator.
The smallest micro-gripper, grown on optical fibers, is operated remotely with light
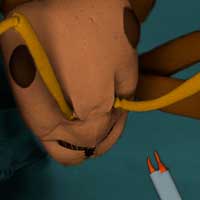 The 200-micrometer gripers are controlled remotely, without electric wiring or pneumatic tubing, with green light delivered through the fibers - absorbed light energy is directly converted into the gripper jaws' action.
The 200-micrometer gripers are controlled remotely, without electric wiring or pneumatic tubing, with green light delivered through the fibers - absorbed light energy is directly converted into the gripper jaws' action.
Using magnetic worms to engineer nanoscale communication systems
 Researchers have shown that electromagnetic waves coupled to precisely engineered structures known as artificial ferromagnetic quasicrystals allow for more efficient information transmission and processing at the nanoscale. Their research also represents the first practical demonstration of Conway worms, a theoretical concept for the description of quasicrystals.
Researchers have shown that electromagnetic waves coupled to precisely engineered structures known as artificial ferromagnetic quasicrystals allow for more efficient information transmission and processing at the nanoscale. Their research also represents the first practical demonstration of Conway worms, a theoretical concept for the description of quasicrystals.
Scientists identify new 2D material with potential for brain-like computing
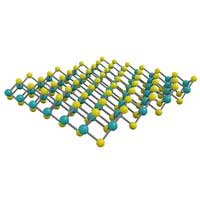 The work demonstrates the effectiveness of a design strategy that functionalizes a 2D material with an organic molecule.
The work demonstrates the effectiveness of a design strategy that functionalizes a 2D material with an organic molecule.
The force necessary to kill a single bacterium
 Scientists quantify the forces that cause critical damage on a single bacterium E.coli under physiological conditions using two combined techniques: AFM nanoindentation and fluorescence imaging.
Scientists quantify the forces that cause critical damage on a single bacterium E.coli under physiological conditions using two combined techniques: AFM nanoindentation and fluorescence imaging.
A nanomaterial path forward for COVID-19 vaccine development
 Nanoengineers detail the current approaches to COVID-19 vaccine development, and highlight how nanotechnology has enabled these advances.
Nanoengineers detail the current approaches to COVID-19 vaccine development, and highlight how nanotechnology has enabled these advances.
Nanocomposites with rich oxygen vacancies promote sensitive electroanalysis of heavy metal ions
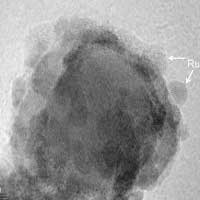 Researchers developed ruthenium-loaded cerium dioxide nanocubes with rich oxygen vacancies to construct electrochemical sensing interface, which was used to detect Hg(II).
Researchers developed ruthenium-loaded cerium dioxide nanocubes with rich oxygen vacancies to construct electrochemical sensing interface, which was used to detect Hg(II).
Unusual state of matter holds promise for transformative quantum technologies
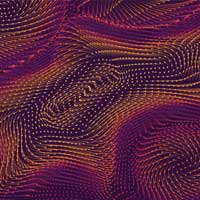 New research provides evidence of a highly unusual quantum state, a quantum spin liquid for potential use in the development of spintronic devices, quantum computers and other transformative quantum technologies.
New research provides evidence of a highly unusual quantum state, a quantum spin liquid for potential use in the development of spintronic devices, quantum computers and other transformative quantum technologies.
Turning hair into water sensors
 Researchers synthesised carbon dots from human hair waste which can detect trace amounts of chloroform in water, a major by-product of water disinfection.
Researchers synthesised carbon dots from human hair waste which can detect trace amounts of chloroform in water, a major by-product of water disinfection.
International collaboration unlocks van der Waals heterostructure
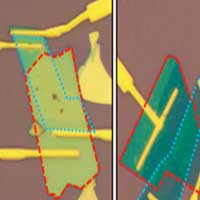 Researchers designed and fabricated a heterostructure comprising two layered transition metal dichalcogenides. Such a heterojunction enables multifunctional operation - as a highly-responsive, high-speed photodetector as well as a photovoltaic device with large open-circuit voltage.
Researchers designed and fabricated a heterostructure comprising two layered transition metal dichalcogenides. Such a heterojunction enables multifunctional operation - as a highly-responsive, high-speed photodetector as well as a photovoltaic device with large open-circuit voltage.
Scientists construct 'DNA droplets' comprising designed DNA nanostructures
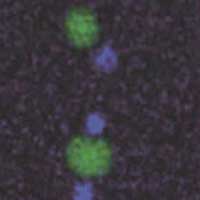 The droplets exhibit dynamic functions such as fusion, fission, Janus-shape formation, and protein capture. Their technique is expected to be applicable to a wide variety of biomaterials, opening doors to many promising applications in materials design, drug delivery, and even artificial cell-like molecular systems.
The droplets exhibit dynamic functions such as fusion, fission, Janus-shape formation, and protein capture. Their technique is expected to be applicable to a wide variety of biomaterials, opening doors to many promising applications in materials design, drug delivery, and even artificial cell-like molecular systems.
Researchers develop 'dielectrophoretic tweezer' technology for toxic nanoparticles
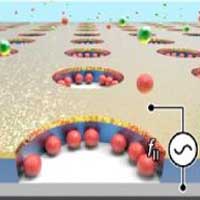 Technology developments for 'nanogap electrodes' to purify various ultra-fine floating particles in the air and water. Scalable massive methodology control makes application in the environmental and medical sciences possible.
Technology developments for 'nanogap electrodes' to purify various ultra-fine floating particles in the air and water. Scalable massive methodology control makes application in the environmental and medical sciences possible.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
