 When glass blower Karen Cunningham made art using diamond and glass she had no idea it would inspire a new kind of hybrid material. Now a consortium of scientists are using the technology to make a new class of quantum sensors.
When glass blower Karen Cunningham made art using diamond and glass she had no idea it would inspire a new kind of hybrid material. Now a consortium of scientists are using the technology to make a new class of quantum sensors.
Tuesday, August 11, 2020
Glass blowing inspires new class of quantum sensors
 When glass blower Karen Cunningham made art using diamond and glass she had no idea it would inspire a new kind of hybrid material. Now a consortium of scientists are using the technology to make a new class of quantum sensors.
When glass blower Karen Cunningham made art using diamond and glass she had no idea it would inspire a new kind of hybrid material. Now a consortium of scientists are using the technology to make a new class of quantum sensors.
Scientists develop principles for the creation of an 'acoustic diode'
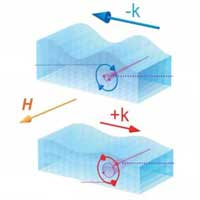 Scientists have used the principle of magneto-rotation coupling to suppress the transmission of sound waves on the surface of a film in one direction while allowing them to travel in the other. This could lead to the development of 'acoustic rectifiers'.
Scientists have used the principle of magneto-rotation coupling to suppress the transmission of sound waves on the surface of a film in one direction while allowing them to travel in the other. This could lead to the development of 'acoustic rectifiers'.
Pressure-induced 2D-3D conversion in hybrid lead iodide layered perovskite
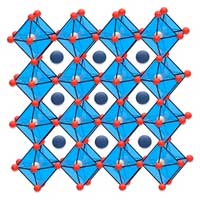 Researchers report permanent and irreversible transition of 2D hybrid Dion-Jacobson lead iodide perovskite to 3D perovskite phase at ambient conditions after pressure treatment.
Researchers report permanent and irreversible transition of 2D hybrid Dion-Jacobson lead iodide perovskite to 3D perovskite phase at ambient conditions after pressure treatment.
Stack and twist: physicists accelerate the hunt for revolutionary new materials
 Scientists take an important step towards understanding the interaction between layers of atomically thin materials arranged in stacks.
Scientists take an important step towards understanding the interaction between layers of atomically thin materials arranged in stacks.
Storing energy in red bricks
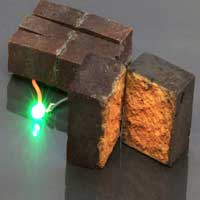 Red bricks - some of the world's cheapest and most familiar building materials - can be converted into energy storage units that can be charged to hold electricity, like a battery.
Red bricks - some of the world's cheapest and most familiar building materials - can be converted into energy storage units that can be charged to hold electricity, like a battery.
Nanoscale research exposes new vulnerability for SARS-CoV-2
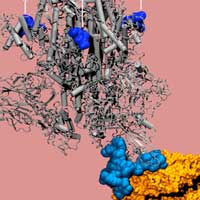 Using nanometer-level simulations, researchers discovered a positively charged site located 10 nanometers from the actual binding site on the spike protein. The positively charged site allows strong bonding between the virus protein and the negatively charged human-cell receptors.
Using nanometer-level simulations, researchers discovered a positively charged site located 10 nanometers from the actual binding site on the spike protein. The positively charged site allows strong bonding between the virus protein and the negatively charged human-cell receptors.
Investigating a thermal challenge for MOFs
 New research examines thermal transport in metal organic frameworks.
New research examines thermal transport in metal organic frameworks.
X-rays indicate that water can behave like a liquid crystal
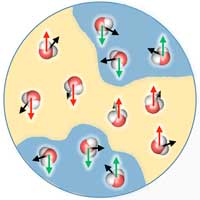 Scientists have discovered that water can exhibit a similar behavior like a liquid crystal when illuminated with laser light. This effect originates by the alignment of water molecules, which exhibit a mixture of low- and high-density domains that are more or less prone to alignment.
Scientists have discovered that water can exhibit a similar behavior like a liquid crystal when illuminated with laser light. This effect originates by the alignment of water molecules, which exhibit a mixture of low- and high-density domains that are more or less prone to alignment.
Light swirls provide insights into the quantum world
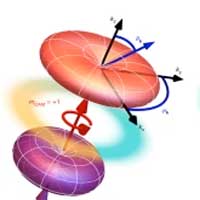 A new method uses swirls of light to enable researchers to observe previously invisible quantum states of electrons. It promises to deliver new insights into electron motion, which is crucial in understanding material properties such as electrical conductivity, magnetism and molecular structures.
A new method uses swirls of light to enable researchers to observe previously invisible quantum states of electrons. It promises to deliver new insights into electron motion, which is crucial in understanding material properties such as electrical conductivity, magnetism and molecular structures.
A wound dressing that kills bacteria
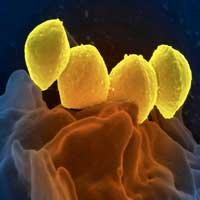 In order to combat bacterial wound infections, researchers have developed cellulose membranes equipped with antimicrobial peptides. Initial results show: The skin-friendly membranes made of plant-based materials kill bacteria very efficiently.
In order to combat bacterial wound infections, researchers have developed cellulose membranes equipped with antimicrobial peptides. Initial results show: The skin-friendly membranes made of plant-based materials kill bacteria very efficiently.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
