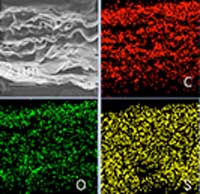
 Researchers have developed high volumetric-energy-density and long-life lithium sulfur (Li-S) batteries based on the free-standing, densely compact, and integrated cathode.
Researchers have developed high volumetric-energy-density and long-life lithium sulfur (Li-S) batteries based on the free-standing, densely compact, and integrated cathode.
Tuesday, May 21, 2019
Graphene/carbon nanotube aerogels for ultrahigh energy-density Li-S batteries
 Researchers have developed high volumetric-energy-density and long-life lithium sulfur (Li-S) batteries based on the free-standing, densely compact, and integrated cathode.
Researchers have developed high volumetric-energy-density and long-life lithium sulfur (Li-S) batteries based on the free-standing, densely compact, and integrated cathode.
Neutrons unlock the secrets of limoncello
 If you're looking for a liquid to study with neutron scattering, lemon liqueur probably isn't your first thought. But this research is a nice example on how neutron scattering can be used to probe the structure of very diverse systems.
If you're looking for a liquid to study with neutron scattering, lemon liqueur probably isn't your first thought. But this research is a nice example on how neutron scattering can be used to probe the structure of very diverse systems.
Strain enables new applications of 2D materials
 Scientists are pleased to find that the application of mechanical strain appears to manipulate the conductivity of low-dimensional materials, including graphene.
Scientists are pleased to find that the application of mechanical strain appears to manipulate the conductivity of low-dimensional materials, including graphene.
Laser focus shines light on how nanoparticles form
 Supercomputer tells origin story of nanoparticle size distributions with large-scale simulations.
Supercomputer tells origin story of nanoparticle size distributions with large-scale simulations.
Noteworthy nanotechnology book releases May 2019
 A collection of interesting, newly published nanotechnology books.
A collection of interesting, newly published nanotechnology books.
Mathematical technique quickly tunes next-generation lenses
 Metasurfaces that manipulate light at tiny scales could find uses in cellphone lenses, smart-car sensors, and optical fibers.
Metasurfaces that manipulate light at tiny scales could find uses in cellphone lenses, smart-car sensors, and optical fibers.
Infographic: Understanding graphene
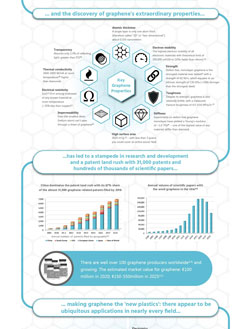 Nanowerk has put together an infographic that summarizes key properties, facts and application areas of graphene.
Nanowerk has put together an infographic that summarizes key properties, facts and application areas of graphene.
Some of our foods have nanoparticles in them - should we be worried?
 Some people are concerned nanoparticles may present health risks. Here's what we know about nanotechnology in food.
Some people are concerned nanoparticles may present health risks. Here's what we know about nanotechnology in food.
How to program materials
 Can the properties of composite materials be predicted? Scientists have mastered this feat and thus can help achieve research objectives faster. This leads, for instance, to better recycling techniques and electrically conductive synthetic materials for the solar industry.
Can the properties of composite materials be predicted? Scientists have mastered this feat and thus can help achieve research objectives faster. This leads, for instance, to better recycling techniques and electrically conductive synthetic materials for the solar industry.
Using plant viruses as nanoparticles for targeted pesticide delivery
 Scientists have discovered that a biological nanoparticle - a plant virus - is capable of delivering pesticide molecules deeper below the ground, to places that are normally beyond their reach.
Scientists have discovered that a biological nanoparticle - a plant virus - is capable of delivering pesticide molecules deeper below the ground, to places that are normally beyond their reach.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
