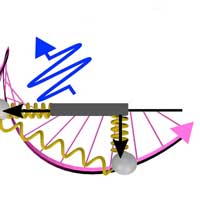
 Scientists have discovered details about a novel type of polarized light-matter interaction with light that literally turns end over end as it propagates from a source. Their find could help study molecules like those in light-harvesting antennas anticipated to have unique sensitivity to the phenomenon.
Scientists have discovered details about a novel type of polarized light-matter interaction with light that literally turns end over end as it propagates from a source. Their find could help study molecules like those in light-harvesting antennas anticipated to have unique sensitivity to the phenomenon.
Monday, June 29, 2020
Cartwheeling light reveals new optical phenomenon
 Scientists have discovered details about a novel type of polarized light-matter interaction with light that literally turns end over end as it propagates from a source. Their find could help study molecules like those in light-harvesting antennas anticipated to have unique sensitivity to the phenomenon.
Scientists have discovered details about a novel type of polarized light-matter interaction with light that literally turns end over end as it propagates from a source. Their find could help study molecules like those in light-harvesting antennas anticipated to have unique sensitivity to the phenomenon.
Researchers catch a wave to determine how forces control granular material properties
 Physicists used X-ray measurements and analyses to show that velocity scaling and dispersion in wave transmission is based on grainy particle arrangements and chains of force between them, while reduction of wave intensity is caused mainly from grainy particle arrangements alone.
Physicists used X-ray measurements and analyses to show that velocity scaling and dispersion in wave transmission is based on grainy particle arrangements and chains of force between them, while reduction of wave intensity is caused mainly from grainy particle arrangements alone.
Multifunctional nanofiber protects against explosions
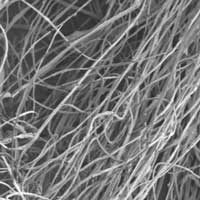 Researchers have developed a lightweight, multifunctional nanofiber material that can protect wearers from both extreme temperatures and ballistic threats.
Researchers have developed a lightweight, multifunctional nanofiber material that can protect wearers from both extreme temperatures and ballistic threats.
Producing a gaseous messenger molecule inside the body, on demand
 Method could shed light on nitric oxide's role in the neural, circulatory, and immune systems.
Method could shed light on nitric oxide's role in the neural, circulatory, and immune systems.
Engineers use 'DNA origami' to identify vaccine design rules
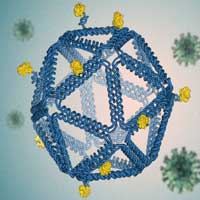 In lab tests, virus-like DNA structures coated with viral proteins provoke a strong immune response in human B cells.
In lab tests, virus-like DNA structures coated with viral proteins provoke a strong immune response in human B cells.
The first liquid retina prosthesis
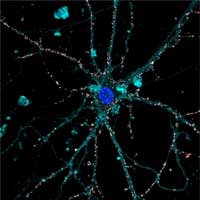 Liquid, biocompatible and micro-injectable, the new retinal prosthesis is an aqueous suspension of photoactive nanoparticles that functionally replace the photoreceptors of the retina damaged by degenerative diseases and aging.
Liquid, biocompatible and micro-injectable, the new retinal prosthesis is an aqueous suspension of photoactive nanoparticles that functionally replace the photoreceptors of the retina damaged by degenerative diseases and aging.
Physicists see surprisingly strong light, high heat from nanogaps between plasmonic electrodes
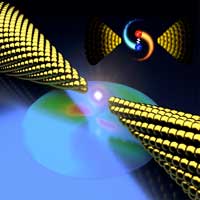 Seeing light emerge from a nanoscale experiment didn't come as a big surprise to physicists. But it got their attention when that light was 10,000 times brighter than they expected.
Seeing light emerge from a nanoscale experiment didn't come as a big surprise to physicists. But it got their attention when that light was 10,000 times brighter than they expected.
Researchers control elusive spin fluctuations in 2D magnets
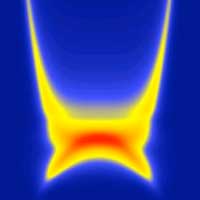 Researchers developed a new imaging technique that is fast and sensitive enough to observe these elusive critical fluctuations in two-dimensional magnets. This real-time imaging allows researchers to control the fluctuations and switch magnetism via a 'passive' mechanism that could eventually lead to more energy-efficient magnetic storage devices.
Researchers developed a new imaging technique that is fast and sensitive enough to observe these elusive critical fluctuations in two-dimensional magnets. This real-time imaging allows researchers to control the fluctuations and switch magnetism via a 'passive' mechanism that could eventually lead to more energy-efficient magnetic storage devices.
A new theory for semiconductors made of nanocrystals
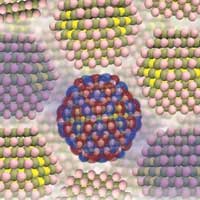 Scientists have provided the first theoretical explanation for how electrical current is conducted in semiconductors made of nanocrystals. In the future, this could lead to the development of new sensors, lasers or LEDs for TV screens.
Scientists have provided the first theoretical explanation for how electrical current is conducted in semiconductors made of nanocrystals. In the future, this could lead to the development of new sensors, lasers or LEDs for TV screens.
Stopping the unstoppable with atomic bricks
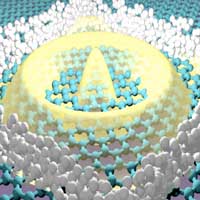 A research team developed method for trapping elusive electrons.
A research team developed method for trapping elusive electrons.
Researchers print, tune graphene sensors to monitor food freshness, safety
 Researchers are using high-resolution printing technology and the unique properties of graphene to make low-cost biosensors to monitor food safety and livestock health.
Researchers are using high-resolution printing technology and the unique properties of graphene to make low-cost biosensors to monitor food safety and livestock health.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
