Thursday, March 8, 2018
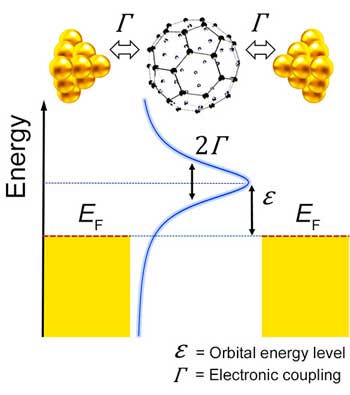
Across the metal?molecule interface: Observing fluctuations on the single-molecule scale
Scientists have developed a technique for analyzing structural and electronic fluctuations on the single-molecule scale across the metal?molecule interface in an organic electronic device. This technique provides information that cannot be obtained using the conventional method, and it has important implications for devices such as organic solar cells.
Building a better ion channel
Synthetic channel with a strong preference for potassium ions offers rapid transport through artificial membrane.

Quantum matter - A surface that makes light work
The quantum states on the surface of conducting materials can strongly interact with light.

Faster data transfer through plasmons
A transducer that converts electrical signals directly into surface plasmons could allow rapid data transfer and link photonic devices to electronics.
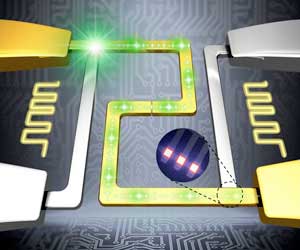
Nature inspires light, robust lattice structures
New technique for creating lightweight materials that are stiffer and stronger than previously possible.
'Floating' nanostructures for better color
Extremely high-resolution color images are produced using silicon nanostructures that imitate particles floating in free space.
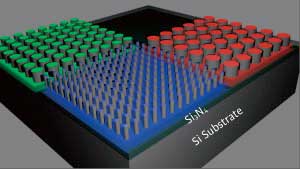
Scientists develop new tool for imprinting biochips
The new technology could allow researchers to fit more biochemical probes onto a single biochip and reduce the cost of screening and analyzing changes associated with disease development, detecting bioterrorism agents, and other areas of research.
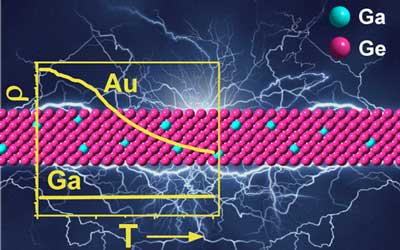
Nanostructures made of previously impossible material
How do you combine different elements in a crystal? Researchers have developed a method for incorporating previously unattainably high proportions of foreign atoms into crystals.
For nanomedicine, cell sex matmonoclonal antibodies are crucial to fighting emerging infectious diseases
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) have shown promise in the fight against cancer and autoimmune diseases. They also may play a role in future battles against emerging infectious disease outbreaks.
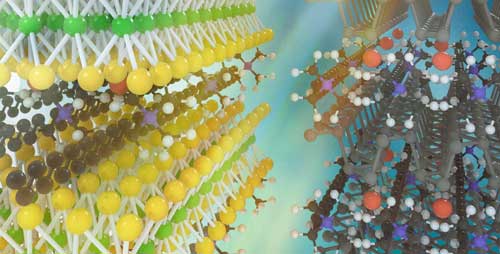
Researchers develop a new class of two-dimensional materials
New kinds of 'superlattices' could lead to improvements in electronics, from transistors to LEDs.
Revolutionizing cancer research with nanodiamond
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is being revolutionized: With the nanodiamond the tumor tissue can be detected sooner and distinguished better from the healthy surrounding tissue.
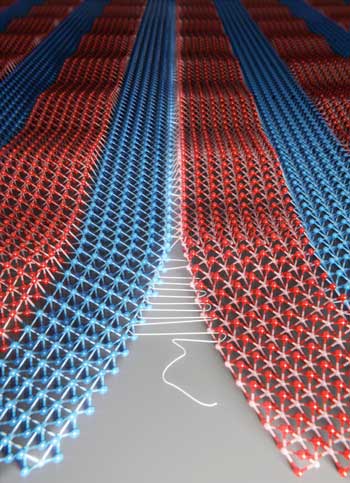
Researchers sew atomic lattices seamlessly together
Scientists have revealed a technique to 'sew' two patches of crystals seamlessly together at the atomic level to create atomically-thin fabrics.
A new paradigm: Designing materials one atom at a time
New grant to develop molecular machines that self-replicate, producing pounds of 100-percent pure material.

Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
