 Scientists have demonstrated how superatoms of a desired valency, stability, and volume can be synthesized in a solution medium by altering the number of atoms in a cluster structure. This is an important step in realizing the practical application of superatom clusters as substitutes for elements in chemical reactions.
Scientists have demonstrated how superatoms of a desired valency, stability, and volume can be synthesized in a solution medium by altering the number of atoms in a cluster structure. This is an important step in realizing the practical application of superatom clusters as substitutes for elements in chemical reactions.
Monday, February 24, 2020
Synthesizing a superatom
 Scientists have demonstrated how superatoms of a desired valency, stability, and volume can be synthesized in a solution medium by altering the number of atoms in a cluster structure. This is an important step in realizing the practical application of superatom clusters as substitutes for elements in chemical reactions.
Scientists have demonstrated how superatoms of a desired valency, stability, and volume can be synthesized in a solution medium by altering the number of atoms in a cluster structure. This is an important step in realizing the practical application of superatom clusters as substitutes for elements in chemical reactions.
Shining a new light on biomimetic materials
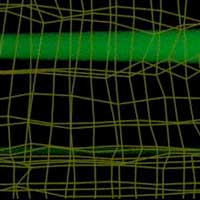 Researchers have merged optical, chemical and materials sciences to utilize light to control the local dynamic behavior within a hydrogel, much like the ability of the iris and pupil in the eye to dynamically respond to incoming light.
Researchers have merged optical, chemical and materials sciences to utilize light to control the local dynamic behavior within a hydrogel, much like the ability of the iris and pupil in the eye to dynamically respond to incoming light.
Defects add color to quantum systems
 Researchers are investigating light-emitting defects in materials that may someday form the basis of quantum-based technologies, such as quantum computers, quantum networks or engines that run on light. Once understood, these defects can become controllable features.
Researchers are investigating light-emitting defects in materials that may someday form the basis of quantum-based technologies, such as quantum computers, quantum networks or engines that run on light. Once understood, these defects can become controllable features.
A simple retrofit transforms electron microscopes into high-speed atom-scale cameras
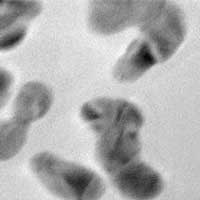 Patented 'beam chopper' provides cost-effective way to investigate super-fast processes important for tomorrow's technology.
Patented 'beam chopper' provides cost-effective way to investigate super-fast processes important for tomorrow's technology.
Going super small to get super strong metals
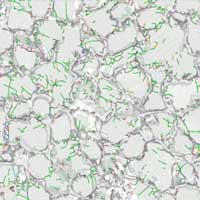 A new study has resulted in a new understanding of how individual atoms of metal grains interact with each other, as well as a way to use those physics to achieve super-strong metals.
A new study has resulted in a new understanding of how individual atoms of metal grains interact with each other, as well as a way to use those physics to achieve super-strong metals.
Developing lensless imaging at the nanoscale
 Researchers are planning to develop imaging that can look at biological systems at a much higher resolution and definition.
Researchers are planning to develop imaging that can look at biological systems at a much higher resolution and definition.
An exceptionally stable single-atom catalyst
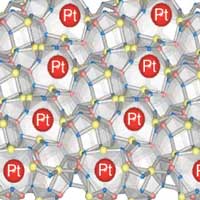 Scientists have shown that single platinum atoms trapped in C12A7 crystals act as a stable and effective catalyst for the hydrogenation of nitroarenes, an essential process in the production of many kinds of fine chemicals.
Scientists have shown that single platinum atoms trapped in C12A7 crystals act as a stable and effective catalyst for the hydrogenation of nitroarenes, an essential process in the production of many kinds of fine chemicals.
Directing nanoparticles straight to tumors
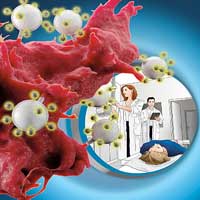 A team of researchers has produced tiny nanoparticles that are designed to specifically target cancer cells. They can navigate directly to the tumor cells and visualize those using advanced imaging techniques.
A team of researchers has produced tiny nanoparticles that are designed to specifically target cancer cells. They can navigate directly to the tumor cells and visualize those using advanced imaging techniques.
Short film of a magnetic nano-vortex
 For the first time, researchers have recorded a '3D film' of magnetic processes on the nanometer scale. This reveals a variety of dynamics inside the material, including the motion of swirling boundaries between different magnetic domains.
For the first time, researchers have recorded a '3D film' of magnetic processes on the nanometer scale. This reveals a variety of dynamics inside the material, including the motion of swirling boundaries between different magnetic domains.
Watching magnetic nano 'tornadoes' in 3-D
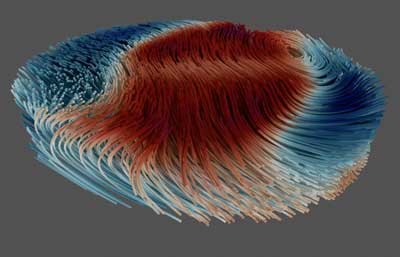 Scientists have developed a three-dimensional imaging technique to observe complex behaviours in magnets, including fast-moving waves and 'tornadoes' thousands of times thinner than a human hair.
Scientists have developed a three-dimensional imaging technique to observe complex behaviours in magnets, including fast-moving waves and 'tornadoes' thousands of times thinner than a human hair.
Novel gold nanocatalyst with high activity and excellent stability
 Researchers prepared a SiO2 modified gold nanocatalyst through co-deposition of gold and silica precursors on the TiO2 support and subsequent high temperature calcination.
Researchers prepared a SiO2 modified gold nanocatalyst through co-deposition of gold and silica precursors on the TiO2 support and subsequent high temperature calcination.
DNA nanostructures suit up for future missions
 A broadly applicable and simple chemical protection strategy removes a major roadblock in the development of therapeutic and diagnostic DNA nanostructures.
A broadly applicable and simple chemical protection strategy removes a major roadblock in the development of therapeutic and diagnostic DNA nanostructures.
When plasmons reach atomic flatland
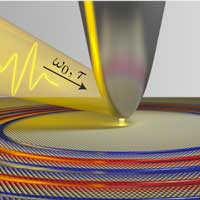 Researchers have discovered a significant new fundamental kind of quantum electronic oscillations, or plasmons, in atomically thin materials. Their work has potential implications for novel imaging techniques and photochemical reactions at the nanoscale.
Researchers have discovered a significant new fundamental kind of quantum electronic oscillations, or plasmons, in atomically thin materials. Their work has potential implications for novel imaging techniques and photochemical reactions at the nanoscale.
Sneaking up on nanocrystals with electron diffraction
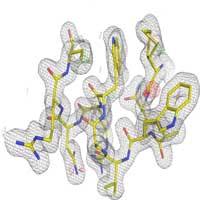 Scientists present a method for serial electron diffraction of protein nanocrystals combining the benefits of serial X-ray crystallography and rotation electron diffraction.
Scientists present a method for serial electron diffraction of protein nanocrystals combining the benefits of serial X-ray crystallography and rotation electron diffraction.
Cellulose nanocrystals and water form an 'eco' super-glue
 Plant-based cellulose nanocrystals have remarkable inherent properties, and when combined with water, a powerful adhesive is formed that competes in strength with Superglue, without the need for toxic solvents.
Plant-based cellulose nanocrystals have remarkable inherent properties, and when combined with water, a powerful adhesive is formed that competes in strength with Superglue, without the need for toxic solvents.
Printable organic photodiodes that can distinguish wavelengths
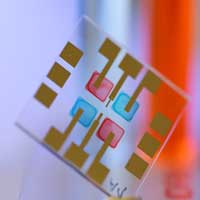 Researchers develop printable organic photodiodes that can distinguish wavelengths and, hence, enable data transmission by light.
Researchers develop printable organic photodiodes that can distinguish wavelengths and, hence, enable data transmission by light.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
