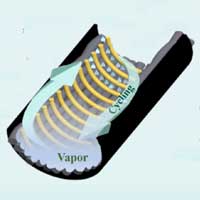
 Researchers have found that graphene-based heat pipes can help solve the problems of cooling electronics and power systems used in avionics, data centres, and other power electronics.
Researchers have found that graphene-based heat pipes can help solve the problems of cooling electronics and power systems used in avionics, data centres, and other power electronics.
Wednesday, December 2, 2020
Cooling electronics efficiently with graphene-enhanced heat pipes
 Researchers have found that graphene-based heat pipes can help solve the problems of cooling electronics and power systems used in avionics, data centres, and other power electronics.
Researchers have found that graphene-based heat pipes can help solve the problems of cooling electronics and power systems used in avionics, data centres, and other power electronics.
Graphene nanoparticles - a new type of amorphous solid bodies
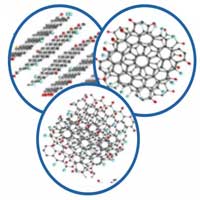 Amorphous forms of solid carbon do not have a fixed crystal structure and consist of structural units - nanosized graphene particles. A team of physicists studied the structure of amorphous carbon and suggested classifying it as a separate type of amorphous solid bodies: a molecular amorphic with enforced fragmentation.
Amorphous forms of solid carbon do not have a fixed crystal structure and consist of structural units - nanosized graphene particles. A team of physicists studied the structure of amorphous carbon and suggested classifying it as a separate type of amorphous solid bodies: a molecular amorphic with enforced fragmentation.
New platform generates hybrid light-matter excitations in highly charged graphene
 Researchers use static charge between 2D atomic layers to provide a new route for generating graphene plasmon polaritons without an external power source or chemical dopants; discovery has broad application in nanotechnology.
Researchers use static charge between 2D atomic layers to provide a new route for generating graphene plasmon polaritons without an external power source or chemical dopants; discovery has broad application in nanotechnology.
Nanomaterials enable dual-mode heating and cooling device
 The invention uses a combination of mechanics and nanomaterials to either harness or expel certain wavelengths of light. Depending on conditions, rollers move a sheet back and forth to expose either heat-trapping materials or cooling materials.
The invention uses a combination of mechanics and nanomaterials to either harness or expel certain wavelengths of light. Depending on conditions, rollers move a sheet back and forth to expose either heat-trapping materials or cooling materials.
Promising nanomaterial can store solar energy for months or years
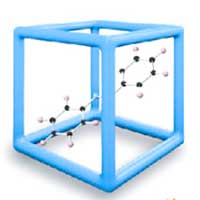 Researchers studying a metal-organic framework (MOF) have discovered it has properties that allow it to capture energy from the sun. The energy can be stored for several months at room temperature, and it can be released on demand as heat.
Researchers studying a metal-organic framework (MOF) have discovered it has properties that allow it to capture energy from the sun. The energy can be stored for several months at room temperature, and it can be released on demand as heat.
Novel metal-organic framework nanosheets for anticorrosive coatings
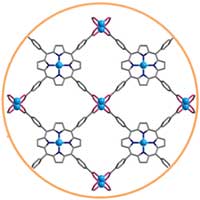 Newly developed two-dimensional (2D) MOF nanosheets enhanced anticorrosion properties of composite coatings.
Newly developed two-dimensional (2D) MOF nanosheets enhanced anticorrosion properties of composite coatings.
Decorating semiconductors at the atomic scale
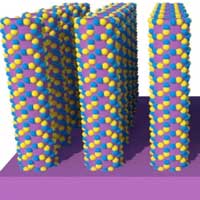 Researchers formed semiconductors from different components by adding one atomic layer at a time.
Researchers formed semiconductors from different components by adding one atomic layer at a time.
New glue sticks easily, holds strongly, and is a gas to pull apart
 Scientists have discovered a class of molecular materials that can be used to make temporary adhesives that don't require force for removal. These non-permanent glues won't be available as home or office supplies, but they can lead to new manufacturing techniques and pharmaceutical design.
Scientists have discovered a class of molecular materials that can be used to make temporary adhesives that don't require force for removal. These non-permanent glues won't be available as home or office supplies, but they can lead to new manufacturing techniques and pharmaceutical design.
Engineering a living plant nanobionic sensor to monitor arsenic levels in soil
 New class of living plant-based sensor interfaces wild-type plants with engineered optical nanosensors, able to detect arsenic levels as low as 0.2 parts per billion.
New class of living plant-based sensor interfaces wild-type plants with engineered optical nanosensors, able to detect arsenic levels as low as 0.2 parts per billion.
New butterfly-inspired hydrogen sensor is powered by light
 Inspired by the surface of butterfly wings, researchers have developed a light-activated hydrogen sensor that produces ultra-precise results at room temperature.
Inspired by the surface of butterfly wings, researchers have developed a light-activated hydrogen sensor that produces ultra-precise results at room temperature.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
