 A nanoscale gold butterfly provides a more precise route for growing/synthesizing nanosized semiconductors that can be used in nano-lasers and other applications.
A nanoscale gold butterfly provides a more precise route for growing/synthesizing nanosized semiconductors that can be used in nano-lasers and other applications.
Wednesday, February 5, 2020
A nanoscale gold butterfly can make its own semiconductor skin
 A nanoscale gold butterfly provides a more precise route for growing/synthesizing nanosized semiconductors that can be used in nano-lasers and other applications.
A nanoscale gold butterfly provides a more precise route for growing/synthesizing nanosized semiconductors that can be used in nano-lasers and other applications.
Improved ruthenium nanocatalyst branches out and outperforms
 By creating branched nanoparticles from the metal ruthenium, researchers developed a way to increase the speed of catalysis while maintaining the catalyst's stability. Because they have precise control over the nanoparticle?s crystal structure, they can create a reaction that is both highly active and highly stable.
By creating branched nanoparticles from the metal ruthenium, researchers developed a way to increase the speed of catalysis while maintaining the catalyst's stability. Because they have precise control over the nanoparticle?s crystal structure, they can create a reaction that is both highly active and highly stable.
How manipulating ligand interactions in metal clusters can spur advances in nanotechnology
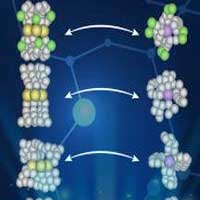 Researchers uncover how interactions among ligands dictate the final structure of metal clusters, which have various applications in modern electronic devices.
Researchers uncover how interactions among ligands dictate the final structure of metal clusters, which have various applications in modern electronic devices.
Crystal-stacking process can produce new materials for high-tech devices
 Stacking ultrathin complex oxide single-crystal layers allows researchers to create new structures with hybrid properties and multiple functions. Now, using a new platform, researchers will be able to make these stacked-crystal materials in virtually unlimited combinations.
Stacking ultrathin complex oxide single-crystal layers allows researchers to create new structures with hybrid properties and multiple functions. Now, using a new platform, researchers will be able to make these stacked-crystal materials in virtually unlimited combinations.
A new way to trace nanoparticles inside the skin
 Scientists have conducted a series of experiments with upconversion luminescent nanoparticles and various models of human skin to determine how many nanoparticles penetrated the skin and how quickly and deep they moved.
Scientists have conducted a series of experiments with upconversion luminescent nanoparticles and various models of human skin to determine how many nanoparticles penetrated the skin and how quickly and deep they moved.
Scientists create artificial virus in the fight against superbugs
 Scientists have developed a mechanism of antibacterial persistence to combat persistent and resistant bacterial infections.
Scientists have developed a mechanism of antibacterial persistence to combat persistent and resistant bacterial infections.
Building upon carbon nanotubes to create a novel functional structure
 For the first time, researchers have grown crystals of various materials uniformly onto the surface of carbon nanotubes. They hope these modified structures will exhibit functions useful in electronic, chemical or other applications.
For the first time, researchers have grown crystals of various materials uniformly onto the surface of carbon nanotubes. They hope these modified structures will exhibit functions useful in electronic, chemical or other applications.
Cathode 'defects' improve battery performance
 A counterintuitive finding revealed by high-precision powder diffraction analyses suggests a new strategy for building better batteries.
A counterintuitive finding revealed by high-precision powder diffraction analyses suggests a new strategy for building better batteries.
Researchers propose new concept for DNA-based nanorobot to fight cancer
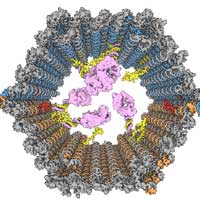 This is the first ever nanorobot to combine two functions: cancer diagnostics and treatment. Made of DNA fragments, the nano-sized robot detects a pathogenic RNA strand in a gene and destroys it so cancer cells stop multiplying. And it will cost just $20!
This is the first ever nanorobot to combine two functions: cancer diagnostics and treatment. Made of DNA fragments, the nano-sized robot detects a pathogenic RNA strand in a gene and destroys it so cancer cells stop multiplying. And it will cost just $20!
Bending diamond at the nanoscale
 Researchers discovered diamond can be bent and deformed, creating possibilities for the design and engineering of new nanoscale devices.
Researchers discovered diamond can be bent and deformed, creating possibilities for the design and engineering of new nanoscale devices.
Machine learning accelerates metamaterial design
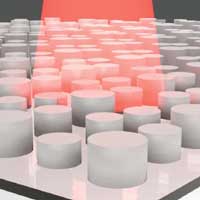 Scientists used machine learning techniques to analyze databases of information. The computer program predicted the ideal metamaterial design for absorbing low-energy light. Conventional models would have taken more than two thousand years to find the best metamaterial.
Scientists used machine learning techniques to analyze databases of information. The computer program predicted the ideal metamaterial design for absorbing low-energy light. Conventional models would have taken more than two thousand years to find the best metamaterial.
No strain, no gain! breakthrough in 2D material that produces single photons
 Scientists discovered a new method to generate single photons. They used strain in a 2D material made of tungsten and selenium. By grafting a thin film of the WSe2 onto an ultra-sharp tip made of silicon dioxide, they created specific, well-separated spaces on the thin film that created photons.
Scientists discovered a new method to generate single photons. They used strain in a 2D material made of tungsten and selenium. By grafting a thin film of the WSe2 onto an ultra-sharp tip made of silicon dioxide, they created specific, well-separated spaces on the thin film that created photons.
Silica particles may lead to new treatments for obesity and diabetes
 Engineered ingestible molecular traps created from mesoporous silica particles introduced to the gut can have an effect on food efficiency and metabolic risk factors. The results from studies on mice demonstrate the potential to reduce the energy uptake into the body and could lead to new treatments for obesity and diabetes.
Engineered ingestible molecular traps created from mesoporous silica particles introduced to the gut can have an effect on food efficiency and metabolic risk factors. The results from studies on mice demonstrate the potential to reduce the energy uptake into the body and could lead to new treatments for obesity and diabetes.
Fireproof, lightweight solid electrolyte for safer lithium-ion batteries
 Researchers have developed a solid-state electrolyte that won't burn up.
Researchers have developed a solid-state electrolyte that won't burn up.
Fastest high-precision 3D printer for metamaterials with sub-micrometer accuracy
 Researchers have developed a system to print highly precise, centimeter-sized objects with submicrometer details at a so far unmatched speed.
Researchers have developed a system to print highly precise, centimeter-sized objects with submicrometer details at a so far unmatched speed.
Researchers successfully test coin-sized smart insulin patch, potential diabetes treatment
 Biomedical engineers led preclinical experiments for a new device to automatically manage glucose levels and deliver needed insulin quickly.
Biomedical engineers led preclinical experiments for a new device to automatically manage glucose levels and deliver needed insulin quickly.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
