 New research suggests that a novel magnetism-based drug delivery approach could help ensure drugs are not removed from where they are needed in the body.
New research suggests that a novel magnetism-based drug delivery approach could help ensure drugs are not removed from where they are needed in the body.
Thursday, April 30, 2020
'Magnetic drugs' could stay at disease sites longer
 New research suggests that a novel magnetism-based drug delivery approach could help ensure drugs are not removed from where they are needed in the body.
New research suggests that a novel magnetism-based drug delivery approach could help ensure drugs are not removed from where they are needed in the body.
'Breathable' electronics pave the way for more functional wearable tech
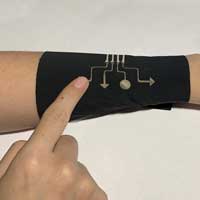 Engineering researchers have created ultrathin, stretchable electronic material that is gas permeable, allowing the material to 'breathe'.
Engineering researchers have created ultrathin, stretchable electronic material that is gas permeable, allowing the material to 'breathe'.
Optical 'nanomixer': Scientists propose new method for mixing liquids
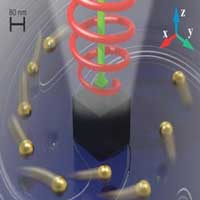 Scientists propose a method that can help solve problem of controlling over the mixing speed: they decided to use the so-called radiation pressure.
Scientists propose a method that can help solve problem of controlling over the mixing speed: they decided to use the so-called radiation pressure.
Groovy photoelectrodes: How a textured surface can dramatically boost their performance
 Researchers find that a promising photoelectrode material for producing hydrogen using sunlight can be made even better by increasing its surface roughness.
Researchers find that a promising photoelectrode material for producing hydrogen using sunlight can be made even better by increasing its surface roughness.
Nanodevices for the brain could thwart formation of Alzheimer's plaques
 In a multidisciplinary study, scientists have developed an approach to prevent plaque formation by engineering a nano-sized device that captures the dangerous peptides before they can self-assemble.
In a multidisciplinary study, scientists have developed an approach to prevent plaque formation by engineering a nano-sized device that captures the dangerous peptides before they can self-assemble.
Scientists reveal the magnetic states of nanoscale gyroids
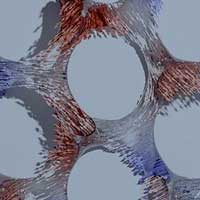 Researchers revealed the magnetic states of nanoscale gyroids, 3D chiral network-like nanostructures. The findings add a new candidate system for research into unconventional information processing and emergent phenomena relevant to spintronics.
Researchers revealed the magnetic states of nanoscale gyroids, 3D chiral network-like nanostructures. The findings add a new candidate system for research into unconventional information processing and emergent phenomena relevant to spintronics.
Scientists prove the existence of Skyrmion tubes
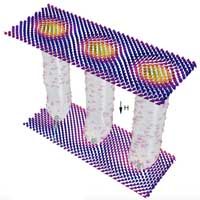 For the first time, an international team of researchers succeeded in demonstrating the previously unknown structure of magnetic skyrmion tubes in 3D. This knowledge makes it possible to better understand the formation and destruction of skyrmions and to use the magnetic structures in spintronic storage devices.
For the first time, an international team of researchers succeeded in demonstrating the previously unknown structure of magnetic skyrmion tubes in 3D. This knowledge makes it possible to better understand the formation and destruction of skyrmions and to use the magnetic structures in spintronic storage devices.
Wednesday, April 29, 2020
Molecules with a spin on a topological insulator: a hybrid approach to magnetic topological states of matter
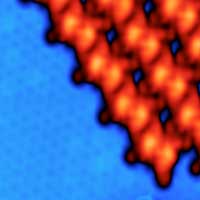 Controlling the interactions at the interface of a magnetic/topological insulator heterostructure is an outstanding challenge with implications in fundamental science and technology. New resesearch has shown that ligands from metal-organic molecules can be used to tailor the properties of these interfaces.
Controlling the interactions at the interface of a magnetic/topological insulator heterostructure is an outstanding challenge with implications in fundamental science and technology. New resesearch has shown that ligands from metal-organic molecules can be used to tailor the properties of these interfaces.
Researchers measure cancer cell mechanics in living animals using nanoparticles
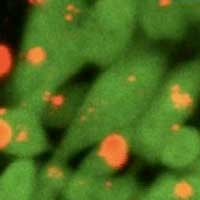 Scientists have developed a first-of-its-kind nanoparticle-based in vivo imaging technique that may one day be used to help diagnose and even treat cancer.
Scientists have developed a first-of-its-kind nanoparticle-based in vivo imaging technique that may one day be used to help diagnose and even treat cancer.
Stretchable lithium-ion battery is based on new micro-honeycomb structure
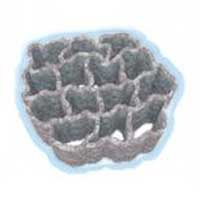 Researchers developed a lithium-ion battery that is flexible enough to be stretched.
Researchers developed a lithium-ion battery that is flexible enough to be stretched.
Scientists proposed a new approach for efficient nanomaterials' modeling
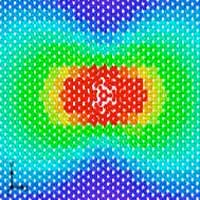 With the new modeling method, the calculations became simpler, which gives a possibility to predict the mechanical response to tension and to study its failure mechanism.
With the new modeling method, the calculations became simpler, which gives a possibility to predict the mechanical response to tension and to study its failure mechanism.
'Strange effect' raises possibility of smaller, smarter optical filters
 Polarization, in sync. On the macro, everyday level, it reads as an oxymoron. To nanoscientists, though, the apparent contradiction makes a kind of harmonious sense.
Polarization, in sync. On the macro, everyday level, it reads as an oxymoron. To nanoscientists, though, the apparent contradiction makes a kind of harmonious sense.
Perovskite/graphene nanosensor detects nitrogen dioxide with 300% improved sensitivity
 Graphene and perovskites hybrid resulted in a material that can more sensitively detect these kinds of gas.
Graphene and perovskites hybrid resulted in a material that can more sensitively detect these kinds of gas.
MRI scanning assists with next generation battery design
 Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can provide an effective way of supporting the development of the next generation of high-performance rechargeable batteries.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can provide an effective way of supporting the development of the next generation of high-performance rechargeable batteries.
MOF material offers optical sensing of NO2 pollutant for air quality measurements
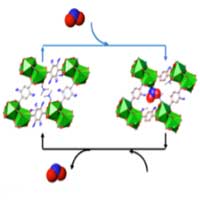 This proof-of-concept material would be sensitive enough to detect straightforward low concentration of NO2 in conventional luminescence displays.
This proof-of-concept material would be sensitive enough to detect straightforward low concentration of NO2 in conventional luminescence displays.
Scientists outsmart nature by building super liquid-repellent dry adhesives
 A specific fibril tip shape design is the key to achieving elastic dry fibril adhesives with super liquid repellency. This new bioinspired material opens up many possibilities for use, as it prevents any form of liquid droplet or layer from hindering or degrading its adhesion.
A specific fibril tip shape design is the key to achieving elastic dry fibril adhesives with super liquid repellency. This new bioinspired material opens up many possibilities for use, as it prevents any form of liquid droplet or layer from hindering or degrading its adhesion.
Tuesday, April 28, 2020
Polymer membranes could benefit from taking a dip
 A simple pretreatment step enables membranes to be enhanced using atomic layer deposition, a technique that can improve performance and introduce new surface properties.
A simple pretreatment step enables membranes to be enhanced using atomic layer deposition, a technique that can improve performance and introduce new surface properties.
Nanoarchitected metamaterial with material achieves the theoretic limits of stiffness and strength
 The strength of the carbon plate structures was up to 639% stronger and up to 522% stiffer than same-weight beam nanolattices of the same material. This is the first experimental evidence that plate-architecture is superior to the established beam-architecture.
The strength of the carbon plate structures was up to 639% stronger and up to 522% stiffer than same-weight beam nanolattices of the same material. This is the first experimental evidence that plate-architecture is superior to the established beam-architecture.
Success in specific detection of molecules using deformation of a single graphene sheet
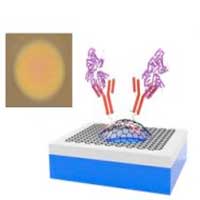 Researchers developed a test chip using graphene. The chip has a trampoline structure with a narrow gap of 1 micrometer or less formed under a monoatomic graphene film, and can specifically trap a biomarker, a protein included in bodily fluids, on graphene.
Researchers developed a test chip using graphene. The chip has a trampoline structure with a narrow gap of 1 micrometer or less formed under a monoatomic graphene film, and can specifically trap a biomarker, a protein included in bodily fluids, on graphene.
Novel nanostructure design lends extraordinary strength to a promising battery anode
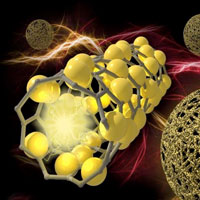 Researchers developed a unique nanostructure that limits silicon's expansion while fortifying it with carbon. Their work could inform new electrode material designs for other types of batteries and eventually help increase the energy capacity of the lithium-ion batteries in electric cars, electronic devices, and other equipment.
Researchers developed a unique nanostructure that limits silicon's expansion while fortifying it with carbon. Their work could inform new electrode material designs for other types of batteries and eventually help increase the energy capacity of the lithium-ion batteries in electric cars, electronic devices, and other equipment.
Monday, April 27, 2020
New study reveals how impurities affect the electrical properties in anisotropic 2D materials
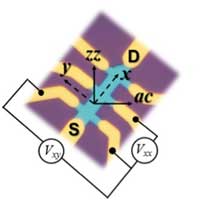 A new study shows how impurities affect the electrical properties in anisotropic germanium arsenide (GeAs).
A new study shows how impurities affect the electrical properties in anisotropic germanium arsenide (GeAs).
Abundant element to power small devices
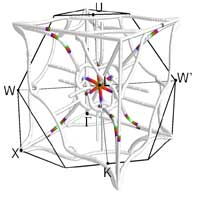 A thin, iron-based generator uses waste heat to provide small amounts of power.
A thin, iron-based generator uses waste heat to provide small amounts of power.
Two steps closer to flexible, powerful, fast bioelectronic devices
 Researchers design biocompatible ion-driven soft transistors that can perform real-time neurologically relevant computation and a mixed-conducting particulate composite that allows creation of electronic components out of a single material.
Researchers design biocompatible ion-driven soft transistors that can perform real-time neurologically relevant computation and a mixed-conducting particulate composite that allows creation of electronic components out of a single material.
Electronics for high-altitude use can get smaller and sturdier with new nanomaterials
 Scientists are creating new metal-based nanomaterials for circuit boards that could be resistant to the high-altitude radiation encountered by electronics in aerospace equipment, fighter jets and weapon systems.
Scientists are creating new metal-based nanomaterials for circuit boards that could be resistant to the high-altitude radiation encountered by electronics in aerospace equipment, fighter jets and weapon systems.
New metasurface laser produces world's first super-chiral light
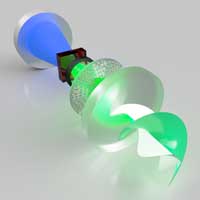 Researchers have demonstrated the world's first metasurface laser that produces 'super-chiral light': light with ultra-high angular momentum. The light from this laser can be used as a type of "optical spanner" to or for encoding information in optical communications.
Researchers have demonstrated the world's first metasurface laser that produces 'super-chiral light': light with ultra-high angular momentum. The light from this laser can be used as a type of "optical spanner" to or for encoding information in optical communications.
Scientists develop stable luminescent composite material based on perovskite nanocrystals
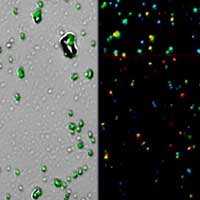 Scientists develop light-emitting composite material based on perovskite nanocrystals with air- and water resilient optical characteristics.
Scientists develop light-emitting composite material based on perovskite nanocrystals with air- and water resilient optical characteristics.
Ultra-fast vector microscopy is a breakthrough in nano-optics
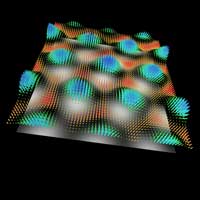 The duration of their snapshot relates to a second as this second does to the age of the universe: Physicists have developed ultra-fast vector microscopy as a means of determining electric fields on surfaces with high temporal and spatial resolution.
The duration of their snapshot relates to a second as this second does to the age of the universe: Physicists have developed ultra-fast vector microscopy as a means of determining electric fields on surfaces with high temporal and spatial resolution.
Sunday, April 26, 2020
Personalized nutrition smart patch to reduce diabetes risk
 A wearable smart patch will deliver precision data to help people personalise their diets and reduce their risk of developing lifestyle-related chronic diseases like Type 2 diabetes.
A wearable smart patch will deliver precision data to help people personalise their diets and reduce their risk of developing lifestyle-related chronic diseases like Type 2 diabetes.
Synthesis of silicon intercalated monolayer blue phosphorus
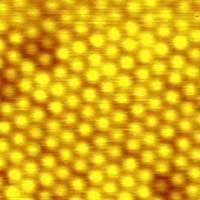 Chemists have developed a method to synthetically produce monolayer blue phosphorus for potential semiconductor applications.
Chemists have developed a method to synthetically produce monolayer blue phosphorus for potential semiconductor applications.
Applying quantum-impurity theory to quantum fluids of light
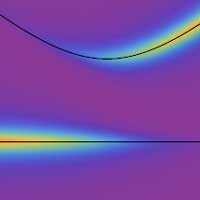 Scientists develop a new approach to directly observe correlated, many-body states in an exciton-polariton system that go beyond classical theories.
Scientists develop a new approach to directly observe correlated, many-body states in an exciton-polariton system that go beyond classical theories.
Friday, April 24, 2020
Engineers open door to big new library of nanoparticles
 A new study expands the landscape of nanomaterials - and what we can do with them.
A new study expands the landscape of nanomaterials - and what we can do with them.
Novel hollow nanostructure is promising for new class of materials
 Researchers created a hollow nanostructure for metal halide perovskites that would allow the material to emit a highly efficient blue light.
Researchers created a hollow nanostructure for metal halide perovskites that would allow the material to emit a highly efficient blue light.
'Decoy' nanoparticles can block HIV and prevent infection
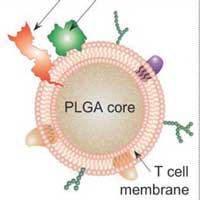 Cloaking nanoparticles in cell membranes draws HIV away from immune cells.
Cloaking nanoparticles in cell membranes draws HIV away from immune cells.
Scientists develop MOF nanomaterial to remove antibiotics in water
 Researchers used a hydrothermal synthesis method to fabricate the nanomaterial that can work as an absorbent to remove norfloxacin, a kind of antibiotics in water.
Researchers used a hydrothermal synthesis method to fabricate the nanomaterial that can work as an absorbent to remove norfloxacin, a kind of antibiotics in water.
New solution to capture microplastics before they enter waterways
 A novel method utilizes nanocellulose structures for early particle identification. Nanocellulose would allow particles to be captured even before they enter waterways.
A novel method utilizes nanocellulose structures for early particle identification. Nanocellulose would allow particles to be captured even before they enter waterways.
Researchers watch the dynamics of plasmonic skyrmions made from light on ultra-smooth gold platelets for the first time
 Researchers have succeeded for the first time in filming light vortex patterns on the nanometer scale, which are named skyrmions after their discoverer Tony Skyrme.
Researchers have succeeded for the first time in filming light vortex patterns on the nanometer scale, which are named skyrmions after their discoverer Tony Skyrme.
Thursday, April 23, 2020
Multi-functionalization of graphene for molecular targeted cancer therapy
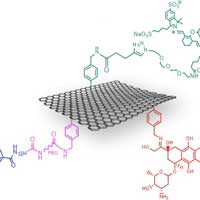 Scientists have developed a type of nanomedicine based on multi-functional graphene that allows for targeted cancer treatment at molecular level.
Scientists have developed a type of nanomedicine based on multi-functional graphene that allows for targeted cancer treatment at molecular level.
Researchers discover ferroelectricity at the atomic scale
 A team of researchers have managed to grow ultra-thin material on silicon that can power small electronic devices.
A team of researchers have managed to grow ultra-thin material on silicon that can power small electronic devices.
Controlling ion transport for energy, environment
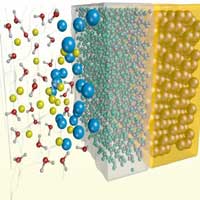 In a recent study, scientists showed that ion transport near a hydrophobic interface is dependent not only on applied voltage, but on the type of ion.
In a recent study, scientists showed that ion transport near a hydrophobic interface is dependent not only on applied voltage, but on the type of ion.
Wiring the quantum computer of the future: a novel simple build with existing technology
 The basic units of a quantum computer can be rearranged in 2D to solve typical design and operation challenges.
The basic units of a quantum computer can be rearranged in 2D to solve typical design and operation challenges.
Ultrashort laser pulses induce point defects in fused silica for anti-counterfeiting
 Researchers report tunable point defects in hydroxyl fused silica enabled by ultrashort laser pulses for anti-counterfeiting and functional module fabrication.
Researchers report tunable point defects in hydroxyl fused silica enabled by ultrashort laser pulses for anti-counterfeiting and functional module fabrication.
Wednesday, April 22, 2020
New dual-action coating keeps bacteria from cross-contaminating fresh produce
 Over the course of their journey from the open fields to the produce displays at grocery stores, fresh vegetables and fruits can sometimes become contaminated by microorganisms. These items can then spoil other produce, spreading the contamination further and increasing the number of food items that can cause illnesses. A new nanoparticle coating prevents that.
Over the course of their journey from the open fields to the produce displays at grocery stores, fresh vegetables and fruits can sometimes become contaminated by microorganisms. These items can then spoil other produce, spreading the contamination further and increasing the number of food items that can cause illnesses. A new nanoparticle coating prevents that.
Electronic skin fully powered by sweat can monitor health
 Electronic skin monitors body's vitals signs while being powered by sweat.
Electronic skin monitors body's vitals signs while being powered by sweat.
A novel method to precisely deliver therapeutics inside the body
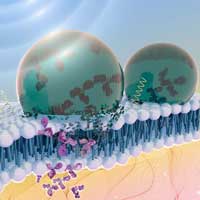 A new way to deliver therapeutic proteins inside the body uses an acoustically sensitive carrier to encapsulate the proteins and ultrasound to image and guide the package to the exact location required. Ultrasound then breaks the capsule, allowing the protein to enter the cell.
A new way to deliver therapeutic proteins inside the body uses an acoustically sensitive carrier to encapsulate the proteins and ultrasound to image and guide the package to the exact location required. Ultrasound then breaks the capsule, allowing the protein to enter the cell.
Novel method for gentle laser processing of perovskites at the nanoscale
 Scientists have developed a method for precise, fast and high-quality laser processing of halide perovskites, promising light-emitting materials for solar energy, optical electronics, and metamaterials.
Scientists have developed a method for precise, fast and high-quality laser processing of halide perovskites, promising light-emitting materials for solar energy, optical electronics, and metamaterials.
Spider combs tame unruly nanofibers
 Researchers have patterned an antiadhesive nanostructure inspired by the comb on spiders'legs onto a foil surface, creating a handy tool to control sticky lab-made nanomaterials for medical, smart textile and other applications.
Researchers have patterned an antiadhesive nanostructure inspired by the comb on spiders'legs onto a foil surface, creating a handy tool to control sticky lab-made nanomaterials for medical, smart textile and other applications.
Windows will soon generate electricity, following solar cell breakthrough
 Two square metres of solar window will do the same job as a standard rooftop solar panel.
Two square metres of solar window will do the same job as a standard rooftop solar panel.
The future of semiconductors is clear
 A clear semiconductor based on tin could improve solar power generation.
A clear semiconductor based on tin could improve solar power generation.
Scientists uncover major cause of resistance in solid electrolytes
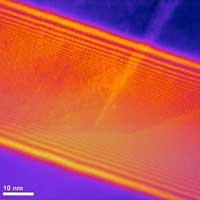 The study involved two powerful techniques - electron holography and atom probe tomography - that allowed scientists to observe the boundaries at an unprecedentedly small scale. The resulting insights provide new avenues for tuning chemical properties in the material to improve performance.
The study involved two powerful techniques - electron holography and atom probe tomography - that allowed scientists to observe the boundaries at an unprecedentedly small scale. The resulting insights provide new avenues for tuning chemical properties in the material to improve performance.
A hydrogel to cool down electronic devices, recover waste heat
 Researchers have developed a hydrogel that can both cool down electronics, such as cell phone batteries, and convert their waste heat into electricity.
Researchers have developed a hydrogel that can both cool down electronics, such as cell phone batteries, and convert their waste heat into electricity.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
