Monday, March 26, 2018
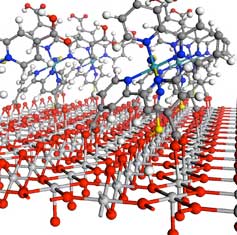
Understanding charge transfers in molecular electronics
An international research team has found a way to understand and manipulate the transition of charges in molecular junctions.
Atomically thin light-emitting device opens the possibility for 'invisible' displays
Engineers have built a bright-light emitting device that is millimeters wide and fully transparent when turned off. The light emitting material in this device is a monolayer semiconductor, which is just three atoms thick.

Harvesting energy from light fluctuations
Hybrid plasmonic and pyroelectric harvesting of light fluctuations.

Self-assembling, tunable interfaces found in quantum materials
Highly adaptive electronics could be created using quantum features.
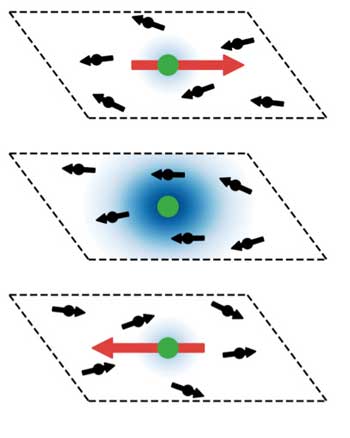
Atomistic insights into electrocatalysis
Scientists found out that the topmost atomic layers of electrocatalysts contain chemical species, which determine their efficiency and reveal how they can be influenced to speed-up water splitting.
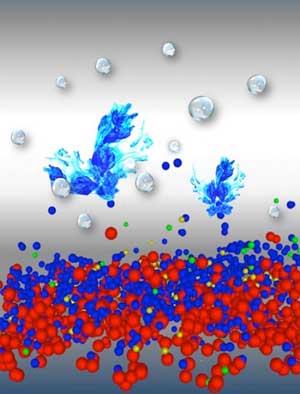
Edges and corners increase efficiency of catalytic converters
X-rays reveal oxide islands on noble metal nanoparticles.
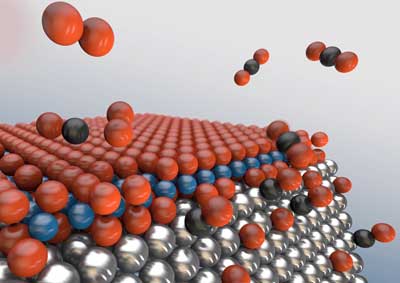
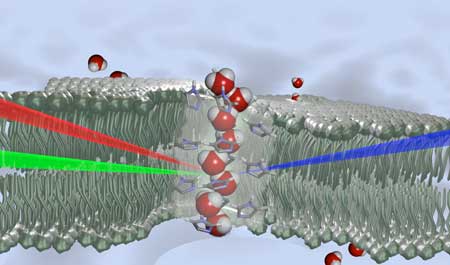
Artificial bio-inspired membranes for water filtration
Inspired by cellular proteins, researchers have developed membranes with asymmetric artificial channels in the interior, from which they were able to observe 'chiral' water.
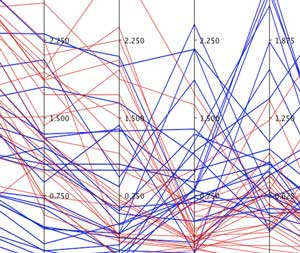
Improving human-data interaction to speed nanomaterials innovation
New application of data analysis, visualization techniques achieves better representation of multidimensional materials data.
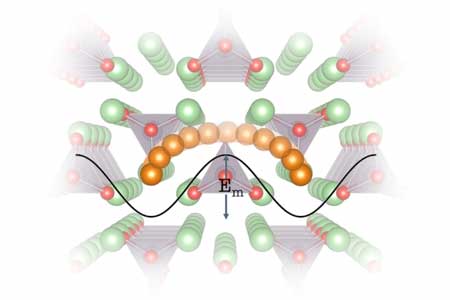
A new way to find better battery materials
Design principles could point to better electrolytes for next-generation lithium batteries.
A simple method developed for 3D bio-fabrication based on bacterial nanocellulose
Researchers have developed a simple and customizable process that uses superhydrophobic interfaces to finely engineer the bacteria access to oxygen in three dimensions and in multiple length scales, resulting in hollow, seamless, nanocellulose-based pre-determined objects.

Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
