Wednesday, March 21, 2018
Researchers discover new accuracies in cancer-fighting, nanomedicine drug delivery
A promising discovery for advanced cancer therapy reveals that the efficiency of drug delivery in DNA nanostructures depends on their shapes.
Design approach developed for important new catalysts for energy conversion and storage
New method could aid in design of pharmaceuticals and optical and data storage materials.
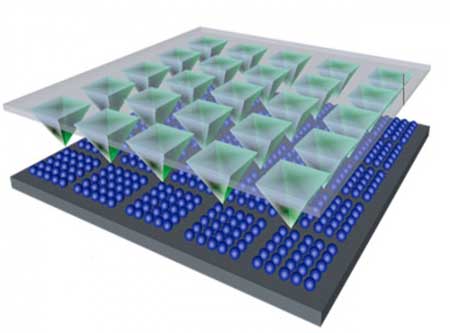
Designing a new material for improved ultrasound
Development of a theoretical basis for ultrahigh piezoelectricity in ferroelectric materials led to a new material with twice the piezo response of any existing commercial ferroelectric ceramics.
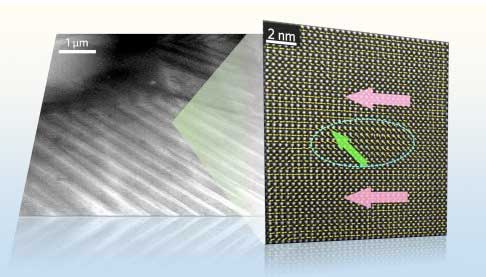
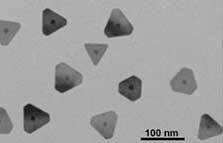
Researchers explore enzymetic activities based on nanocomplex sensors
A team of researchers compared the susceptibility of different triangle silver nanoprisms (TSNPRs) towards H2O2 and elucidated the influence of capping agents and structural size on the etching process, with the aim of optimizing TSNPRs for H2O2 etching-based biosensors, such as glucose and glucose oxidase.
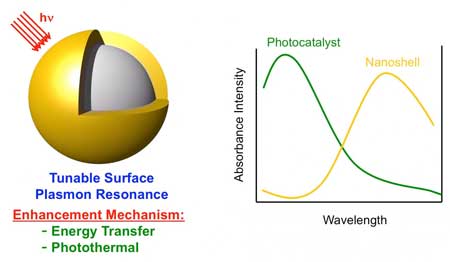
Nanomaterials hold promise for producing hydrogen from water
Scientists use hollow gold-silver nanoshells to boost the efficiency of photocatalysts, where the combined nanocomposite materials generate hydrogen from water, powered only by sunlight.
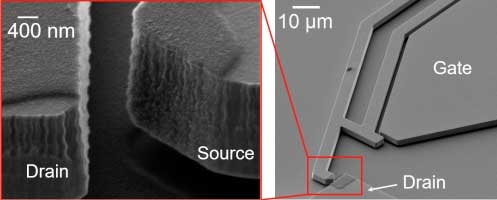
Nanocrystalline graphite enables new class of harsh environment electronics
Researchers have demonstrated reliable operation of microelectromechanical relays by coating the contacts with nanocrystalline layers of graphite, to enable ultra-low-power electronics for harsh environments.
Cellulose nanofibers won from elephant and cow manure for sustainably making paper
It's likely not the first thing you think of when you see elephant dung, but this material turns out to be an excellent source of cellulose for paper manufacturing in countries where trees are scarce, scientists report.

2D materials for aerosolizable nanoelectronics
Tiny floating robots could be useful in all kinds of ways, for example, to probe the human gut for disease or to search the environment for pollutants. In a step toward such devices, researchers describe a new marriage of materials, combining ultrathin 2-D electronics with miniature particles to create microscopic machines.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
