Wednesday, April 11, 2018
Chaos makes quantum sensors work more precisely
Physicists have developed a method with which the measurement accuracy of high-precision sensors could be improved by a further 70 percent.
Biologically inspired nanomembrane purges coal-fired smoke of greenhouse gases
Scientists have developed a biologically inspired membrane intended to cleanse carbon dioxide almost completely from the smoke of coal-fired power plants.
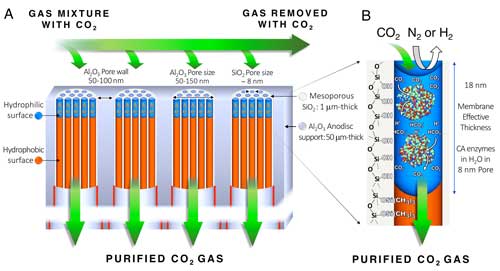
Researchers engineer new pathways for self-assembled nanostructures
Self-assembly is driven mainly by the system?s desire to minimize its energy and achieve equilibrium, but kinetic effects can also play a strong role. Typically, these effects are viewed as complications to be overcome, but a collaboration of researchers has recently shown that these effects can be exploited to engineer a nanostructure in a polymer thin film.
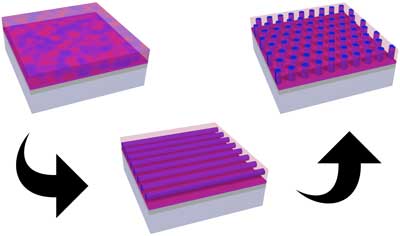
Sensing interactions between molecules
Nanoscientists have developed an atomically defined probe tip with extraordinary stability which enables them to image molecular structures by atomic force microscopy.
World's first biosensor chips based on copper and graphene oxide
Researchers have developed biosensor chips of unprecedented sensitivity, which are based on copper instead of the conventionally used gold.

Smart printing: power generating films and luminescent glass
New inks for inkjet printers make it possible to print organic displays or solar cells on film and glass for the use in architecture, the textile industry and many other industries.

Nanoparticles for lung cancer pass next test
Non-small cell lung cancer nanoparticles pass the next stage of development in preclinical test.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
