
Thursday, April 19, 2018
New record on squeezing light to one atom: Atomic Lego guides light below one nanometer
Scientists have been able to confine light down to a space one atom thick in dimension, the smallest confinement ever possible.
A novel way of creating gold nanoparticles in water
An experiment that, by design, was not supposed to turn up anything of note instead produced a 'bewildering' surprise, according to the scientists who made the discovery: a new way of creating gold nanoparticles and nanowires using water droplets.
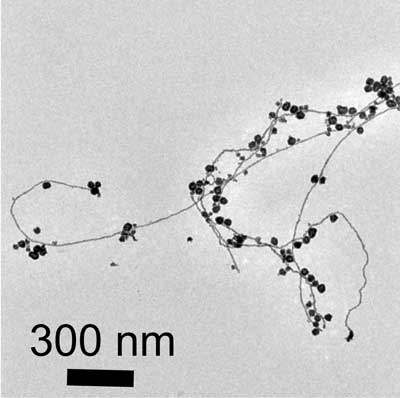
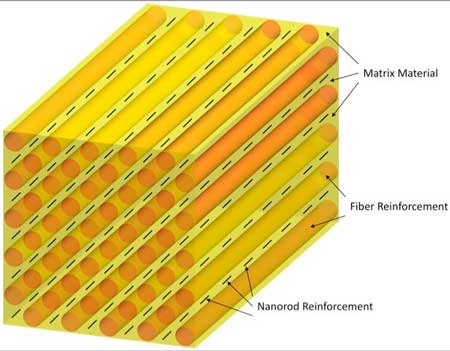
Spider silk key to new bone-fixing composite
Researchers have created a biodegradable composite made of silk fibers that can be used to repair broken load-bearing bones without the complications sometimes presented by other materials.
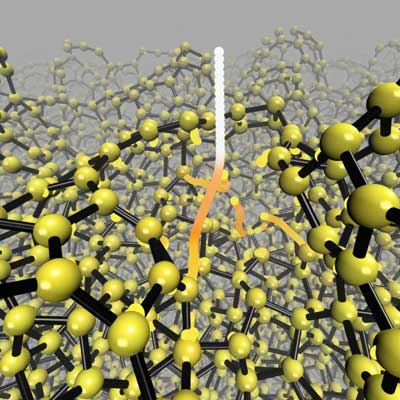
Diamond-like carbon is formed differently to what was believed
Researchers have made a significant breakthrough in computational science by combining atomic-level modelling and machine learning. For the first time, the method has been used to realistically model how an amorphous material is formed at the atomic level.
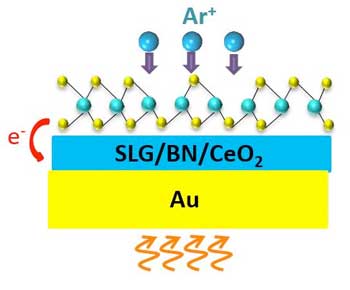
Electrochemical tuning of single layer materials relies on defects
Perfection is not everything, according to an international team of researchers whose 2-D materials study shows that defects can enhance a material's physical, electrochemical, magnetic, energy and catalytic properties.
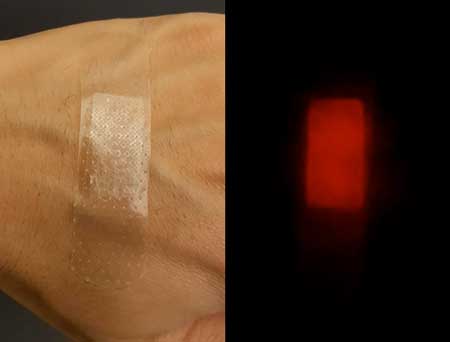
Far-red fluorescent silk can kill harmful bacteria as biomedical and environmental remedy
A silk hybrid material attacks bacteria when illuminated by a green light, thanks to a far-red fluorescent protein researchers transferred to its genetic makeup.
Energy conversion: Optical 'overtones' for solar cells
Scientists have found a new effect regarding the optical excitation of charge carriers in a solar semiconductor. It could facilitate the utilization of infrared light, which is normally lost in solar devices.

New cancer monitoring technology worth its weight in gold
A new blood test using gold nanoparticles could soon give oncologists an early and more accurate prognosis of how cancer treatment is progressing and help guide the on-going therapy of patients.

Using tooth sensors to detect disease (w/video)
Collaborative research team developing biological sensors that would analyze saliva, send information electronically to doctors.
Peptide induces chirality evolution in a single gold nanoparticle
For the first time, scientists have successfully created optically active, chiral gold nanoparticles using amino acids and peptides.
Graphene changes elastic properties depending on applied force
Researchers find a universal feature defining unique elastic and electrical graphene properties.

Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
