Thursday, February 28, 2019
Organic electronics: A high-performance unipolar n-type thin-film transistor
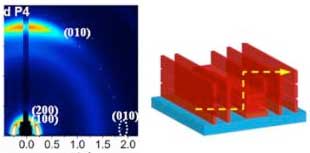
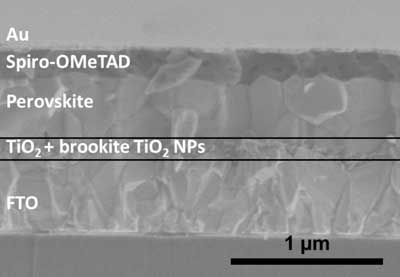
Layering titanium oxide's different mineral forms for better solar cells
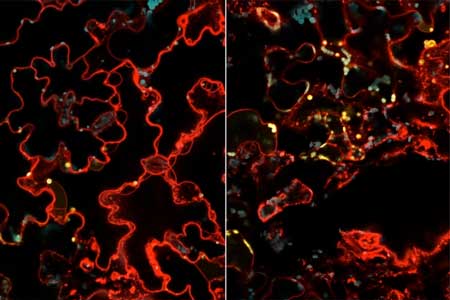
An easier way to engineer plants
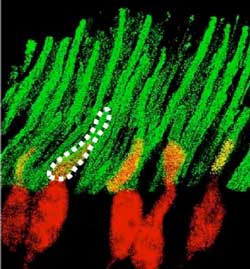
Nanotechnology makes it possible for mice to see in infrared
Hall effect becomes viscous in graphene
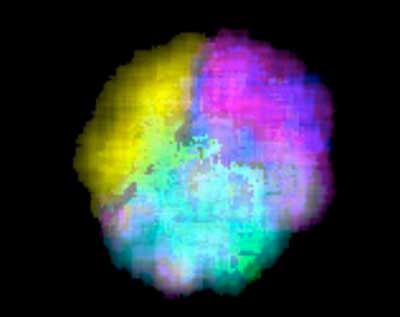
New blueprint for understanding, predicting and optimizing complex nanoparticles
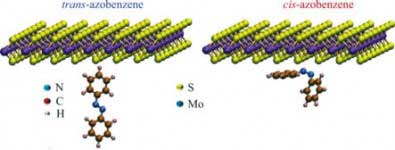
Hybrid material may outperform graphene in several applications
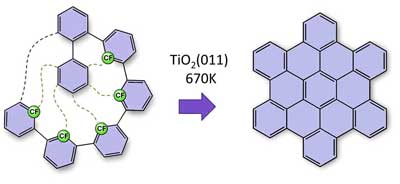
Zips on the nanoscale
In-depth insights into glass corrosion
Easing bacterial traffic jams
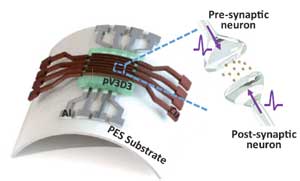
Researchers develop analog memristive synapses for neuromorphic chips
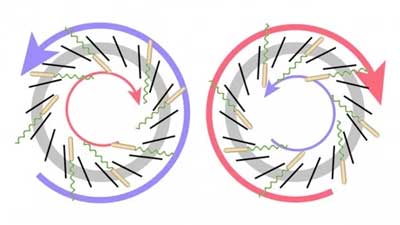
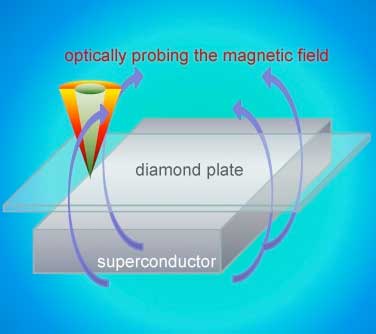
Scientists measure exact edge between superconducting and magnetic states
Wednesday, February 27, 2019
Engineers make clear droplets produce iridescent colors (w/video)

Good news for future tech: Exotic topological materials are surprisingly common
Fast, flexible ionic transistors for bioelectronic devices

A new method for precision drug delivery: painting
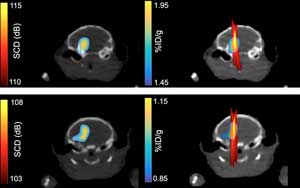
Packaging insecticides in nanocapsules may make them more toxic
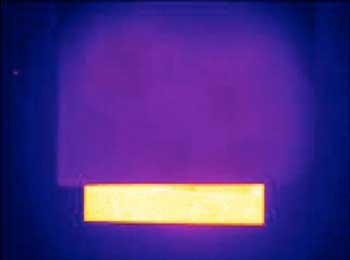
Now you see heat, now you don't
Directed evolution builds nanoparticles
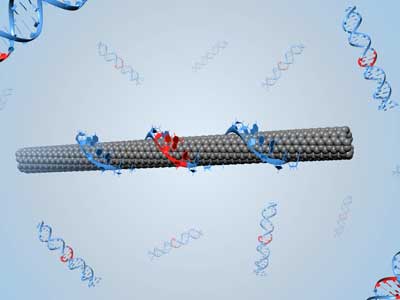
Examining silver nanoparticles in natural environments

Tuesday, February 26, 2019
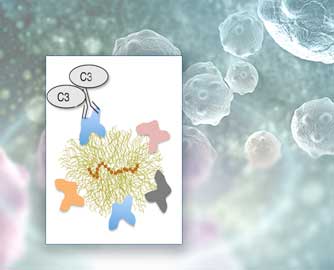
Antibodies on nanoparticle surfaces may foster or fluster therapies
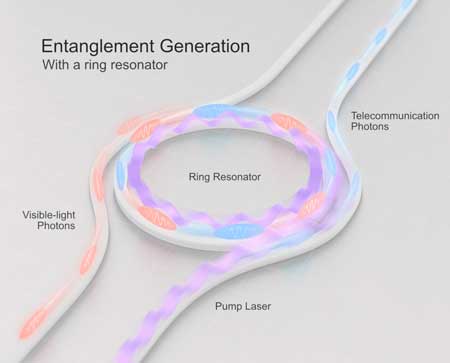
Entangling photons of different colors
'Immunizing' quantum bits so that they can grow up
The EU gets specific about nanomaterials

Electrically-heated silicate glass appears to defy Joule's first law

A new spin in nanoelectronics
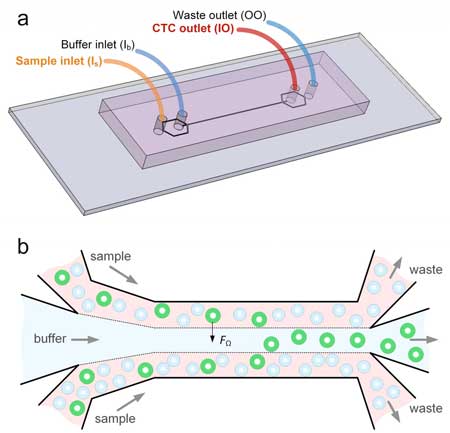
New microfluidics device can detect cancer cells in blood
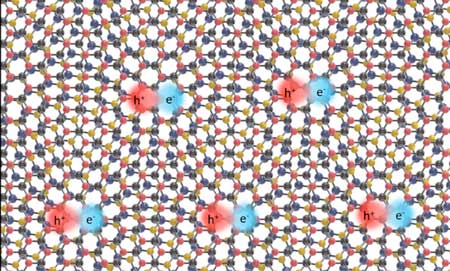
Avoiding the crack of doom
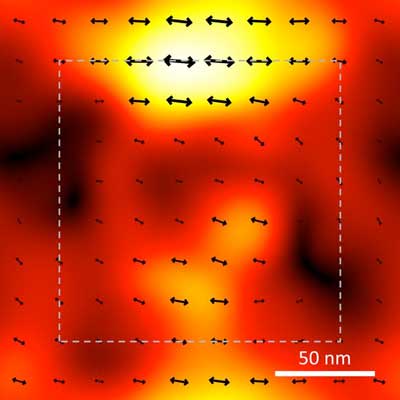
It's all in the twist: Physicists stack 2D materials at angles to trap particles on the nanoscale
Monday, February 25, 2019
Graphite offers up new quantum surprise
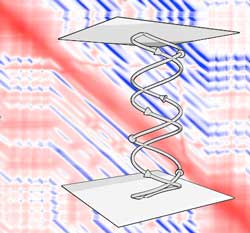
With nanotubes, genetic engineering in plants is easy-peasy

Topological defects could be key to future nano-electronics

Nanoparticle computing takes a giant step forward
Liquid has structure, which may be key to understanding metallic glass

Saturday, February 23, 2019
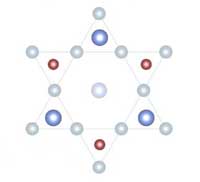
A quantum magnet with a topological twist
Friday, February 22, 2019
Understanding high efficiency of deep ultraviolet LEDs

Magnetization reversal achieved at room temperature using only an electric field

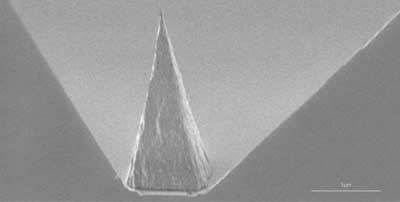
A tip for future nanoscale sensing
Thursday, February 21, 2019
With nanopore sensing, physicists detect subtle changes in single particles
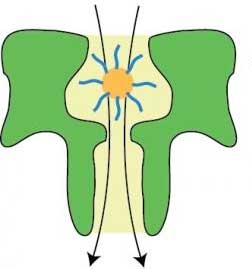
More flexible nanomaterials can make fuel cell cars cheaper
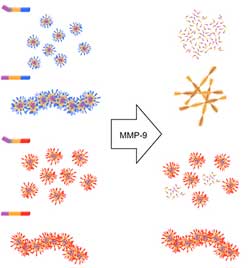
Design principles for disease-sensing nanomaterials
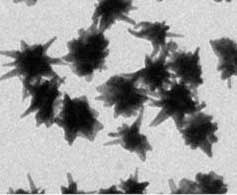
Gold nano-stars for intracellular delivery
Carbon nanotubes can be produced in a new way by twisting ribbon-like graphene
Wednesday, February 20, 2019
Innovative nanocoating technology harnesses sunlight to degrade microplastics

Thermally-painted metasurfaces yield perfect light absorbers for high-tech applications
GraphON: Conductive coatings and materials breakthrough

Physicists 'flash-freeze' crystal of 150 ions
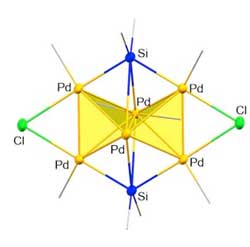
'Butterfly-shaped' palladium subnano cluster built in 3-D
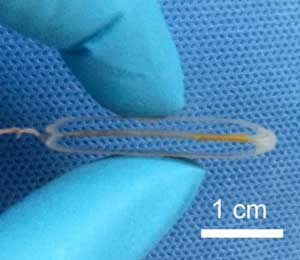
Powering a pacemaker with a patient's heartbeat
The holy grail of nanowire production
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
