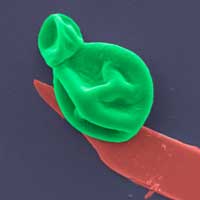
 Researchers have developed a new superbug-destroying coating that could be used on wound dressings and implants to prevent and treat potentially deadly bacterial and fungal infections. The material is one of the thinnest antimicrobial coatings developed to date and is effective against a broad range of drug-resistant bacteria and fungal cells, while leaving human cells unharmed.
Researchers have developed a new superbug-destroying coating that could be used on wound dressings and implants to prevent and treat potentially deadly bacterial and fungal infections. The material is one of the thinnest antimicrobial coatings developed to date and is effective against a broad range of drug-resistant bacteria and fungal cells, while leaving human cells unharmed.
Tuesday, April 13, 2021
Superbug killer: New nanotechnology destroys bacteria and fungal cells
 Researchers have developed a new superbug-destroying coating that could be used on wound dressings and implants to prevent and treat potentially deadly bacterial and fungal infections. The material is one of the thinnest antimicrobial coatings developed to date and is effective against a broad range of drug-resistant bacteria and fungal cells, while leaving human cells unharmed.
Researchers have developed a new superbug-destroying coating that could be used on wound dressings and implants to prevent and treat potentially deadly bacterial and fungal infections. The material is one of the thinnest antimicrobial coatings developed to date and is effective against a broad range of drug-resistant bacteria and fungal cells, while leaving human cells unharmed.
New nanosensor holds promise for diagnosing, treating neurological disease
 Scientists have developed a new type of nanosensor that allows scientists to image communication between the brain and the body in real time.
Scientists have developed a new type of nanosensor that allows scientists to image communication between the brain and the body in real time.
New sensor tracks 'stress hormone' in real time
 Researchers have developed a fluorescence-based sensor prototype for continuous detection of cortisol concentrations in real time, which can help monitor various health conditions.
Researchers have developed a fluorescence-based sensor prototype for continuous detection of cortisol concentrations in real time, which can help monitor various health conditions.
Combining nanomaterials in 3D to build next-generation imaging devices
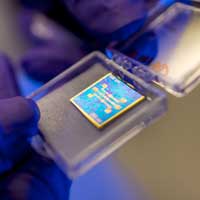 Researchers are integrating different nanoscale materials together in 3D to create an entirely new generation of devices for environmental monitoring, energy harvesting and biomedical applications.
Researchers are integrating different nanoscale materials together in 3D to create an entirely new generation of devices for environmental monitoring, energy harvesting and biomedical applications.
A novel tunable force in electrolyte solutions
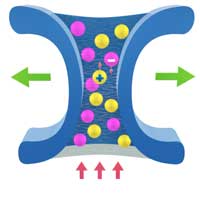 Solutions that conduct electricity, 'electrolytes', are ubiquitous not only in batteries and capacitors but also in biofluids including blood plasma; of great practical importance is thus to understand how electrolytes can be utilised to control living cells or other objects that are immersed in them.
Solutions that conduct electricity, 'electrolytes', are ubiquitous not only in batteries and capacitors but also in biofluids including blood plasma; of great practical importance is thus to understand how electrolytes can be utilised to control living cells or other objects that are immersed in them.
Researchers develop a haptic film activated by LEDs
 LED-based film-type haptic technology implements localized vibration. various tactile sensations are now possible via independantly controllable vibrations.
LED-based film-type haptic technology implements localized vibration. various tactile sensations are now possible via independantly controllable vibrations.
Scientists achieve self-assembly of superstructures at all scales
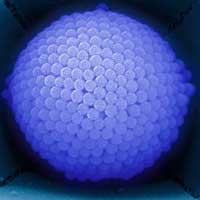 Researchers report a robust and straightforward assembly strategy to create uniform superstructures at defined positions by introducing primary particles into templating holes via a transient emulsion.
Researchers report a robust and straightforward assembly strategy to create uniform superstructures at defined positions by introducing primary particles into templating holes via a transient emulsion.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
