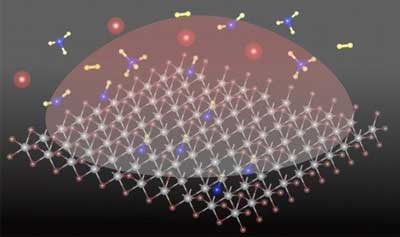
 A technique to substitute carbon-hydrogen species into a single atomic layer of the semiconducting material tungsten disulfide, a transition metal dichalcogenide (TMD), dramatically changes the electronic properties of the material.
A technique to substitute carbon-hydrogen species into a single atomic layer of the semiconducting material tungsten disulfide, a transition metal dichalcogenide (TMD), dramatically changes the electronic properties of the material.
Friday, May 24, 2019
Adding a carbon atom transforms 2-D semiconducting material
 A technique to substitute carbon-hydrogen species into a single atomic layer of the semiconducting material tungsten disulfide, a transition metal dichalcogenide (TMD), dramatically changes the electronic properties of the material.
A technique to substitute carbon-hydrogen species into a single atomic layer of the semiconducting material tungsten disulfide, a transition metal dichalcogenide (TMD), dramatically changes the electronic properties of the material.
Rare iron oxide could be combined with 2D materials for electronic, spintronic devices
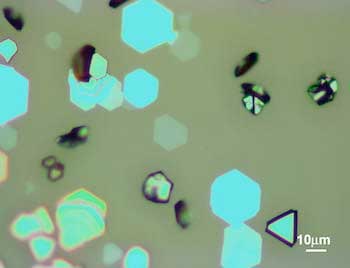 Researchers have simplified the synthesis of a unique, nearly two-dimensional form of iron oxide with strong magnetic properties that is easy to stack atop other 2D materials.
Researchers have simplified the synthesis of a unique, nearly two-dimensional form of iron oxide with strong magnetic properties that is easy to stack atop other 2D materials.
Researchers create soft, flexible materials with enhanced properties
 A team of polymer chemists and engineers have developed a new methodology that can be used to create a class of stretchable polymer composites with enhanced electrical and thermal properties.
A team of polymer chemists and engineers have developed a new methodology that can be used to create a class of stretchable polymer composites with enhanced electrical and thermal properties.
Mathematically designed graphene has improved electrocatalytic activity
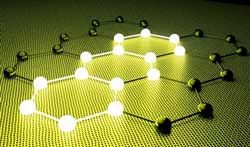 An international research group has improved graphene's ability to catalyse the 'hydrogen evolution reaction', which releases hydrogen as a result of passing an electronic current through water.
An international research group has improved graphene's ability to catalyse the 'hydrogen evolution reaction', which releases hydrogen as a result of passing an electronic current through water.
Tiny vortices could one day haul microscopic cargo
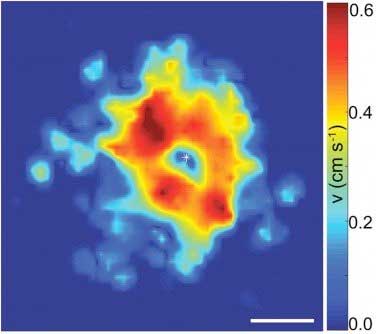 The behavior of active magnetic liquids suggests new pathways to transport particles across surfaces and build materials that self-heal.
The behavior of active magnetic liquids suggests new pathways to transport particles across surfaces and build materials that self-heal.
Scientists discover signalling circuit boards inside body's cells
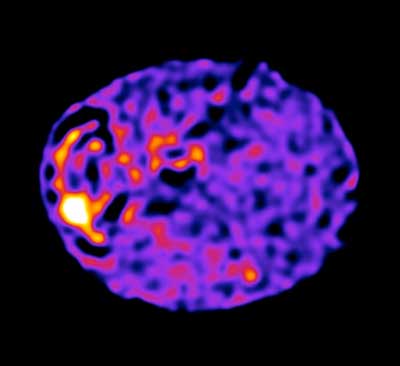 Scientists found that cell function is coordinated by a network of nanotubes, similar to the carbon nanotubes used in nanoelectronics
Scientists found that cell function is coordinated by a network of nanotubes, similar to the carbon nanotubes used in nanoelectronics
Nature inspires a novel new form of computing, using light
 Researchers perform simple calculations by shining light patterns through a translucent cube.
Researchers perform simple calculations by shining light patterns through a translucent cube.
Superconductor films convert heat into electricity
 Films of a superconductor show excellent thermoelectric properties at very low film thicknesses.
Films of a superconductor show excellent thermoelectric properties at very low film thicknesses.
Plumbene, graphene's latest cousin, realized on a 'nano water cube'
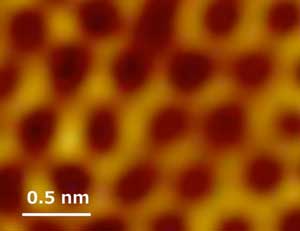 Scientists have created 'plumbene', a 2D-honeycomb sheet of lead atoms. Plumbene has the largest spin-orbit interaction of any Group 14 elemental 2D material, potentially making it a robust 2D topological insulator in which the Quantum Spin Hall Effect might occur even above room temperature.
Scientists have created 'plumbene', a 2D-honeycomb sheet of lead atoms. Plumbene has the largest spin-orbit interaction of any Group 14 elemental 2D material, potentially making it a robust 2D topological insulator in which the Quantum Spin Hall Effect might occur even above room temperature.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
