
Monday, May 21, 2018
Nanoparticles could offer a new way to help eradicate polio
The vaccine, which delivers multiple doses in just one injection, could make it easier to immunize children in remote regions of Pakistan and other countries where the disease is still found.
A better way to control crystal vibrations
Researchers have shown that by swapping out just a small fraction of a material's atoms with atoms of a different element, they can control the speed and frequencies of these vibrations.
Discovery for grouping atoms invokes Pasteur
A new dimension in chemistry could herald new materials, drugs, computers.
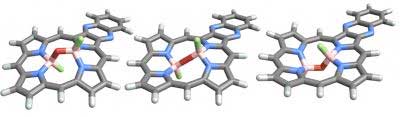
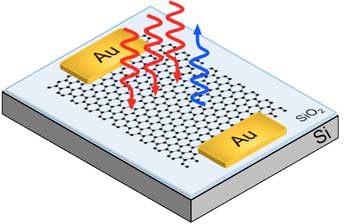
Graphene paves the way to faster high-speed optical communications
Researchers created a technology that could lead to new devices for faster, more reliable ultra-broad bandwidth transfers.
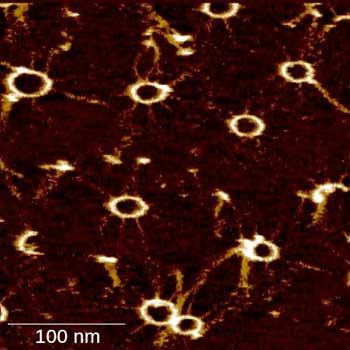
Observing cellular activity, one molecule at a time
Using a new mode of atomic force microscopy, researchers have found a way to see and measure protein assembly in real time and with unprecedented detail.
New technique reveals 3D shape of nanostructure's polariton interaction
New method improves upon common spectroscopic imaging technique: scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscopy (s-SNOM), makes it possible to obtain polaritonic, mechanical and electrical information simultaneously with one measurement.

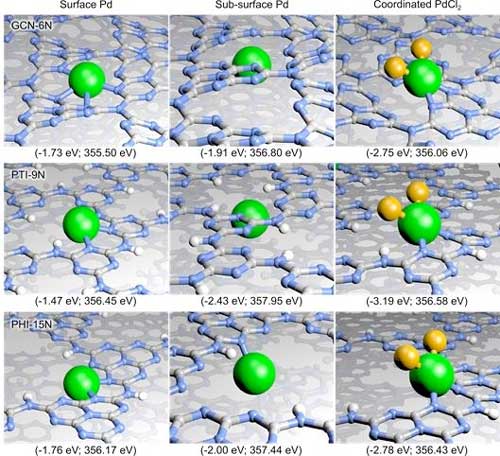
Framework diversity of carbon nitrides offers rich platform for single atom catalysis
Scientists demonstrate broad scope of carbon nitrides as single atom hosts.
New nano building block takes a bow
Researchers enhance boron nitride nanotubes for next-gen composites.
Alchemists of the cell environment
Scientists create gold catalysts capable of working as artificial enzymes inside living cells, thus triggering chemical reactions which do not exist in nature.

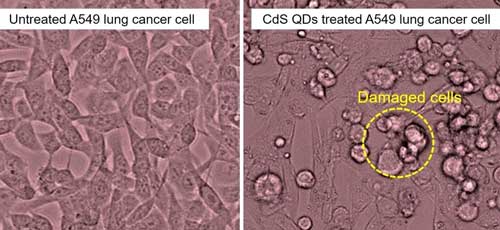
Nanoparticles derived from tea leaves destroy lung cancer cells
New research shows that nanoparticles derived from tea leaves inhibit the growth of lung cancer cells, destroying up to 80% of them.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
