
Monday, April 30, 2018
Magnetic nanoparticles leap from lab bench to breast cancer clinical trials
Magnetic nanoparticles will be used for their first breast cancer clinical trial later this year.
Water-repellent surfaces can efficiently boil water, keep electronics cool
Surfaces that repel water can support efficient boiling if all air and vapor is removed from a system first.

Scientists create nanomaterials that reconfigure in response to biochemical signals
Researchers are developing self-assembling electronic nanomaterials that can respond to biochemical signals for potential therapeutic use.
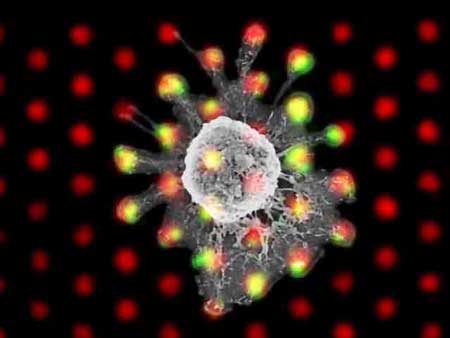
Geometry is key to T-cell triggering
Engineers discover geometric underpinnings of T-cell stimulation through precise engineering of T-cell receptor geometry, building a 3D nanofabricated biomimetic surface that simulates the key components of an antigen-presenting cell.
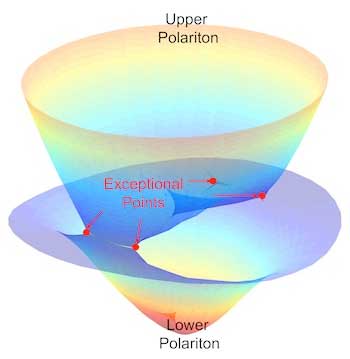
Scientists make tunable light-matter couplings in nanotube films
Researchers discover exceptional points in a unique material they created.
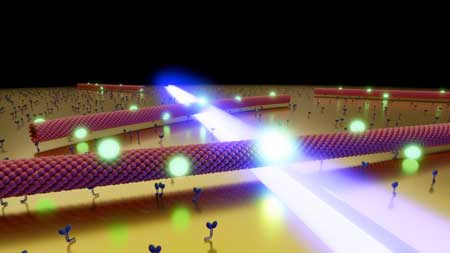
Stagediving with biomolecules improves optical microscopy
Physicists have developed a novel method for optical microscopy. Using biological motors and single quantum dots, they acquire ultra-high-resolution images.
Topological insulator 'flips' for superconductivity
Topology meets superconductivity through innovative reverse-order sample preparation.
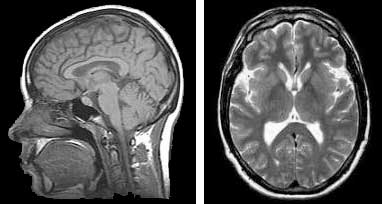
Nanoparticles developed to improve magnetic resonance scan images
Clinical use of these nanoparticles in MRI scans could facilitate the diagnosis of hepatic, pulmonary and cardiovascular pathologies, as well as many types of tumours.
Friday, April 27, 2018
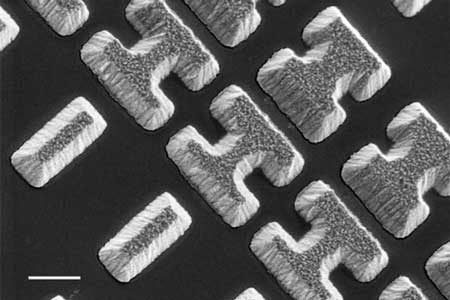
Improving mid-infrared imaging and sensing
Artificial optical materials could allow cheaper, flatter, more efficient detectors for night vision and other uses.
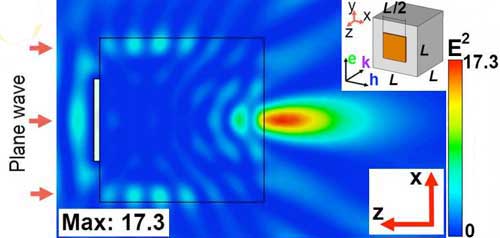
Scientists verify a way of how to improve resolution of most powerful microscopes
The resolution and intensity of powerful nanoscopes could be enhanced by over 30% via non-spherical particle lenses.
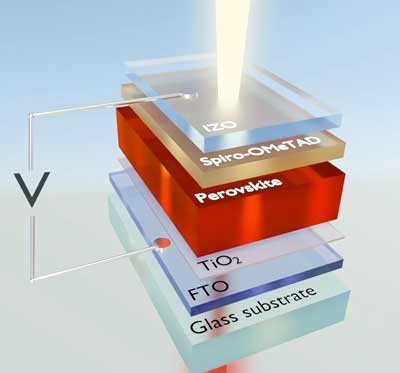
New all-inorganic perovskite solar cells tackle key challenges in solar cell technology: efficiency, stability, and cost
Scientists are using a new perovskite material that is stable, efficient and relatively cheap to produce, paving the way for their use in the solar cells of tomorrow.
A new way to produce hydrogen with nanoparticles
The ground-breaking new research centres on the use of a revolutionary photo-electrode made from nanoparticles of the elements lanthanum, iron and oxygen.

Scientists create tiny, super-thin sheets of flowing water that shimmer like soap bubbles
The liquid sheets - less than 100 water molecules thick - will let researchers probe chemical, physical and biological processes, and even the nature of water itself, in a way they could never do before.

Thursday, April 26, 2018
Discovery of new material is key step toward more powerful computing
Scientists have developed an inorganic compound that adopts a crystal structure capable of sustaining a new state of matter known as quantum spin liquid, an important advance toward quantum computing.
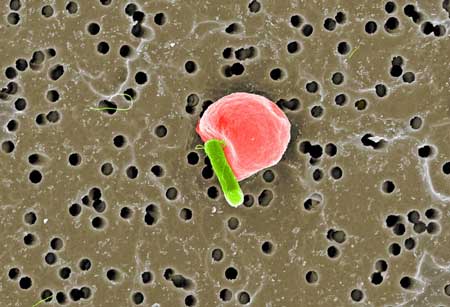
Multifunctional bacterial microswimmer able to deliver cargo and destroy itself
The untethered biohybrid microswimmer is able to transport and deliver cargo encapsulated into a guidable red blood cell, while an attached bacterium, one of the most efficient swimmers in nature, acts as a propeller to move it forward. Once it has reached its destination and delivered its cargo, the scientists can destroy the microswimmer using infrared light.
Punching holes in graphene to boost hydrogen production
Researchers develop electrode based on 'holey' graphene for efficient hydrogen evolution in acidic electrolyte.

Engineers develop novel method for resolving spin texture of topological surface states using transport measurements
All-electric measurement of spin texture used for spin current generation will contribute to easier and cheaper way of developing spintronic devices.
Twisting graphene into spirals
Researchers report for the first time the successful synthesis of hexa-peri-hexabenzo[7]helicene, or 'helical nanographene'.

Wednesday, April 25, 2018
Einstein's 'spooky action' goes massive
A research team has shown that entanglement of massive objects can be generated and detected.

Unusual magnetic structure may support next-generation technology
Although helical structures are typically formed by magnetic moments that wind around an axis in a set direction, researchers discovered that Fe3PO7 does not pick a particular direction and allows only short-range helical structures to form. These structures may provide novel technological capabilities.

Breaking bottlenecks to the electronic-photonic information technology revolution
Researchers have achieved an optical communications breakthrough that could revolutionize information technology.
A promising nanoparticle delivery method for immunotherapy combination
Using nanoparticles to bind molecules that can unleash and stimulate immune cells, researchers found they could more effectively trigger the body's defenses system against cancer in laboratory studies.

Novel technique achieves 32-fold increase in bactericidal effects of nanosilver
Silver nanoparticles used in hospital materials and cutting-edge medical research can be obtained by a method that intensifies their potency and also reduces production costs.
A high-tech spin on spider silk
This game-changing technology can transform polymers from soft and thermally insulating materials to an ultra-strong and thermally conductive material.
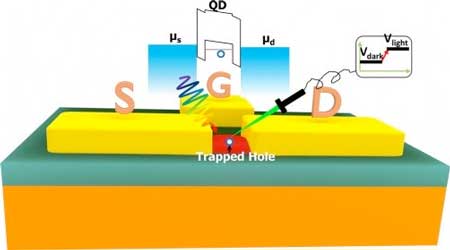
Quantum dots enable faster, easier photon detection, more secure data
Scientists developed a method of detecting single photons using tiny semiconductors called quantum dots.
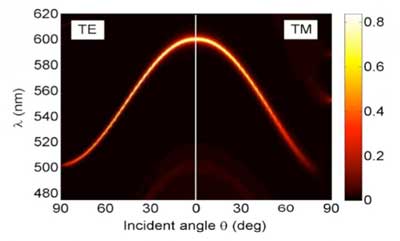
Turning graphene into light nanosensors
Tuning the graphene embedded in a photonic crystal by varying the external temperature can transform it into a light-sensitive sensor.
Researchers create precision optical components with inkjet printing
New additive manufacturing technique could be used to combine optics, microfluidics and electronics on a single chip.
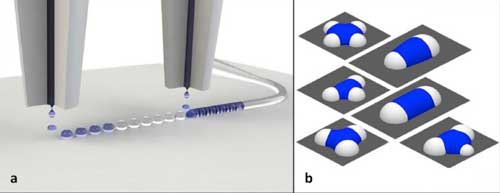
Engineers get a grip on slippery surfactants
Researchers extend formulas to account for complex surfactants in enhanced oil recovery.
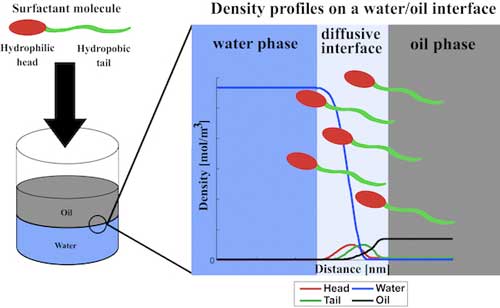
Nanowires could make lithium ion batteries safer
In an effort to develop a safer battery, scientists report that the addition of nanowires can not only enhance the battery's fire-resistant capabilities, but also its other properties.
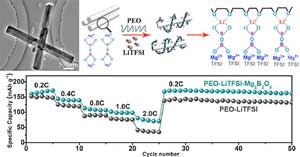
Watching nanomaterials form in 4-D
Novel technology allows researchers to see dynamic reactions as they happen at the nanoscale.
Why perovskite solar cells are so efficient
Scientists have gained fundamental insight into the function of perovskite solar cells. They found that bound states of electron-hole pairs can form during the absorption of light.
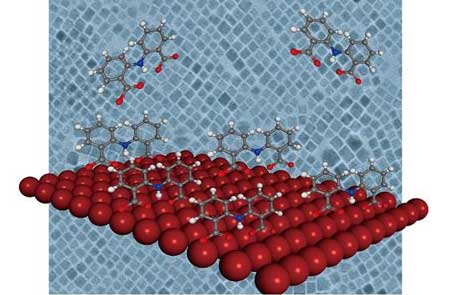
Surface engineering gets the red light
Perovskite particles could improve the performance of solar cells and light-emitting diodes via a simple process to stabilize the nanocrystal surface.
Tuesday, April 24, 2018
Why we need erasable MRI scans
Gas-filled protein structures could one day be used as 'erasable' contrast agents for MRI scans.

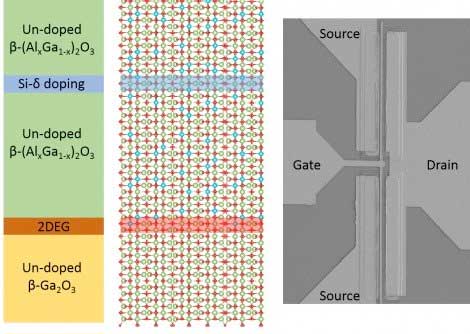
Getting electrons to move in a semiconductor
Gallium oxide shows high electron mobility, making it promising for better and cheaper devices.
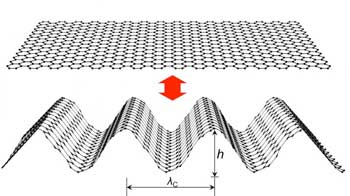
Graphene origami as a mechanically tunable plasmonic structure for infrared detection
Researchers have successfully developed a tunable infrared filter made from graphene, which would allow to change the frequency of a filter simply by controlled mechanical deformation of the filter (i.e., graphene origami), and not by replacing the substance on the goggles used to filter a particular spectrum of colors.
The dispute about the origins of terahertz photoresponse in graphene results in a draw
A new paper not only puts a period to a long-lasting debate about the origins of direct current in graphene illuminated by high-frequency radiation but also sets the stage for the development of high-sensitivity terahertz detectors.
Getting a better look at living cells
Nanoscale-level imaging of living cells has become a reality in the past few years using transmission electron microscopy and sealed sample holders that keep cells alive in a liquid environment. But do the high-resolution images obtained using these tools truly reflect the structures and functions of cells?
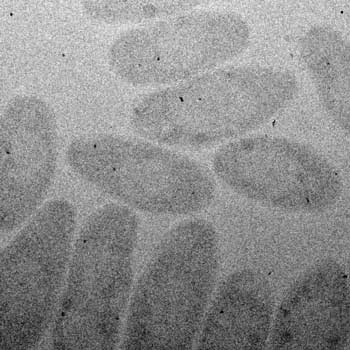
Nanosculpturing process to join metals without welding
Scientists have developed a versatile alternative to conventional welding and gluing processes.

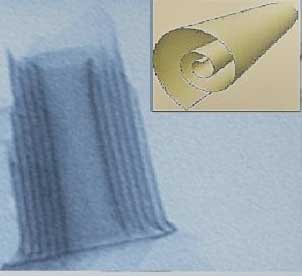
2D sheets of cadmium telluride can spontaneously fold into nanoscrolls
Researchers have discovered that two-dimensional sheets of cadmium telluride can spontaneously fold into nanoscrolls. This effect may be used in electronics and photonics.
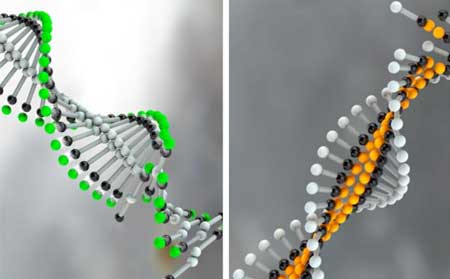
Lighting up DNA-based nanostructures
Scientists describe a mode of super-resolution microscopy that enables all the strands within these nanostructures to be visualized individually.

Monday, April 23, 2018
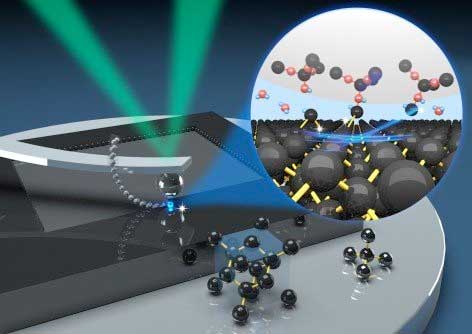
A simple method etches patterns at the atomic scale
Researchers have developed a precise chemical-free method for etching nanoscale features on silicon wafers.
Paint job transforms walls into sensors, interactive surface (w/video)
Smart walls react to human touch, sense activity in room.

Neutrons provide insights into increased performance for hybrid perovskite solar cells
Neutron scattering has revealed, in real time, the fundamental mechanisms behind the conversion of sunlight into energy in hybrid perovskite materials. A better understanding of this behavior will enable manufacturers to design solar cells with increased efficiency.
Liquid cell transmission electron microscopy makes a window into the nanoscale
Engineers have developed an LC-TEM device that uses multiple windows and patterned features to explore the impacts of high-energy electron bombardment on nanoparticles and sensitive biological samples.

A better fake leather, inspired by plants
Researchers invent nanocoating for synthetic leather that cleans itself - and won't get sticky on a hot day.
Nanoparticle breakthrough could capture unseen light for solar energy conversion
Scientists demonstrate how organic dyes work as antennas to help harness, convert light .
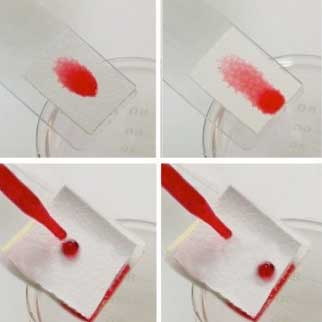
Nanoengineering concrete with graphene drastically reduces carbon footprint
The new composite material also is more than twice as strong and four times more water resistant than existing concretes.

Molecules brilliantly illuminated
Pjysicists have developed a high-power laser system that generates ultrashort pulses of light covering a large share of the mid-infrared spectrum. The researchers envisage a wide range of applications for the technology - in the early diagnosis of cancer, for instance.
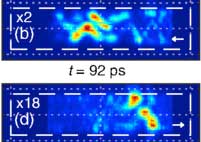
Physicists gain control over transitions between different states of matter
An international group of physicists managed for the first time to experimentally observe the transition between two different states of matter: propagating polariton-solitons and a Bose-Einstein condensate.
Making drugs 'smarter' using nanotechnology
Scientists have devised a new technique to decorate gold nanoparticles with a protein of choice so they can be used to tailor drug to more accurately target an area on the body, such as a cancer tumour.
Friday, April 20, 2018
Scientists propose new arguments for checking the properties of topological insulators
On the shape of the 'petal' for the dissipation curve.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
